Summary
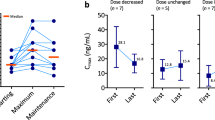
Introduction New therapeutic strategies combining axitinib and immune checkpoint blockers are ongoing in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). These strategies do not consider the pharmacokinetic variability of axitinib. We aimed to describe the risk of axitinib under-exposure using routine pharmacologic therapeutic monitoring (PTM). Methods We analyzed axitinib dosage in nine patients with mRCC. Routine axitinib concentration measurements were centralized at Henri Mondor University Hospital (Créteil, France) using a validated method. The primary objective was to describe the evolution of Cmax dosages (1 to 6 h after oral intake) during routine axitinib titration. Results Nine patients with available Cmax axitinib dosages were included. Four out of the nine patients had axitinib titration and Cmax dosages were performed before and after titration. All but one corrected their plasma axitinib exposure after titration, suggesting of a titration success. The last patient was monitored in the Henri Mondor Hospital routine PTM program and a pharmacokinetic profiling was performed after controlled oral intake. Results suggested a poor axitinib absorption. This patient experienced early tumor progression as best response. Conclusion We report a patient with significant axitinib under-exposure, possibly due to a poor absorption. PTM should be evaluated and considered in drug developments evaluating combination therapies based on axitinib.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rini BI, Melichar B, Fishman MN et al (2015) Axitinib dose titration: analyses of exposure, blood pressure and clinical response from a randomized phase II study in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol 26:1372–1377
Choueiri TK, Larkin J, Oya M et al (2018) Preliminary results for avelumab plus axitinib as first-line therapy in patients with advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma (JAVELIN renal 100): an open-label, dose-finding and dose-expansion, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol 19:451–460
Lubberman FJE, van Erp NP, Ter Heine R et al (2017) Boosting axitinib exposure with a CYP3A4 inhibitor, making axitinib treatment personal. Acta Oncol 56(9):1238–1240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No individual author has conflict of interest in the setting of this article.
Ethical approval
Drug dosage is a standard procedure in France, approved by National Health Institute. No drug dosing modification were performed on the basis of drug dosage. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All patients’ data have been managed in compliance with French law on protection of personal data.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
A. Hulin and Benoit Rousseau participated equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beinse, G., Hulin, A. & Rousseau, B. Axitinib pharmacologic therapeutic monitoring reveals severe under-exposure despite titration in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Invest New Drugs 37, 1289–1291 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-019-00743-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-019-00743-1