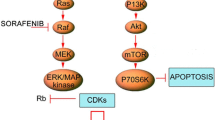
Summary
Background. Sorafenib (a VEGFR and multi-targeted kinase inhibitor) and Bortezomib (a proteasome inhibitor) have clinical antineoplastic activities as single agents, and combine synergistically in preclinical models. Methods. This Phase I study was undertaken to define the toxicity and the maximum tolerated doses (MTD) of the combination in patients with advanced solid tumors. Patients with cytologic or histologic proof of unresectable solid tumors were treated with escalating doses of sorafenib (twice daily) and bortezomib (days 1, 4, 8 and 11 intravenously) with 21-day cycles. Results. Fourteen patients (7 males, median age 65, range 24–74), with renal (3), lung (3), pancreas (2), and breast, adrenal gland, melanoma, spindle cell tumor, chronic lymphocytic leukemia and multiple myeloma (1 each) were enrolled. All patients are off treatment, 10 due to disease progression. DLT was seen in two patients (one grade 3 abdominal pain and grade 4 lipase elevation; one with grade 3 vomiting) at sorafenib 200 mg twice daily and bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2, establishing the MTD. No grade 4 hematologic or grade 5 toxicities were seen. One patient with renal cell cancer had a partial response and 5 patients attained stable disease. Conclusions. The combination of sorafenib and bortezomib was tolerated well. The recommended phase 2 doses are sorafenib 200 mg twice daily continuously with bortezomib 1 mg/m2 on days 1, 4, 8, 11 (21 day cycles). The combination shows preliminary signs of efficacy, supporting phase 2 studies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lowinger TB, Riedl B, Dumas J, Smith RA (2002) Design and discovery of small molecules targeting raf-1 kinase. Curr Pharm Des 8(25):2269–2278
Lyons JF, Wilhelm S, Hibner B, Bollag G (2001) Discovery of a novel Raf kinase inhibitor. Endocr Relat Cancer 8(3):219–225
Bollag G, Freeman S, Lyons JF, Post LE (2003) Raf pathway inhibitors in oncology. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 4(12):1436–1441
Adams J, Palombella VJ, Sausville EA, Johnson J, Destree A, Lazarus DD, Maas J, Pien CS, Prakash S, Elliott PJ (1999) Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents. Cancer Res 59(11):2615–2622
LeBlanc R, Catley LP, Hideshima T, Lentzsch S, Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N, Neuberg D, Goloubeva O, Pien CS, Adams J, Gupta D, Richardson PG, Munshi NC, Anderson KC (2002) Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 inhibits human myeloma cell growth in vivo and prolongs survival in a murine model. Cancer Res 62(17):4996–5000
Cusack JC Jr, Liu R, Houston M, Abendroth K, Elliott PJ, Adams J, Baldwin AS Jr (2001) Enhanced chemosensitivity to CPT-11 with proteasome inhibitor PS-341: implications for systemic nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition. Cancer Res 61(9):3535–3540
Teicher BA, Ara G, Herbst R, Palombella VJ, Adams J (1999) The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 5(9):2638–2645
Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Richardson P, Mitsiades C, Mitsiades N, Hayashi T, Munshi N, Dang L, Castro A, Palombella V, Adams J, Anderson KC (2002) NF-kappa B as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. J Biol Chem 277(19):16639–16647
Yu C, Friday BB, Lai JP, Yang L, Sarkaria J, Kay NE, Carter CA, Roberts LR, Kaufmann SH, Adjei AA (2006) Cytotoxic synergy between the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib and the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in vitro: induction of apoptosis through Akt and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathways. Mol Cancer Ther 5(9):2378–2387. doi:https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0235
Chen KF, Yu HC, Liu TH, Lee SS, Chen PJ, Cheng AL (2009) Synergistic interactions between sorafenib and bortezomib in hepatocellular carcinoma involve PP2A-dependent Akt inactivation. J Hepatol. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2009.10.011
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA, Rolland F, Demkow T, Hutson TE, Gore M, Freeman S, Schwartz B, Shan M, Simantov R, Bukowski RM (2007) Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356(2):125–134. doi:https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa060655
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Haussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359(4):378–390. doi:https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
Fisher RI, Bernstein SH, Kahl BS, Djulbegovic B, Robertson MJ, de Vos S, Epner E, Krishnan A, Leonard JP, Lonial S, Stadtmauer EA, O’Connor OA, Shi H, Boral AL, Goy A (2006) Multicenter phase II study of bortezomib in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 24(30):4867–4874. doi:https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.07.9665
Richardson PG, Sonneveld P, Schuster MW, Irwin D, Stadtmauer EA, Facon T, Harousseau JL, Ben-Yehuda D, Lonial S, Goldschmidt H, Reece D, San-Miguel JF, Blade J, Boccadoro M, Cavenagh J, Dalton WS, Boral AL, Esseltine DL, Porter JB, Schenkein D, Anderson KC (2005) Bortezomib or high-dose dexamethasone for relapsed multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 352(24):2487–2498. doi:https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa043445
