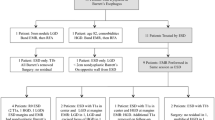
Abstract
Barrett’s esophagus with high-grade dysplasia and early-stage adenocarcinoma is amenable to curative treatment by endoscopic resection. Histopathological correlation has established that mucosal cancer has minimal risk of nodal metastases and that long-term complete remission can be achieved. Although surgery is the gold-standard treatment once there is submucosal involvement, even T1sm1 (submucosal invasion ≤ 500 μm) cases without additional risk factors for nodal metastases might also be cured with endoscopic resection. Endoscopic resection is foremost an initial diagnostic procedure, and once histopathological assessment confirms that curative criteria are met, it will be considered curative. Endoscopic resection may be achieved by endoscopic mucosal resection, which, although easy to perform with relatively low risk, is limited by an inability to achieve en bloc resection for lesions of size more than 1.5 cm. Conversely, the technique of endoscopic submucosal dissection is more technically demanding with higher risk of complications but is able to achieve en bloc resection for lesions larger than 1.5 cm. Endoscopic submucosal dissection would be particularly important in specific situations such as suspected submucosal invasion and lesion size more than 1.5 cm. In other situations, since endoscopic resection would always be combined with radiofrequency ablation to ablate the remaining Barrett’s epithelium, piecemeal endoscopic mucosal resection would suffice since any remnant superficial invisible dysplasia would be ablated.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buskens CJ, Westerterp M, Lagarde SM, Bergman JJ, ten Kate FJ, van Lanschot JJ. Prediction of appropriateness of local endoscopic treatment for high-grade dysplasia and early adenocarcinoma by EUS and histopathologic features. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;60:703–710.
Liu L, Hofstetter WL, Rashid A, et al. Significance of the depth of tumor invasion and lymph node metastasis in superficially invasive (T1) esophageal adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29:1079–1085.
Westerterp M, Koppert LB, Buskens CJ, et al. Outcome of surgical treatment for early adenocarcinoma of the esophagus or gastro-esophageal junction. Virchows Arch. 2005;446:497–504.
Ancona E, Rampado S, Cassaro M, Battaglia G, et al. Prediction of lymph node status in superficial esophageal carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:3278–3288.
Barbour AP, Jones M, Brown I, et al. Risk stratification for early esophageal adenocarcinoma: analysis of lymphatic spread and prognostic factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:2494–2502.
Leers JM, DeMeester SR, Oezcelik A, et al. The prevalence of lymph node metastases in patients with T1 esophageal adenocarcinoma a retrospective review of esophagectomy specimens. Ann Surg. 2011;253:271–278.
Pech O, Bollschweiler E, Manner H, Leers J, Ell C, Hölscher AH. Comparison between endoscopic and surgical resection of mucosal esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus at two high-volume centers. Ann Surg. 2011;254:67–72.
Dunbar KB, Spechler SJ. The risk of lymph-node metastases in patients with high-grade dysplasia or intramucosal carcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107:850–862.
Bollschweiler E, Baldus SE, Schroder W, et al. High rate of lymph node metastasis in submucosal esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. Endoscopy. 2006;38:149–156.
Alvarez Herrero L, Pouw RE, van Vilsteren FG, et al. Risk of lymph node metastasis associated with deeper invasion by early adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and cardia: study based on endoscopic resection specimens. Endoscopy. 2010;42:1030–1036.
Manner H, Pech O, Heldmann Y, et al. Efficacy, safety, and long-term results of endoscopic treatment for early stage adenocarcinoma of the esophagus with low-risk sm1 invasion. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:630–635.
Schölvinck D, Künzli H, Meijer S, et al. Management of patients with T1b esophageal adenocarcinoma: a retrospective cohort study on patient management and risk of metastatic disease. Surg Endosc. 2016;30:4102–4113.
Manner H, Pech O, Heldmann Y, et al. The frequency of lymph node metastasis in early-stage adenocarcinoma of the esophagus with incipient submucosal invasion (pT1b sm1)depending on histological risk patterns. Surg Endosc. 2015;29:1888–1896.
Pech O, May A, Manner H, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of endoscopic resection for patients with mucosal adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:652–660.
Peters FP, Brakenhoff KP, Curvers WL, et al. Histologic evaluation of resection specimens obtained at 293 endoscopic resections in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;67:604–609.
Pech O, Gossner L, Manner H, et al. Prospective evaluation of the macroscopic types and location of early Barrett’s neoplasia in 380 lesions. Endoscopy. 2007;39:588–593.
Fock KM, Talley N, Goh KL, et al. Asia-Pacific consensus on the management of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: an update focusing on refractory reflux disease and Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut. 2016;65:1402–1415.
Fitzgerald RC, di Pietro M, Ragunath K, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the diagnosis and management of Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut. 2014;63:7–42.
di Pietro M, Fitzgerald RC. BSG Barrett’s guidelines working group. Revised British Society of Gastroenterology recommendation on the diagnosis and management of Barrett’s oesophagus with low-grade dysplasia. Gut. 2018;67:392–393.
