Summary
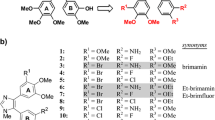
Vascular disrupting agents (VDAs) have emerged as a new kind of anti-cancer drug in recent years. Structural modification of an active parent compound is an effective approach to developing new agents with more activity and fewer adverse reactions. In our study, six synthesized stilbene derivatives were screened for their cytotoxic activity against human tumor cells, and their mechanisms of action were investigated. The MTT assay was used to determine the anti-proliferative activity of these compounds. Polymerization of tubulin was detected by a tubulin assembly assay, and the cellular microtubule network was observed by immunocytochemical analyses. Cell-cycle distribution was detected by flow cytometry. A nude mouse model with xenografted colon cancer was used to demonstrate the in vivo anti-tumor activity, and microvessel density (MVD) was determined by immunohistochemistry. The expression levels of protein and mRNA were detected by Western blot and RT-PCR, respectively. Among the six newly synthesized compounds, (Z)-3,4′,5-trimethoxylstilbene-3′-O-phosphate disodium (M410) showed potent cytotoxic activity toward proliferating tumor cells and exhibited a similar cytotoxicity against multi-drug resistant (MDR) tumor cells. M410 inhibited bovine brain tubulin polymerization in a way similar to that of colchicine. In proliferating human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), 20 nM of M410 induced cellular tubulin depolymerization within 4 h, which led to M phase arrest. Systemic administration of M410 at nontoxic doses in nude mice resulted in inhibition of tumor growth of human colon cancer LoVo xenografts. The tumor vessel density also decreased after M410 treatment, as determined by immunohistochemical staining for CD31. M410 downregulated hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) expression, reduced nuclear HIF-1α, and downregulated vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) mRNA. Our results indicate that M410 is a potent microtubule inhibitor that is cytotoxic, angiogenesis inhibiting and vascular targeting.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285(21):1182–1186
Helmlinger G, Yuan F, Dellian M, Jain RK (1997) Interstitial pH and pO2 gradients in solid tumors in vivo: high-resolution measurements reveal a lack of correlation. Nat Med 3(2):177–182
Hashizume H, Baluk P, Morikawa S, McLean JW, Thurston G, Roberge S, Jain RK, McDonald DM (2000) Openings between defective endothelial cells explain tumor vessel leakiness. Am J Pathol 156(4):1363–1380
Kerbel RS (1991) Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis as a strategy to circumvent acquired resistance to anti-cancer therapeutic agents. Bioessays 13(1):31–36
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL (1995) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(12):5510–5514
Levy AP, Levy NS, Wegner S, Goldberg MA (1995) Transcriptional regulation of the rat vascular endothelial growth factor gene by hypoxia. J Biol Chem 270(22):13333–13340
Bunn HF, Poyton RO (1996) Oxygen sensing and molecular adaptation to hypoxia. Physiol Rev 76(3):839–885
Berra E, Milanini J, Richard DE, Le Gall M, Viñals F, Gothié E, Roux D, Pagès G, Pouysségur J (2000) Signaling angiogenesis via p42/p44 MAP kinase and hypoxia. Biochem Pharmacol 60(8):1171–1178
Giordano FJ, Johnson RS (2001) Angiogenesis: the role of the microenvironment in flipping the switch. Curr Opin Genet Dev 11(1):35–40
Semenza GL (2002) Involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in human cancer. Intern Med 41(2):79–83
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S, Poltorak Z (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. FASEB J 13(1):9–22
