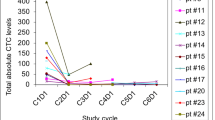
Summary
Background: Integrins mediate invasion and angiogenesis in prostate cancer bone metastases. We conducted a phase II study of Cilengitide, a selective antagonist of αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrins, in non-metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer with rising PSA. Methods: Patients were observed for 4 weeks with PSA monitoring, and then treated with 2,000 mg IV of cilengitide twice weekly until toxicity/progression. PSA, circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and circulating endothelial cells (CECs) were monitored each cycle with imaging performed every three cycles. Primary end point was PSA decline by ≥50%. Secondary endpoints were safety, PSA slope, time to progression (TTP), overall survival (OS), CTCs, CECs and gene expression. Results: 16 pts were enrolled; 13 were eligible with median age 65.5 years, baseline PSA 8.4 ng/mL and median Gleason sum 7. Median of three cycles was administered. Treatment was well tolerated with two grade three toxicities and no grade four toxicities. There were no PSA responses; 11 patients progressed by PSA after three cycles. Median TTP was 1.8 months and median OS has not been reached. Median pre- and on-treatment PSA slopes were 1.1 and 1.8 ng/mL/month. Baseline CTCs were detected in 1/9 patients. CTC increased (0 to 1; 2 pts), remained at 0 (2 pts) or decreased (23 to 0; 1 patient) at progression. Baseline median CEC was 26 (0–61) and at progression, 47 (15–148). Low cell counts precluded gene expression studies. Conclusions: Cilengitide was well tolerated but had no detectable clinical activity. CTCs are of questionable utility in non-metastatic prostate cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith MR, Kabbinavar F, Saad F, Hussain A, Gittelman MC, Bilhartz DL, Wynne C, Murray R, Zinner NR, Schulman C, Linnartz R, Zheng M, Goessl C, Hei YJ, Small EJ, Cook R, Higano CS (2005) Natural history of rising serum prostate-specific antigen in men with castrate nonmetastatic prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(13):2918–2925. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.01.529
Ibrahim T, Flamini E, Mercatali L, Sacanna E, Serra P, Amadori D (2010) Pathogenesis of osteoblastic bone metastases from prostate cancer. Cancer 116(6):1406–1418. doi:10.1002/cncr.24896
Loberg RD, Logothetis CJ, Keller ET, Pienta KJ (2005) Pathogenesis and treatment of prostate cancer bone metastases: Targeting the lethal phenotype. J Clin Oncol 23(32):8232–8241. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.03.0841
Felding-Habermann B (2003) Integrin adhesion receptors in tumor metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 20(3):203–213
Cooper CR, Chay CH, Pienta KJ (2002) The role of alpha(v)beta(3) in prostate cancer progression. Neoplasia 4(3):191–194. doi:10.1038/sj/neo/7900224
Fornaro M, Manes T, Languino LR (2001) Integrins and prostate cancer metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev 20(3–4):321–331
Slack-Davis JK, Parsons JT (2004) Emerging views of integrin signaling: Implications for prostate cancer. J Cell Biochem 91(1):41–46. doi:10.1002/jcb.10665
Zheng DQ, Woodard AS, Fornaro M, Tallini G, Languino LR (1999) Prostatic carcinoma cell migration via alpha(v)beta3 integrin is modulated by a focal adhesion kinase pathway. Cancer Res 59(7):1655–1664
Putz E, Witter K, Offner S, Stosiek P, Zippelius A, Johnson J, Zahn R, Riethmuller G, Pantel K (1999) Phenotypic characteristics of cell lines derived from disseminated cancer cells in bone marrow of patients with solid epithelial tumors: Establishment of working models for human micrometastases. Cancer Res 59(1):241–248
Zheng DQ, Woodard AS, Tallini G, Languino LR (2000) Substrate specificity of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin-mediated cell migration and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt pathway activation. J Biol Chem 275(32):24565–24574. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002646200
McCabe NP, De S, Vasanji A, Brainard J, Byzova TV (2007) Prostate cancer specific integrin alphavbeta3 modulates bone metastatic growth and tissue remodeling. Oncogene 26(42):6238–6243. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210429
Keller ET, Brown J (2004) Prostate cancer bone metastases promote both osteolytic and osteoblastic activity. J Cell Biochem 91(4):718–729. doi:10.1002/jcb.10662