Weusten B, Bisschops R, Coron E, et al. Endoscopic management of Barrett’s esophagus: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Position Statement. Endoscopy. 2017;49:191–198.
Shaheen NJ, Falk GW, Iyer PG, Gerson LB. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis and management of Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111:30–50.
Seewald S, Ang TL, Gotoda T, Soehendra N. Total endoscopic resection of Barrett esophagus. Endoscopy. 2008;40:1016–1020.
Inoue H, Endo M, Takeshita K, Yoshino K, Muraoka Y, Yoneshima H. A new simplified technique of endoscopic esophageal mucosal resection using a cap-fitted panendoscope (EMRC). Surg Endosc. 1992;6:264–265.
Soehendra N, Seewald S, Groth S, et al. Use of modified multiband ligator facilitates circumferential EMR in Barrett’s esophagus (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:847–852.
Pouw RE, van Vilsteren FG, Peters FP, et al. Randomized trial on endoscopic resection-cap versus multiband mucosectomy for piecemeal endoscopic resection of early Barrett’s neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;74:35–43.
Oyama T. Esophageal ESD: technique and prevention of complications. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014;24:201–212.
Guo HM, Zhang XQ, Chen M, Huang SL, Zou XP. Endoscopic submucosal dissection vs endoscopic mucosal resection for superficial esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:5540–5547.
Terheggen G, Horn EM, Vieth M, et al. A randomised trial of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection for early Barrett’s neoplasia. Gut. 2017;66:783–793.
Pimentel-Nunes P, Dinis-Ribeiro M, Ponchon T, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy. 2015;47:829–854.
Tomizawa Y, Iyer PG, Wong Kee Song LM, Buttar NS, Lutzke LS, Wang KK. Safety of endoscopic mucosal resection for Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:1440–1447.
Hwang JH, Konda V, Abu Dayyeh BK, et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82:215–226.
Belghazi K, Wang KK, Milano RV, et al. Safety of the six-shooter multiband mucosectomy device for endoscopic resection in Barrett’s esophagus in 7743 resections: a retrospective international multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87:AB83.
Yang D, Zou F, Xiong S, Forde JJ, Wang Y, Draganov PV. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early Barrett’s neoplasia: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;87:1383–1393.
van Vilsteren FG, Pouw RE, Seewald S, et al. Stepwise radical endoscopic resection versus radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s oesophagus with high-grade dysplasia or early cancer: a multicentre randomised trial. Gut. 2011;60:765–773.
Bahin FF, Jayanna M, Hourigan LF, et al. Long-term outcomes of a primary complete endoscopic resection strategy for short-segment Barrett’s esophagus with high-grade dysplasia and/or early esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;83:68–77.
Subramaniam S, Chedgy F, Longcroft-Wheaton G, et al. Complex early Barrett’s neoplasia at 3 Western centers: European Barrett’s Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection Trial (E-BEST). Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86:608–618.
Phoa KN, Pouw RE, Bisschops R, et al. Multimodality endoscopic eradication for neoplastic Barrett oesophagus: results of an European multicentre study (EURO-II). Gut. 2016;65:555–562.
Desai M, Saligram S, Gupta N, et al. Efficacy and safety outcomes of multimodal endoscopic eradication therapy in Barrett’s esophagus-related neoplasia: a systematic review and pooled analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85:482–495.
Neuhaus H, Terheggen G, Rutz EM, Vieth M, Schumacher B. Endoscopic submucosal dissection plus radiofrequency ablation of neoplastic Barrett’s esophagus. Endoscopy. 2012;44:1105–1113.
Kagemoto K, Oka S, Tanaka S, et al. Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial Barrett’s adenocarcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;80:239–245.
Chevaux JB, Piessevaux H, Jouret-Mourin A, Yeung R, Danse E, Deprez PH. Clinical outcome in patients treated with endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial Barrett’s neoplasia. Endoscopy. 2015;47:103–112.
Probst A, Aust D, Märkl B, Anthuber M, Messmann H. Early esophageal cancer in Europe: endoscopic treatment by endoscopic submucosal dissection. Endoscopy. 2015;47:113–121.
Yang D, Coman RM, Kahaleh M, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for Barrett’s early neoplasia: a multicenter study in the United States. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86:600–607.
Shimizu T, Fujisaki J, Omae M, et al. Treatment outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for adenocarcinoma originating from long-segment Barrett’s Esophagus versus short-segment Barrett’s Esophagus. Digestion. 2018;97:316–323.
Pohl H, Sonnenberg A, Strobel S, Eckardt A, Rösch T. Endoscopic versus surgical therapy for early cancer in Barrett’s esophagus: a decision analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:623–631.
Bourke MJ, Neuhaus H, Bergman JJ. Endoscopic submucosal dissection: indications and application in western endoscopy practice. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:1887–1900.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seewald, S., Ang, T.L., Pouw, R.E. et al. Management of Early-Stage Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus: Endoscopic Mucosal Resection and Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection. Dig Dis Sci 63, 2146–2154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5158-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5158-5