Abstract
Background
Protein phosphatase 1γ (PP1γ), as a member of the protein phosphatase 1 family, may be involved in regulation of multiple cellular processes, such as mitosis, cell survival, and apoptosis. However, little is known about the underlying mechanisms by which PP1γ regulates hepatocellular carcinoma development.
Aim
We investigated the expression profile of PP1γ in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines and human HCC specimens, as well as its potential prognostic significance in HCC.
Methods
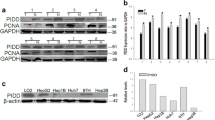
PP1γ expression profile was detected in 94 HCC specimens using immunohistochemistry. PP1γ levels in HCC cells were downregulated by small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection. Cell cycle progression and proliferation status of HCC cells and the effectiveness of doxorubicin were evaluated by flow cytometry and CCK-8 assay. The levels of PP1γ, CyclinD1, PCNA, Mdmx, p53, p21, and active caspase-3 were evaluated by Western blot analysis.
Results
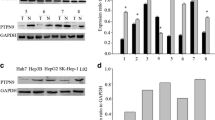
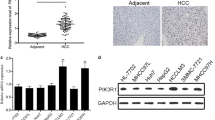
PP1γ was upregulated in tumorous specimens, compared with adjacent nontumorous tissues. Univariate and multivariate survival analyses were conducted to determine the prognostic significance of PP1γ in HCC. The expression pattern of PP1γ was positively correlated with tumor size, histological grade, Ki-67 expression, and poor prognosis in HCC. In addition, depletion of PP1γ by siRNA could inhibit cell proliferation, resulted in G1 phase arrest, and attenuated resistance to doxorubicin in Huh7 cells.
Conclusions
PP1γ is upregulated in HCC cell lines and HCC specimens, promotes cancer cell proliferation through regulation of p53, and may be a potential target for treatment of HCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruix J, Reig M, Sherman M. Evidence-based diagnosis, staging, and treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:835–853.
Zhang X, Ng HL, Lu A, et al. Drug delivery system targeting advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: current and future. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2016;12:853–869.
Cohen PT. Protein phosphatase 1—targeted in many directions. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:241–256.
Comerford KM, Leonard MO, Cummins EP, et al. Regulation of protein phosphatase 1gamma activity in hypoxia through increased interaction with NIPP1: implications for cellular metabolism. J Cell Physiol. 2006;209:211–218.
Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Andersen J, Lam YW, Moorhead G, Mann M, Lamond AI. Repo-MAN recruits PP1 gamma to chromatin and is essential for cell viability. J Cell Biol. 2006;172:679–692.
Vietri M, Bianchi M, Ludlow JW, Mittnacht S, Villa-Moruzzi E. Direct interaction between the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1 and pRb. Cancer Cell Int. 2006;6:3.
Lu Z, Wan G, Guo H, Zhang X, Lu X. Protein phosphatase 1 inhibits p53 signaling by dephosphorylating and stabilizing Mdmx. Cell Signal. 2013;25:796–804.
Theurillat JP, Metzler SC, Henzi N, et al. URI is an oncogene amplified in ovarian cancer cells and is required for their survival. Cancer Cell. 2011;19:317–332.
Winter SL, Bosnoyan-Collins L, Pinnaduwage D, Andrulis IL. The interaction of PP1 with BRCA1 and analysis of their expression in breast tumors. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:85.
Jiang D, Hu B, Wei L, et al. High expression of vacuolar protein sorting 4B (VPS4B) is associated with accelerated cell proliferation and poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2015;211:240–247.
Bao Z, Duan C, Gong C, et al. Protein phosphatase 1gamma regulates the proliferation of human glioma via the NF-kappaB pathway. Oncol Rep. 2016;35:2916–2926.
Wan C, Hou S, Ni R, et al. MIF4G domain containing protein regulates cell cycle and hepatic carcinogenesis by antagonizing CDK2-dependent p27 stability. Oncogene. 2015;34:237–245.
Zhang S, Shi W, Chen Y, et al. Overexpression of SYF2 correlates with enhanced cell growth and poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;410:1–9.
Li Y, Jenkins CW, Nichols MA, Xiong Y. Cell cycle expression and p53 regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21. Oncogene. 1994;9:2261–2268.
Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Giovannini C, et al. MiR-122/cyclin G1 interaction modulates p53 activity and affects doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69:5761–5767.
Rampone B, Schiavone B, Martino A, Viviano C, Confuorto G. Current management strategy of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:3210–3216.
Meng X, Franklin DA, Dong J, Zhang Y. MDM2-p53 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2014;74:7161–7167.
Opaluch AM, Schneider M, Chiang CY, et al. Positive regulation of TRAF6-dependent innate immune responses by protein phosphatase PP1-gamma. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e89284.
Dhillon AS, Meikle S, Yazici Z, Eulitz M, Kolch W. Regulation of Raf-1 activation and signalling by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 2002;21:64–71.
Mitsuhashi S, Shima H, Tanuma N, et al. Usage of tautomycetin, a novel inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1), reveals that PP1 is a positive regulator of Raf-1 in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:82–88.
Djouder N, Metzler SC, Schmidt A, et al. S6K1-mediated disassembly of mitochondrial URI/PP1gamma complexes activates a negative feedback program that counters S6K1 survival signaling. Mol Cell. 2007;28:28–40.
Tummala KS, Gomes AL, Yilmaz M, et al. Inhibition of de novo NAD(+) synthesis by oncogenic URI causes liver tumorigenesis through DNA damage. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:826–839.
Wang X, Simpson ER, Brown KA. p53: protection against tumor growth beyond effects on cell cycle and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2015;75:5001–5007.
Shen HM, Ong CN. Mutations of the p53 tumor suppressor gene and ras oncogenes in aflatoxin hepatocarcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 1996;366:23–44.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Project Foundation of Nantong (Nos. MS22015044, MS12015051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Chunsun Li and Miaomiao Wu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Wu, M., Zong, G. et al. Overexpression of Protein Phosphatase 1γ (PP1γ) Is Associated with Enhanced Cell Proliferation and Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 62, 133–142 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-016-4365-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-016-4365-1