Abstract
Background
MiR-141 and long noncoding RNA MEG3 have been independently reported to be tumor suppressor genes in various cancers. However, their expression has never been previously associated with gastric cancer (GC).
Aims
To investigate the interaction of miR-141 and MEG3 in GC.
Methods
QRT-PCR was used to detect miR-141, MEG3, and E2F3 in gastric tissues and cells. CCK-8 and flow cytometry analysis were used to detect cell functions. Western blot and luciferase activity were used to identify E2F3 as one of the direct targets of miR-141.
Results
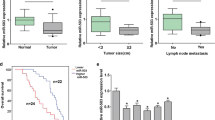
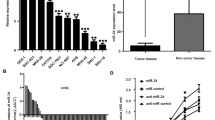
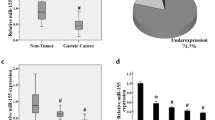
We found that expression of both miR-141 and MEG3 was significantly reduced in GC compared with levels in matched nonmalignant tissues. Positive correlation between miR-141 and MEG3 was found in both tumor tissues and control tissues. Furthermore, the over-expression of either miR-141 or MEG3 in 7901 and MKN45 cells inhibited cell proliferation and cell cycle progression and promoted cell apoptosis. E2F3 was identified as a target of miR-141, and its inhibition significantly reduced MEG3 expression. E2F3 expression was also found to be negatively associated with both MEG3 and miR-141. E2F3 over-expression partly reversed the changes caused by transfection of miR-141 mimic, and inhibition of miR-141 or MEG3 overrides MEG3- or miR-141-induced modulation of cell growth in GC.
Conclusions
These findings together suggested that miR-141 could be interacting with MEG3 and targeting E2F3, and these factors may play important anti-tumor effects in GC pathogenesis and provide therapeutic targets in the clinics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fock KM. Review article: the epidemiology and prevention of gastric cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40:250–260.
Yang W, Raufi A, Klempner SJ. Targeted therapy for gastric cancer: molecular pathways and ongoing investigations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1846:232–237.
Ma J, Hong L, Chen Z, Nie Y, Fan D. Epigenetic regulation of microRNAs in gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:716–723.
Pérez-Ortín JE, Alepuz P, Chávez S, et al. Eukaryotic mRNA decay: methodologies, pathways, and links to other stages of gene expression. J Mol Biol. 2013;425:3750–3775.
Yang YF, Wang F, Xiao JJ, et al. MiR-222 overexpression promotes proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells by downregulating p27. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7:893–902.
Miao L, Liu K, Xie M, et al. miR-375 inhibits Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric carcinogenesis by blocking JAK2-STAT3 signaling. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014;63:699–711.
Zhang L, Wang X, Chen P. MiR-204 down regulates SIRT1 and reverts SIRT1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition, anoikis resistance and invasion in gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:290.
Otsubo T, Akiyama Y, Hashimoto Y, et al. MicroRNA-126 inhibits SOX2 expression and contributes to gastric carcinogenesis. PLoS One. 2011;6:e16617.
Arita T, Ichikawa D, Konishi H, et al. Circulating long non-coding RNAs in plasma of patients with gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:3185–3193.
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature. 2014;505:344–352.
Zhou X, Xia Y, Su J, et al. Down-regulation of miR-141 induced by helicobacter pylori promotes the invasion of gastric cancer by targeting STAT4. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33:1003–1012.
Sun M, Xia R, Jin F, et al. Downregulated long noncoding RNA MEG3 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:1065–1073.
Yeh TS, Wang F, Chen TC, et al. Expression profile of microRNA-200 family in hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct tumor thrombus. Ann Surg.. 2014;259:346–354.
Anwar SL, Krech T, Hasemeier B, et al. Loss of imprinting and allelic switching at the DLK1-MEG3 locus in human hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 2012;7:e49462.
Ratert N, Meyer HA, Jung M, et al. miRNA profiling identifies candidate mirnas for bladder cancer diagnosis and clinical outcome. J Mol Diagn. 2013;15:695–705.
Ying L, Huang Y, Chen H, et al. Downregulated MEG3 activates autophagy and increases cell proliferation in bladder cancer. Mol Biosyst. 2013;9:407–411.
Sørensen KD, Ørntoft TF. Discovery of prostate cancer biomarkers by microarray gene expression profiling. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2010;10:49–64.
Zhao J, Ohsumi TK, Kung JT, et al. Genome-wide identification of polycomb-associated RNAs by RIP-seq. Mol Cell. 2010;40:939–953.
Braconi C, Kogure T, Valeri N, et al. microRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene. 2011;30:4750–4756.
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, et al. MicroRNA-200c modulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human colorectal cancer metastasis. Gut. 2013;62:1315–1326.
Li X, Roslan S, Johnstone CN, et al. MiR-200 can repress breast cancer metastasis through ZEB1-independent but moesin-dependent pathways. Oncogene. 2014;3:4077–4088.
van Jaarsveld MT, Helleman J, Boersma AW, et al. miR-141 regulates KEAP1 and modulates cisplatin sensitivity in ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene. 2013;32:4284–4293.
Al-Khalaf HH, Mohideen P, Nallar SC, et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16INK4a physically interacts with transcription factor Sp1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 4 to transactivate microRNA-141 and microRNA-146b-5p spontaneously and in response to ultraviolet light-induced DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:35511–35525.
Julian LM, Vandenbosch R, Pakenham CA, et al. Opposing regulation of Sox2 by cell-cycle effectors E2f3a and E2f3b in neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12:440–452.
Prost S, Lu P, Caldwell H, et al. E2F regulates DDB2: consequences for DNA repair in Rb-deficient cells. Oncogene. 2007;26:3572–3581.
Chen D, Chen Y, Forrest D, et al. E2f2 induces cone photoreceptor apoptosis independent of E2f1 and E2f3. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20:931–940.
Xiao F, Zhang W, Chen L, et al. MicroRNA-503 inhibits the G1/S transition by downregulating cyclin D3 and E2F3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med. 2013;11:195.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81470830), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (JX10231801), and Jiangsu postgraduate scientific research and innovation projects (CXZZ13_0574).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no potential conflict to disclose.
Additional information
Xiaoying Zhou, Guoping Ji, and Huiyuan Gu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Ji, G., Ke, X. et al. MiR-141 Inhibits Gastric Cancer Proliferation by Interacting with Long Noncoding RNA MEG3 and Down-Regulating E2F3 Expression. Dig Dis Sci 60, 3271–3282 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-015-3782-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-015-3782-x