Abstract
Background
Circular RNA (circRNA) has been shown to be closely associated with cancer progression, including gastric cancer (GC). However, the function of circ_0004104 in GC progression has not been clarified.
Aims
The purpose of this study was to explore the role of circ_0004104 in GC progression.
Methods
The expression levels of circ_0004104, miR-539-3p, and ring finger protein 2 (RNF2) were assessed using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Cell proliferation was measured by 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2 thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide assay, and cell migration and invasion were detected using transwell assay. The levels of glutamine, glutamate, and α-ketoglutarate were determined to evaluate the glutaminolysis of cells, and the protein levels of glutaminolysis-related markers and RNF2 were detected using western blot analysis. Furthermore, Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay was employed to assess the interaction between miR-539-3p and circ_0004104 or RNF2. Animal experiments were carried out to evaluate the effect of circ_0004104 silencing on GC tumor growth in vivo.
Results
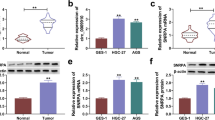
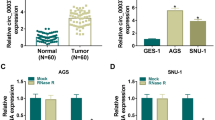
Circ_0004104 was upregulated in GC, and its knockdown repressed the proliferation, metastasis, and glutaminolysis of GC cells in vitro and reduced GC tumor growth in vivo. Furthermore, we discovered that circ_0004104 could sponge miR-539-3p and miR-539-3p could target RNF2. The rescue experiments suggested that miR-539-3p inhibitor could reverse the suppressive effect of circ_0004104 silencing on GC progression, and RNF2 overexpression also reversed the inhibition effect of miR-539-3p mimic on GC progression.
Conclusion
Circ_0004104 accelerated GC progression via regulating the miR-539-3p/RNF2 axis, indicating that circ_0004104 might be a potential therapeutic target for GC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Cutsem E, Sagaert X, Topal B, Haustermans K, Prenen H. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:2654–2664.
Zhang XY, Zhang PY. Gastric cancer: somatic genetics as a guide to therapy. J Med Genet. 2017;54:305–312.
Kinami S, Funaki H, Fujita H, Nakano Y, Ueda N, Kosaka T. Local resection of the stomach for gastric cancer. Surg Today. 2017;47:651–659.
Ratti M, Lampis A, Hahne JC, Passalacqua R, Valeri N. Microsatellite instability in gastric cancer: molecular bases, clinical perspectives, and new treatment approaches. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS. 2018;75:4151–4162.
Coutzac C, Pernot S, Chaput N, Zaanan A. Immunotherapy in advanced gastric cancer, is it the future? Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol. 2019;133:25–32.
Patel TH, Cecchini M. Targeted therapies in advanced gastric cancer. Curr Treat Opt Oncol. 2020;21:70.
Figueiredo C, Camargo MC, Leite M, Fuentes-Panana EM, Rabkin CS, Machado JC. Pathogenesis of gastric cancer: genetics and molecular classification. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;400:277–304.
Hamashima C. Current issues and future perspectives of gastric cancer screening. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:13767–13774.
Zhao ZJ, Shen J. Circular RNA participates in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of cancer. RNA Biol. 2017;14:514–521.
Chen B, Huang S. Circular RNA: an emerging non-coding RNA as a regulator and biomarker in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018;418:41–50.
Jin C, Zhao W, Zhang Z, Liu W. CircLMTK2 acts as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer via regulating the expression of microRNA-183. Life Sci. 2020;241:117097.
Zhang X, Wang S, Wang H, et al. Circular RNA circNRIP1 acts as a microRNA-149-5p sponge to promote gastric cancer progression via the AKT1/mTOR pathway. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:20.
Qiu Y, Pu C, Li Y, Qi B. Construction of a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network based on competitive endogenous RNA reveals the function of circRNAs in osteosarcoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:48.
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, et al. Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:79.
Hu K, Qin X, Shao Y, Zhou Y, Ye G, Xu S. Circular RNA MTO1 suppresses tumorigenesis of gastric carcinoma by sponging miR-3200-5p and targeting PEBP1. Mol Cell Probes 2020:101562.
Ma Y, Cong X, Zhang Y, Yin X, Zhu Z, Xue Y. CircPIP5K1A facilitates gastric cancer progression via miR-376c-3p/ZNF146 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:81.
Zhang L, Chang X, Zhai T, Yu J, Wang W, Du A, et al. A novel circular RNA, circ-ATAD1, contributes to gastric cancer cell progression by targeting miR-140-3p/YY1/PCIF1 signaling axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020.
Wang L, Shen C, Wang Y, et al. Identification of circular RNA Hsa_circ_0001879 and Hsa_circ_0004104 as novel biomarkers for coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2019;286:88–96.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA: A Cancer J Clin 2018;68:7–30.
Ling H, Girnita L, Buda O, Calin GA. Non-coding RNAs: the cancer genome dark matter that matters! Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017;55:705–714.
Slaby O, Laga R, Sedlacek O. Therapeutic targeting of non-coding RNAs in cancer. Biochem J. 2017;474:4219–4251.
Chen L, Dzakah EE, Shan G. Targetable long non-coding RNAs in cancer treatments. Cancer Lett. 2018;418:119–124.
Thorns C, Kuba J, Bernard V, et al. Deregulation of a distinct set of microRNAs is associated with transformation of gastritis into MALT lymphoma. Virchows Archiv Int J Pathol. 2012;460:371–377.
Zhou J, Su M, Zhang H, Wang J, Chen Y. miR-539-3P inhibits proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting CTBP1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12:1618–1625.
Ding S, Zhang Y. MicroRNA539 inhibits the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by targeting SRYbox 5 gene. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20:2533–2540.
Jin W, Han H, Liu D. Downregulation miR-539 is associated with poor prognosis of gastric cancer patients and aggressive progression of gastric cancer cells. Cancer Biomark Sect A Dis Mark. 2019;26:183–191.
Vidal M. Role of polycomb proteins Ring1A and Ring1B in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Int J Dev Biol. 2009;53:355–370.
Wen W, Peng C, Kim MO, et al. Knockdown of RNF2 induces apoptosis by regulating MDM2 and p53 stability. Oncogene. 2014;33:421–428.
Su WJ, Fang JS, Cheng F, Liu C, Zhou F, Zhang J. RNF2/Ring1b negatively regulates p53 expression in selective cancer cell types to promote tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:1720–1725.
Qi H, Xiao Z, Wang Y. Long non-coding RNA LINC00665 gastric cancer tumorigenesis by regulation miR-149-3p/RNF2 axis. OncoTargets Therapy. 2019;12:6981–6990.
Zhang J, Sun Z, Han Y, et al. Rnf2 knockdown reduces cell viability and promotes cell cycle arrest in gastric cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2017;13:3817–3822.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, F., Peng, K., Zhang, L. et al. Circ_0004104 Accelerates the Progression of Gastric Cancer by Regulating the miR-539-3p/RNF2 Axis. Dig Dis Sci 66, 4290–4301 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06802-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06802-5