Jośko J, Gwóźdź B, Jedrzejowska-Szypułka H, Hendryk S (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its effect on angiogenesis. Med Sci Monit 6(5):1047–1052
Pettit GR, Singh SB, Hamel E, Lin CM, Alberts DS, Garcia-Kendall D (1989) Isolation and structure of the strong cell growth and tubulin inhibitor combretastatin A-4. Experientia 45(2):209–211
Pettit GR, Temple C Jr, Narayanan VL, Varma R, Simpson MJ, Boyd MR, Rener GA, Bansal N (1995) Antineoplastic agents 322. synthesis of Combretastatin A-4 prodrugs. Anticancer Drug Des 10(4):299–309
Stevenson JP, Rosen M, Sun W, Gallagher M, Haller DG, Vaughn D, Giantonio B, Zimmer R, Petros WP, Stratford M, Chaplin D, Young SL, Schnall M, O'Dwyer PJ (2003) Phase I trial of the antivascular agent combretastatin A4 phosphate on a 5-Day schedule to patients with cancer: magnetic resonance imaging evidence for altered tumor blood flow. J Clin Oncol 21(23):4428–4438
Tozer GM, Prise VE, Wilson J, Locke RJ, Vojnovic B, Stratford MR, Dennis MF, Chaplin DJ (1999) Combretastatin A-4 phosphate as a tumor vascular-targeting agent: early effects in tumors and normal tissues. Cancer Res 59(7):1626–1634
Dark GG, Hill SA, Prise VE, Tozer GM, Pettit GR, Chaplin DJ (1997) Combretastatin A-4, an agent that displays potent and selective toxicity toward tumor vasculature. Cancer Res 57(10):1829–1834
Beauregard DA, Thelwall PE, Chaplin DJ, Hill SA, Adams GE, Brindle KM (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy of combretastatin A4 prodrug-induced disruption of tumour perfusion and energetic status. Br J Cancer 77(11):1761–1767
Beauregard DA, Hill SA, Chaplin DJ, Brindle KM (2001) The susceptibility of tumors to the antivascular drug combretastatin A4 phosphate correlates with vascular permeability. Cancer Res 61(18):6811–6815
Malcontenti-Wilson C, Muralidharan V, Skinner S, Christophi C, Sherris D, O’Brien PE (2001) Combretastatin A4 prodrug study of effect on the growth and the microvasculature of colorectal liver metastases in a murine model. Clin Cancer Res 7(4):1052–1060
Griggs J, Brindle KM, Metcalfe JC, Hill SA, Smith GA, Beauregard DA, Hesketh R (2001) Potent anti-metastatic activity of combretastatin-A4. Int J Oncol 19(4):821–825
Rustin GJ, Galbraith SM, Anderson H, Stratford M, Folkes LK, Sena L, Gumbrell L, Price PM (2003) Phase I clinical trial of weekly combretastatin A4 phosphate: clinical and pharmacokinetic results. J Clin Oncol 21(15):2815–2822
Zou Y, Wang ZX, Zhang XJ, Zhou Y, He SJ, Lin HZ Water soluble phosphate ester salt of (Z)-3'-hydroxy-3,4',5-trimethoxystilbene, and its preparation method, pharmaceutical composition and uses. Chinese Patent Office, ZL 200610033788.1
Zou Y, Xiao CF, Zhong RQ, Wei W, Huang WM, He SJ (2008) Synthesis of Combretastatin A-4 and Erianin. J Chem Res 6:354–356
Hotchkiss KA, Ashton AW, Mahmood R, Russell RG, Sparano JA, Schwartz EL (2002) Inhibition of endothelial cell function in vitro and angiogenesis in vivo by docetaxel (Taxotere): association with impaired repositioning of the microtubule organizing center. Mol Cancer Ther 1(13):1191–1200
Tozer GM, Prise VE, Wilson J, Cemazar M, Shan S, Dewhirst MW, Barber PR, Vojnovic B, Chaplin DJ (2001) Mechanisms associated with tumor vascular shut-down induced by combretastatin A-4 phosphate: intravital microscopy and measurement of vascular permeability. Cancer Res 61(17):6413–6422
Grosios K, Holwell SE, McGown AT, Pettit GR, Bibby MC (1999) In vivo and in vitro evaluation of combretastatin A-4 and its sodium phosphate prodrug. Br J Cancer 81(8):1318–1327
Nabha SM, Mohammad RM, Wall NR, Dutcher JA, Salkini BM, Pettit GR, Al-Katib AM (2001) Evaluation of combretastatin A-4 prodrug in a non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma xenograft model: preclinical efficacy. Anti Canc Drugs 12(1):57–63
