Summary
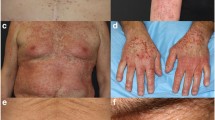
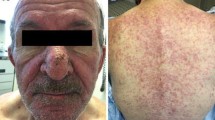
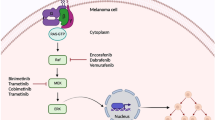
Background Selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) is a second generation MEK inhibitor that is currently in clinical trials for various solid malignancies. MEK kinase inhibitors are associated with dermatologic toxicities. While reactions affecting the skin, hair and nails to other targeted agents, such as epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors (EGFRIs) have been abundantly described in recent years, the dermatologic toxicities associated with MEK inhibitors have not been well characterized. Similarly, their management may present a challenge in clinical trials. We reviewed the clinical presentation, evolution and management of dermatologic toxicities associated with selumetinib. Methods A retrospective review of medical records of 11 patients referred to the Dermatology Service with dermatologic toxicities secondary to selumetinib was performed. Data from two phase II trials in which selumetinib was used to treat advanced metastatic cutaneous, mucosal, or uveal melanomas were reviewed. Parameters studied included the time to onset, clinical presentation, histology and management. In addition, the clinical database was accessed to retrieve clinical photographs when available. Results Eight patients received selumetinib suspension orally at 100 mg twice a day and three patients received a newer capsule formulation at the maximum tolerated dose of 75 mg with the same frequency. The following adverse effects were observed: papulopustular rash (100%), xerosis (36%), pruritus (45%), fissures (9%), telangiectasias (27%), hyperpigmentation (9%), alopecia (9%), angular cheilitis (9%), and paronychia (9%). In addition, secondary bacterial infection with Staphylococcus aureus was documented in 3 patients (27%). Conclusions Dermatologic side-effects associated with selumetinib were similar to those seen with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors (EGFRIs). Treatment approaches used for EGFRI-induced dermatologic reactions may be potentially utilized to manage those associated with selumetinib.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lacouture ME (2006) Mechanisms of cutaneous toxicities to EGFR inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 6(10):803–812
Robert C, Soria JC, Spatz A, Le Cesne A, Malka D, Pautier P, Wechsler J, Lhomme C, Escudier B, Boige V et al (2005) Cutaneous side-effects of kinase inhibitors and blocking antibodies. Lancet Oncol 6(7):491–500
Lacouture ME, Wu S, Robert C, Atkins MB, Kong HH, Guitart J, Garbe C, Hauschild A, Puzanov I, Alexandrescu DT et al (2008) Evolving strategies for the management of hand-foot skin reaction associated with the multitargeted kinase inhibitors sorafenib and sunitinib. Oncologist 13(9):1001–1011
Yeh TC, Marsh V, Bernat BA, Ballard J, Colwell H, Evans RJ, Parry J, Smith D, Brandhuber BJ, Gross S et al (2007) Biological characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a potent, highly selective mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res 13(5):1576–1583
Huynh H, Soo KC, Chow PK, Tran E (2007) Targeted inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase pathway with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 6(1):138–146
Davies BR, Logie A, McKay JS, Martin P, Steele S, Jenkins R, Cockerill M, Cartlidge S, Smith PD (2007) AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), a potent inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 kinases: mechanism of action in vivo, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship, and potential for combination in preclinical models. Mol Cancer Ther 6(8):2209–2219
Haass NK, Sproesser K, Nguyen TK, Contractor R, Medina CA, Nathanson KL, Herlyn M, Smalley KS (2008) The mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) induces growth arrest in melanoma cells and tumor regression when combined with docetaxel. Clin Cancer Res 14(1):230–239
Lorusso PM, Adjei AA, Varterasian M, Gadgeel S, Reid J, Mitchell DY, Hanson L, DeLuca P, Bruzek L, Piens J et al (2005) Phase I and pharmacodynamic study of the oral MEK inhibitor CI-1040 in patients with advanced malignancies. J Clin Oncol 23(23):5281–5293
Lorusso P, Krishnamurthi S, Rinehart J, Nabell L, Croghan G, Chapman P, Selaru P, Kim S, Ricart A, Wilner K (6 (2007) 3649 s (abstr. B109)) Clinical aspects of a phase I study of PD-0325901, a second generation oral MEK inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
Adjei AA, Cohen RB, Franklin W, Morris C, Wilson D, Molina JR, Hanson LJ, Gore L, Chow L, Leong S et al (2008) Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers. J Clin Oncol 26(13):2139–2146
Desar IM, Bovenschen HJ, Timmer-Bonte AJ, Cantarini MV, Van Der Graaf WT, Van Rossum MM, Van Herpen CM (2010) Case studies showing clinical signs and management of cutaneous toxicity of the MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with solid tumours. Acta Oncol 49(1):110–113
Rinehart J, Adjei AA, Lorusso PM, Waterhouse D, Hecht JR, Natale RB, Hamid O, Varterasian M, Asbury P, Kaldjian EP et al (2004) Multicenter phase II study of the oral MEK inhibitor, CI-1040, in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung, breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(22):4456–4462
Perez-Soler R, Delord JP, Halpern A, Kelly K, Krueger J, Sureda BM, von Pawel J, Temel J, Siena S, Soulieres D et al (2005) HER1/EGFR inhibitor-associated rash: future directions for management and investigation outcomes from the HER1/EGFR inhibitor rash management forum. Oncologist 10(5):345–356
Li T, Perez-Soler R (2009) Skin toxicities associated with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Target Oncol 4(2):107–119
Melosky B, Burkes R, Rayson D, Alcindor T, Shear N, Lacouture M (2009) Management of skin rash during egfr-targeted monoclonal antibody treatment for gastrointestinal malignancies: Canadian recommendations. Curr Oncol 16(1):16–26
Agero AL, Dusza SW, Benvenuto-Andrade C, Busam KJ, Myskowski P, Halpern AC (2006) Dermatologic side effects associated with the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. J Am Acad Dermatol 55(4):657–670
Lacouture ME, Boerner SA, Lorusso PM (2006) Non-rash skin toxicities associated with novel targeted therapies. Clin Lung Cancer 8(Suppl 1):S36–42
Lynch TJ Jr, Kim ES, Eaby B, Garey J, West DP, Lacouture ME (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-associated cutaneous toxicities: an evolving paradigm in clinical management. Oncologist 12(5):610–621
Segaert S, Van Cutsem E (2005) Clinical signs, pathophysiology and management of skin toxicity during therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Ann Oncol 16(9):1425–1433
Jost M, Kari C, Rodeck U (2000) The EGF receptor—an essential regulator of multiple epidermal functions. Eur J Dermatol 10(7):505–510
Eilers RE Jr, Gandhi M, Patel JD, Mulcahy MF, Agulnik M, Hensing T, Lacouture ME (2010) Dermatologic infections in cancer patients treated with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 102(1):47–53
Scope A, Lieb JA, Dusza SW, Phelan DL, Myskowski PL, Saltz L, Halpern AC (2009) A prospective randomized trial of topical pimecrolimus for cetuximab-associated acnelike eruption. J Am Acad Dermatol 61(4):614–620
Acknowledgments
Mario E. Lacouture is supported by a Career Development Award from the Dermatology Foundation; Paul B. Chapman receives grant support from AstraZeneca.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balagula, Y., Barth Huston, K., Busam, K.J. et al. Dermatologic side effects associated with the MEK 1/2 inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886). Invest New Drugs 29, 1114–1121 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9567-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-010-9567-3