Bellmunt J, Eisen T, Fishman M, Quinn D (2010) Experience with sorafenib and adverse event management. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2010.03.006
Kobayashi Y, Kanemitu T, Kamoto A, Satoh M, Mori N, Sekii K, Yoshioka T, Itatani H, Fujimoto T (2010) Painless acute pancreatitis associated with sorafenib treatment: a case report. Med Oncol. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9479-2
Minami H, Kawada K, Ebi H, Kitagawa K, Kim YI, Araki K, Mukai H, Tahara M, Nakajima H, Nakajima K (2008) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of sorafenib, an oral multikinase inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced refractory solid tumors. Cancer Sci 99(7):1492–1498. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00837.x
Li M, Srinivas S (2007) Acute pancreatitis associated with sorafenib. South Med J 100(9):909–911
Kane RC, Farrell AT, Saber H, Tang S, Williams G, Jee JM, Liang C, Booth B, Chidambaram N, Morse D, Sridhara R, Garvey P, Justice R, Pazdur R (2006) Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 12(24):7271–7278. doi:https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1249
Elouni B, Ben Salem C, Zamy M, Sakhri J, Bouraoui K, Biour M (2010) Bortezomib-induced acute pancreatitis. JOP 11(3):275–276
Laber DA, Mushtaq M (2009) Compassionate use of sorafenib in patients with advanced renal cell cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer 7(1):34–38. doi:https://doi.org/10.3816/CGC.2009.n.006
Ng R, Chen EX (2006) Sorafenib (BAY 43–9006): review of clinical development. Curr Clin Pharmacol 1(3):223–228
Kondagunta GV, Drucker B, Schwartz L, Bacik J, Marion S, Russo P, Mazumdar M, Motzer RJ (2004) Phase II trial of bortezomib for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 22(18):3720–3725. doi:https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2004.10.155
Siu LL, Awada A, Takimoto CH, Piccart M, Schwartz B, Giannaris T, Lathia C, Petrenciuc O, Moore MJ (2006) Phase I trial of sorafenib and gemcitabine in advanced solid tumors with an expanded cohort in advanced pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12(1):144–151. doi:https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1571
Blumenschein GR Jr, Gatzemeier U, Fossella F, Stewart DJ, Cupit L, Cihon F, O’Leary J, Reck M (2009) Phase II, multicenter, uncontrolled trial of single-agent sorafenib in patients with relapsed or refractory, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(26):4274–4280. doi:https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.22.0541
Butler C, Butler WM, Rizvi AA (2009) Sustained remission with the kinase inhibitor sorafenib in Stage IV metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocr Pract:1–19. doi:https://doi.org/10.4158/EP09295.CR
Lara PN Jr, Chansky K, Davies AM, Franklin WA, Gumerlock PH, Guaglianone PP, Atkins JN, Farneth N, Mack PC, Crowley JJ, Gandara DR (2006) Bortezomib (PS-341) in relapsed or refractory extensive stage small cell lung cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group phase II trial (S0327). J Thorac Oncol 1(9):996–1001
Scagliotti GV, Germonpre P, Bosquee L, Vansteenkiste J, Gervais R, Planchard D, Reck M, De Marinis F, Lee JS, Park K, Biesma B, Gans S, Ramlau R, Szczesna A, Makhson A, Manikhas G, Morgan B, Zhu Y, Chan KC, von Pawel J (2010) A randomized phase II study of bortezomib and pemetrexed, in combination or alone, in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 68(3):420–426. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.07.011
Ramakrishnan V, Timm M, Haug JL, Kimlinger TK, Wellik LE, Witzig TE, Rajkumar SV, Adjei AA, Kumar S (2010) Sorafenib, a dual Raf kinase/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor has significant anti-myeloma activity and synergizes with common anti-myeloma drugs. Oncogene 29(8):1190–1202. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.403
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to patients participating in this trial and to the enrolling investigators for their interest in and dedication to this study. We also thank the clinical research associates and research protocol specialists at the Mayo Clinic Cancer Center for commitment to the completion of this trial and for administrative assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by National Cancer Institute; CA69912.
Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT00303797
Conflict of Interest
SKK has research funding for clinical trials from Millennium Pharmaceuticals and Onyx Pharmaceuticals, and has participated in advisory boards with Millennium Pharmaceuticals and Onyx Pharmaceuticals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S.K., Jett, J., Marks, R. et al. Phase 1 study of sorafenib in combination with bortezomib in patients with advanced malignancies. Invest New Drugs 31, 1201–1206 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-013-0004-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-013-0004-2