Bisanz K, Yu J, Edlund M, Spohn B, Hung MC, Chung LW, Hsieh CL (2005) Targeting ecm-integrin interaction with liposome-encapsulated small interfering rnas inhibits the growth of human prostate cancer in a bone xenograft imaging model. Mol Ther 12(4):634–643. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2005.05.012
Thalmann GN, Sikes RA, Devoll RE, Kiefer JA, Markwalder R, Klima I, Farach-Carson CM, Studer UE, Chung LW (1999) Osteopontin: Possible role in prostate cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res 5(8):2271–2277
Ross FP, Chappel J, Alvarez JI, Sander D, Butler WT, Farach-Carson MC, Mintz KA, Robey PG, Teitelbaum SL, Cheresh DA (1993) Interactions between the bone matrix proteins osteopontin and bone sialoprotein and the osteoclast integrin alpha v beta 3 potentiate bone resorption. J Biol Chem 268(13):9901–9907
Cheng SL, Lai CF, Fausto A, Chellaiah M, Feng X, McHugh KP, Teitelbaum SL, Civitelli R, Hruska KA, Ross FP, Avioli LV (2000) Regulation of alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5 integrins by dexamethasone in normal human osteoblastic cells. J Cell Biochem 77(2):265–276. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(20000501)77:2<265::AID-JCB9>3.0.CO;2-6
Nemeth JA, Cher ML, Zhou Z, Mullins C, Bhagat S, Trikha M (2003) Inhibition of alpha(v)beta3 integrin reduces angiogenesis, bone turnover, and tumor cell proliferation in experimental prostate cancer bone metastases. Clin Exp Metastasis 20(5):413–420
Manes T, Zheng DQ, Tognin S, Woodard AS, Marchisio PC, Languino LR (2003) Alpha(v)beta3 integrin expression up-regulates cdc2, which modulates cell migration. J Cell Biol 161(4):817–826. doi:10.1083/jcb.200212172
Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA (1994) Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 264(5158):569–571
Malyankar UM, Scatena M, Suchland KL, Yun TJ, Clark EA, Giachelli CM (2000) Osteoprotegerin is an alpha vbeta 3-induced, nf-kappa b-dependent survival factor for endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 275(28):20959–20962. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000290200
Scatena M, Almeida M, Chaisson ML, Fausto N, Nicosia RF, Giachelli CM (1998) Nf-kappab mediates alphavbeta3 integrin-induced endothelial cell survival. J Cell Biol 141(4):1083–1093
Kumar CC, Malkowski M, Yin Z, Tanghetti E, Yaremko B, Nechuta T, Varner J, Liu M, Smith EM, Neustadt B, Presta M, Armstrong L (2001) Inhibition of angiogenesis and tumor growth by sch221153, a dual alpha(v)beta3 and alpha(v)beta5 integrin receptor antagonist. Cancer Res 61(5):2232–2238
Nabors LB, Mikkelsen T, Rosenfeld SS, Hochberg F, Akella NS, Fisher JD, Cloud GA, Zhang Y, Carson K, Wittemer SM, Colevas AD, Grossman SA (2007) Phase i and correlative biology study of cilengitide in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 25(13):1651–1657. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.06.6514
Brooks PC, Montgomery AM, Rosenfeld M, Reisfeld RA, Hu T, Klier G, Cheresh DA (1994) Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 79(7):1157–1164.
Oliveira-Ferrer L, Hauschild J, Fiedler W, Bokemeyer C, Nippgen J, Celik I, Schuch G (2008) Cilengitide induces cellular detachment and apoptosis in endothelial and glioma cells mediated by inhibition of fak/src/akt pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 27:86. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-27-86
Nisato RE, Tille JC, Jonczyk A, Goodman SL, Pepper MS (2003) Alphav beta 3 and alphav beta 5 integrin antagonists inhibit angiogenesis in vitro. Angiogenesis 6(2):105–119. doi:10.1023/B:AGEN.0000011801.98187.f2
MacDonald TJ, Taga T, Shimada H, Tabrizi P, Zlokovic BV, Cheresh DA, Laug WE (2001) Preferential susceptibility of brain tumors to the antiangiogenic effects of an alpha(v) integrin antagonist. Neurosurgery 48(1):151–157
Taga T, Suzuki A, Gonzalez-Gomez I, Gilles FH, Stins M, Shimada H, Barsky L, Weinberg KI, Laug WE (2002) Alpha v-integrin antagonist emd 121974 induces apoptosis in brain tumor cells growing on vitronectin and tenascin. Int J Cancer 98(5):690–697. doi:10.1002/ijc.10265
Eskens FA, Dumez H, Hoekstra R, Perschl A, Brindley C, Bottcher S, Wynendaele W, Drevs J, Verweij J, van Oosterom AT (2003) Phase i and pharmacokinetic study of continuous twice weekly intravenous administration of cilengitide (emd 121974), a novel inhibitor of the integrins alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5 in patients with advanced solid tumours. Eur J Cancer 39(7):917–926.