Medarde M, Ramos AC, Caballero E, Peláez-Lamamié de Clairac R, López JL, Grávalos DG, Feliciano AS (1999) Synthesis and pharmacological activity of diarylindole derivatives. Cytotoxic agents based on combretastatins. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9(16):2303–2308
Cushman M, Nagarathnam D, Gopal D, Chakraborti AK, Lin CM, Hamel E (1991) Synthesis and evaluation of stilbene and dihydrostilbene derivatives as potential anticancer agents that inhibit tubulin polymerization. J Med Chem 34(8):2579–2588
Nam NH, Kim Y, You YJ, Hong DH, Kim HM, Ahn BZ (2002) Synthesis and anti-tumor activity of novel combretastatins: combretocyclopentenones and related analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12(15):1955–1958
Galbraith SM, Chaplin DJ, Lee F, Stratford MR, Locke RJ, Vojnovic B, Tozer GM (2001) Effects of combretastatin A4 phosphate on endothelial cell morphology in vitro and relationship to tumour vascular targeting activity in vivo. Anticancer Res 21(1A):93–102
Davis PD, Dougherty GJ, Blakey DC, Galbraith SM, Tozer GM, Holder AL, Naylor MA, Nolan J, Stratford MR, Chaplin DJ, Hill SA (2002) ZD6126: a novel vascular-targeting agent that causes selective destruction of tumor vasculature. Cancer Res 62(24):7247–7253
Micheletti G, Poli M, Borsotti P, Martinelli M, Imberti B, Taraboletti G, Giavazzi R (2003) Vascular-targeting activity of ZD6126, a novel tubulin-binding agent. Cancer Res 63(7):1534–1537
Chaplin DJ, Pettit GR, Hill SA (1999) Anti-vascular approaches to solid tumor therapy: evaluation of combretastatin A4 phosphate. Anticancer Res 19(1A):189–195
Semenza GL (1998) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: master regulator of O2 homeostasis. Curr Opin Genet Dev 8(5):588–594
Birner P, Schindl M, Obermair A, Breitenecker G, Oberhuber G (2001) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in epithelial ovarian tumors: its impact on prognosis and on response to chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 7(6):1661–1668
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M, Hilton DA, Zagzag D, Buechler P, Isaacs WB, Semenza GL, Simons JW (1999) Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res 59(22):5830–5835
Birner P, Schindl M, Obermair A, Plank C, Breitenecker G, Oberhuber G (2000) Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is a marker for an unfavorable prognosis in early-stage invasive cervical cancer. Cancer Res 60(17):4693–4696
Schindl M, Schoppmann SF, Samonigg H, Hausmaninger H, Kwasny W, Gnant M, Jakesz R, Kubista E, Birner P, Oberhuber G, Austrian Breast and Colorectal Cancer Study Group (2002) Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is associated with an unfavorable prognosis in lymph node-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 8(6):1831–1837
Semenza GL (2002) HIF-1 and tumor progression: pathophysiology and therapeutics. Trends Mol Med 8(4 Suppl):S62–S67
Dachs GU, Steele AJ, Coralli C, Kanthou C, Brooks AC, Gunningham SP, Currie MJ, Watson AI, Robinson BA, Tozer GM (2006) Anti-vascular agent Combretastatin A-4-P modulates hypoxia inducible factor-1 and gene expression. BMC Cancer 6:280
Acknowledgements
We thank the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province and Strategic Cooperation Program Between Guangdong Province and Chinese Academy of Sciences, P. R. China (2003B31603, 2006B35604002, 2009B091300125) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, YC., Zou, Y., Ye, YL. et al. Anti-tumor activity and mechanisms of a novel vascular disrupting agent, (Z)-3,4′,5-trimethoxylstilbene-3′-O-phosphate disodium (M410). Invest New Drugs 29, 300–311 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-009-9366-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-009-9366-x