Abstract
Introduction
Loss of HBeAg and development of anti-HBe (seroconversion) is seen as a milestone and endpoint in the treatment of HBeAg-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). Among patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogs (NA), recurrent viremia is common after discontinuation of therapy. Entecavir (ETV) and tenofovir (TDF) are highly potent NA. The durability of virological response and HBeAg seroconversion in patients treated with these agents is not well studied.
Methods
We retrospectively studied the outcomes of 54 HBeAg-positive CHB patients who were treated with either ETV (n = 30) or TDF (23) or both (n = 1) that achieved virological response and underwent seroconversion and consolidation therapy before cessation of treatment.
Results
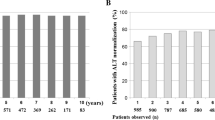
Only 4 (7 %) patients had sustained virological, serological, and biochemical remission. Thirteen patients (24 %) continued to have HBV DNA levels below 2000 IU/mL and normal alanine aminotransferase activity (ALT). Thirty-seven patients (69 %) developed HBV DNA >2000 IU/mL, with 20 having elevated ALT. Among these 37 patients, 23 (62 %) remained HBeAg negative/anti-HBe positive, 12 (32 %) became HBeAg positive, and 2 (5 %) were HBeAg and anti-HBe negative. Duration of consolidation therapy did not correlate with low versus high level of virological relapse.
Conclusions
Durability of HBeAg seroconversion associated with ETV or TDF was not superior to that reported in patients treated with less potent NA. Our results, aggregated with others, suggest HBeAg seroconversion should not be considered as a treatment endpoint for most HBeAg-positive patients treated with NA. Future updates of treatment guidelines should reconsider HBeAg seroconversion as an endpoint to therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fattovich G, Rugge M, Brollo L, et al. Clinical, virologic and histologic outcome following seroconversion from HBeAg to anti-HBe in chronic hepatitis type B. Hepatology. 1986;6:167–172.
Hui CK, Leung N, Shek TW, et al. Sustained disease remission after spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion is associated with reduction in fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis B Chinese patients. Hepatology. 2007;46:690–698.
Liaw YF, Lau GK, Kao JH, Gane E. Hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion: a critical event in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:2727–2734. doi:10.1007/s10620-010-1179-4.
Hsu YS, Chien RN, Yeh CT, et al. Long-term outcome after spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2002;35:1522–1527.
Kuo L-F, Lee C-M, Hung C-H, et al. High risk of hepatitis B virus reactivation in nucleos(t)e analogue-induced hepatitis B e antigen seroconverters older than 40 years. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:2580–2587.
Dienstag JL, Cianciara J, Karayalcin S, et al. Durability of serologic response after lamivudine treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2003;37:748–755.
Poynard T, Hou J-H, Chutaputti A, Manns M, Naoumov N. Sustained durability of HBeAg seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B patients after treatment with telbivudine. J Hepatol. 2008;48:S268.
Song B-C, Suh DJ, Lee HC, Chung Y-H, Lee YS. Hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion after lamivudine therapy is not durable in patients with chronic hepatitis B in Korea. Hepatology. 2000;32:803–806.
Jo K, Dodge JL, Wadley A, Wakil AE, Baron JL, Cooper S. HBeAg seroconversion is lower in Asian versus non-Asian patients during treatment of chronic hepatitis B with tenofovir or entecavir. Hepatology. 2013;58:669A.
Lee CM, Ong G-Y, Lin S-N, et al. Durability of lamivudine-induced HBeAg seroconversion for chronic hepatitis B patients with acute exacerbation. J Hepatol. 2002;37:669–674.
Wang L, Liu F, Li X-Y, Wang J-B, Zhang Z-H, Wang Y-Z. Stringent cessation criterion results in better durability of lamivudine treatment: a prospective clinical study in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B patients. J Viral Hepat. 2010;17:298–304.
Song BC, Cui XJ, Cho YK, et al. New scoring system for predicting relapse after lamivudine-induced hepatitis B e-antigen loss in chronic hepatitis B patients. Hepatol Res. 2009;39:1064–1071.
Fung J, Lai CL, Tanaka Y, et al. The duration of lamivudine therapy for chronic hepatitis B: cessation versus continuation of treatment after HBeAg seroconversion. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:1940–1946.
Jin YJ, Kim KM, Yoo DJ, et al. Clinical course of chronic hepatitis B patients who were off-treated after lamivudine treatment: analysis of 138 consecutive patients. Virol J. 2012;9:239.
Chien R-N, Yeh C-T, Tsai S-L, Chu C-M, Liaw Y-F. Determinants for sustained HBeAg response to lamivudine therapy. Hepatology. 2003;38:1267–1273.