Hariharan S, Gustafson D, Holden S, McConkey D, Davis D, Morrow M, Basche M, Gore L, Zang C, O’Bryant CL, Baron A, Gallemann D, Colevas D, Eckhardt SG (2007) Assessment of the biological and pharmacological effects of the alpha nu beta3 and alpha nu beta5 integrin receptor antagonist, cilengitide (emd 121974), in patients with advanced solid tumors. Ann Oncol 18(8):1400–1407. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdm140
Bubley GJ, Carducci M, Dahut W, Dawson N, Daliani D, Eisenberger M, Figg WD, Freidlin B, Halabi S, Hudes G, Hussain M, Kaplan R, Myers C, Oh W, Petrylak DP, Reed E, Roth B, Sartor O, Scher H, Simons J, Sinibaldi V, Small EJ, Smith MR, Trump DL, Wilding G et al (1999) Eligibility and response guidelines for phase ii clinical trials in androgen-independent prostate cancer: Recommendations from the prostate-specific antigen working group. J Clin Oncol 17(11):3461–3467
Scher HI, Halabi S, Tannock I, Morris M, Sternberg CN, Carducci MA, Eisenberger MA, Higano C, Bubley GJ, Dreicer R, Petrylak D, Kantoff P, Basch E, Kelly WK, Figg WD, Small EJ, Beer TM, Wilding G, Martin A, Hussain M (2008) Design and end points of clinical trials for patients with progressive prostate cancer and castrate levels of testosterone: Recommendations of the prostate cancer clinical trials working group. J Clin Oncol 26(7):1148–1159. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.12.4487
Nelson JB, Love W, Chin JL, Saad F, Schulman CC, Sleep DJ, Qian J, Steinberg J, Carducci M (2008) Phase 3, randomized, controlled trial of atrasentan in patients with nonmetastatic, hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer 113(9):2478–2487. doi:10.1002/cncr.23864
Davis JW, Nakanishi H, Kumar VS, Bhadkamkar VA, McCormack R, Fritsche HA, Handy B, Gornet T, Babaian RJ (2008) Circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood samples from patients with increased serum prostate specific antigen: Initial results in early prostate cancer. J Urol 179 (6):2187–2191; discussion 2191. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2008.01.102
Helo P, Cronin AM, Danila DC, Wenske S, Gonzalez-Espinoza R, Anand A, Koscuiszka M, Vaananen RM, Pettersson K, Chun FK, Steuber T, Huland H, Guillonneau BD, Eastham JA, Scardino PT, Fleisher M, Scher HI, Lilja H (2009) Circulating prostate tumor cells detected by reverse transcription-pcr in men with localized or castration-refractory prostate cancer: Concordance with cellsearch assay and association with bone metastases and with survival. Clin Chem 55(4):765–773. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2008.117952
Maestro LM, Sastre J, Rafael SB, Veganzones SB, Vidaurreta M, Martin M, Olivier C, DELO VB, Garcia-Saenz JA, Alfonso R, Arroyo M, Diaz-Rubio E (2009) Circulating tumor cells in solid tumor in metastatic and localized stages. Anticancer Res 29(11):4839–4843
Danila DC, Heller G, Gignac GA, Gonzalez-Espinoza R, Anand A, Tanaka E, Lilja H, Schwartz L, Larson S, Fleisher M, Scher HI (2007) Circulating tumor cell number and prognosis in progressive castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(23):7053–7058. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1506
de Bono JS, Scher HI, Montgomery RB, Parker C, Miller MC, Tissing H, Doyle GV, Terstappen LW, Pienta KJ, Raghavan D (2008) Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(19):6302–6309. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0872
Strijbos MH, Gratama JW, Schmitz PI, Rao C, Onstenk W, Doyle GV, Miller MC, de Wit R, Terstappen LW, Sleijfer S Circulating endothelial cells, circulating tumour cells, tissue factor, endothelin-1 and overall survival in prostate cancer patients treated with docetaxel. Eur J Cancer. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2010.03.030
Moreno JG, O’Hara SM, Gross S, Doyle G, Fritsche H, Gomella LG, Terstappen LW (2001) Changes in circulating carcinoma cells in patients with metastatic prostate cancer correlate with disease status. Urology 58(3):386–392
Shaffer DR, Leversha MA, Danila DC, Lin O, Gonzalez-Espinoza R, Gu B, Anand A, Smith K, Maslak P, Doyle GV, Terstappen LW, Lilja H, Heller G, Fleisher M, Scher HI (2007) Circulating tumor cell analysis in patients with progressive castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(7):2023–2029. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2701
Smirnov DA, Zweitzig DR, Foulk BW, Miller MC, Doyle GV, Pienta KJ, Meropol NJ, Weiner LM, Cohen SJ, Moreno JG, Connelly MC, Terstappen LW, O'Hara SM (2005) Global gene expression profiling of circulating tumor cells. Cancer Res 65(12):4993–4997. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4330
Stott SL, Lee RJ, Nagrath S, Yu M, Miyamoto DT, Ulkus L, Inserra EJ, Ulman M, Springer S, Nakamura Z, Moore AL, Tsukrov DI, Kempner ME, Dahl DM, Wu CL, Iafrate AJ, Smith MR, Tompkins RG, Sequist LV, Toner M, Haber DA, Maheswaran S Isolation and characterization of circulating tumor cells from patients with localized and metastatic prostate cancer. Sci Transl Med 2 (25):25ra23. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3000403
Georgiou HD, Namdarian B, Corcoran NM, Costello AJ, Hovens CM (2008) Circulating endothelial cells as biomarkers of prostate cancer. Nat Clin Pract Urol 5(8):445–454. doi:10.1038/ncpuro1188
Beerepoot LV, Mehra N, Vermaat JS, Zonnenberg BA, Gebbink MF, Voest EE (2004) Increased levels of viable circulating endothelial cells are an indicator of progressive disease in cancer patients. Ann Oncol 15(1):139–145
Bradley DA, Daignault S, Ryan CJ, Dipaola RS, Smith DC, Small E, Gross ME, Stein MN, Chen A, Hussain M Cilengitide (emd 121974, nsc 707544) in asymptomatic metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer patients: A randomized phase ii trial by the prostate cancer clinical trials consortium. Invest New Drugs. doi:10.1007/s10637-010-9420-8
Petty WJ, Miller AA, McCoy TP, Gallagher PE, Tallant EA, Torti FM (2009) Phase i and pharmacokinetic study of angiotensin-(1–7), an endogenous antiangiogenic hormone. Clin Cancer Res 15(23):7398–7404. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1957
Bradley DA, Daignault S, Ryan CJ, Dipaola RS, Smith DC, Small E, Gross ME, Stein MN, Chen A, Hussain M (2010) Cilengitide (emd 121974, nsc 707544) in asymptomatic metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer patients: A randomized phase ii trial by the prostate cancer clinical trials consortium. Invest New Drugs. doi:10.1007/s10637-010-9420-8
Adjei AA, Christian M, Ivy P (2009) Novel designs and end points for phase ii clinical trials. Clin Cancer Res 15(6):1866–1872. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2035
Fox E, Curt GA, Balis FM (2002) Clinical trial design for target-based therapy. Oncologist 7(5):401–409
Acknowledgement
Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program (CTEP), PC051382, PC051375, Prostate Cancer Foundation (PCF) N008367, Veridex (formerly Immunicon Corp.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was presented in part at the 2010 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary Symposium.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alva, A., Slovin, S., Daignault, S. et al. Phase II study of Cilengitide (EMD 121974, NSC 707544) in patients with non-metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer, NCI-6735. A study by the DOD/PCF prostate cancer clinical trials consortium. Invest New Drugs 30, 749–757 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9573-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9573-5