Byun KS, Kwon OS, Kim JH, et al. Factors related to post-treatment relapse in chronic hepatitis B patients who lost HBeAg after lamivudine therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;20:1838–1842.
Kuo YH, Chen CH, Wang JH, et al. Extended lamivudine consolidation therapy in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B patients improves sustained hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:75–81.
Lee HW, Lee HJ, Hwang JS, et al. Lamivudine maintenance beyond one year after HBeAg seroconversion is a major factor for sustained virologic response in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2010;51:415–421.
Reijnders JGP, Perquin MJ, Zhang N, Hansen BE, Janssen HL. Nucleos(t)ide analogues only induce temporary hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in most patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:491–498.
Chaung KT, Ha NB, Trinh HN, et al. High frequency of recurrent viremia after hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion and consolidation therapy. J Clin Gastrol. 2012;46:865–870.
Marcellin P, Heathcote EJ, Buti M, et al. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate versus adefovir dipivoxil for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2442–2455.
Ahn J, Lee HM, Lim J, et al. Entecavir safety and effectiveness in a natural cohort of chronic hepatitis B patients in the United States. The ENUMERATE study. Hepatology. 2014;60:1100A.
Lok ASF, McMahon B. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2007;45:507–539.
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2012;57:167–185.
Liaw YF, Kao J-H, Piratvisuth T, et al. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2012 update. Hepatol Int. 2012;6:531–561.
Prati D, Taioli E, Zanella A, et al. Updated definitions of healthy ranges for serum alanine aminotransferase levels. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137:1–10.
Gish RG, Lok AS, Chang TT, et al. Entecavir therapy for up to 96 weeks in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1437–1444.
Ridruejo E, Marciano S, Galdane O, et al. Relapse rates in chronic hepatitis B naïve patients after discontinuation of antiviral therapy with entecavir. J Viral Hepat. 2014;21:590–596.
Song MJ, Song DS, Kim HY, et al. Durability of viral response after off-treatment in HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:6277–6283.
Publicover J, Goodsell A, Nishimura S, et al. IL-21 is pivotal in determining age-dependent effectiveness of immune responses in a mouse model of human hepatitis B. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:1154–1162.
Liaw YF, Sung JJ, Chow WC, et al. Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1521–1531.
Wong GL, Chan HL, Mak CW, et al. Entecavir treatment reduces hepatic events and deaths in chronic hepatitis B patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2013;58:1537–1547.
Chang TT, Liaw YF, Wu SS, et al. Long-term entecavir therapy results in the reversal of fibrosis/cirrhosis and continued histological improvement in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2010;52:886–893.
Marcellin P, Gane E, Buti M, et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: a 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet. 2013;381:468–475.
Hosaka T, Suzuki F, Kobayashi M, et al. Long-term entecavir treatment reduces hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 2013;58:98–107.
Wu CY, Lin JT, Ho HJ, et al. Association of nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy with reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a nationwide cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:143–151.
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, et al. REVEAL-HBV Study Group Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA. 2006;295:65–73.
Iloeje UH, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Chen CJ. Risk Evaluation of Viral Load Elevation and Associated Liver Disease/Cancer-In HBV (the REVEAL-HBV) study group. Predicting cirrhosis risk based on the level of circulating hepatitis B viral load. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:678–686.
Zoutendijk R, Reijnders JG, Zoulim F, et al. Virological response to entecavir is associated with a better clinical outcome in chronic hepatitis B patients with cirrhosis. Gut. 2013;62:760–765.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Dat Nghiem for reviewing this manuscript and for his thoughtful comments and suggestions. Authors received the grant support from Gilead Sciences and Daughters of Charity Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Tse-Ling Fong and Myron J Tong: Gilead Sciences; Speaker Bureau, Advisory Board, Research Funding. BMS; Speaker Bureau, Advisory Board, Research Funding. Andy Tien, Kahee J. Jo, Wafa Mohammed, Andrew Velasco, Vinh-Huy LeDuc, Nickolas Nguyen, Yong-Won Cho and Stewart L. Cooper: No industry relationships or conflicts of interest. Danny Chu, Eddie Cheung, Edward A. Mena, Quang-Quoc Phan, Andy Yu, Steven-Bui Han, Ho S. Bae: Gilead Sciences; Speaker Bureau, Advisory Board. BMS; Speaker Bureau, Advisory Board. Mimi Chang: Gilead Sciences; Speaker Bureau. BMS; Speaker Bureau.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fong, TL., Tien, A., Jo, K.J. et al. Durability of Hepatitis B e Antigen Seroconversion in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Treated with Entecavir or Tenofovir. Dig Dis Sci 60, 3465–3472 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-015-3775-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-015-3775-9