Abstract
Background and Aim
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has been implicated in the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. A methionine–choline-deficient (MCD) diet induces robust ER stress response and steatohepatitis, but the effects of ER stress modulation on the course of steatohepatitis remain uncertain. The present study evaluated whether reducing ER stress using the chemical chaperone tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) could limit hepatocyte lipoapoptosis and progression of MCD diet-induced steatohepatitis.
Methods
HuH7 cells stably transfected with sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (HuH-Ntcp cells) and palmitate (PA) were used. Experimental steatohepatitis was induced in male C57BL/6 mice using an MCD diet, and three different doses of TUDCA (500, or 1,000 mg/kg, once daily; or 500 mg/kg twice daily) were administered by gavage from the start of the MCD diet regimen or after 4 weeks.
Results
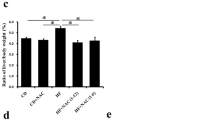
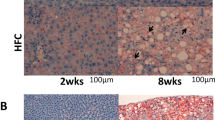
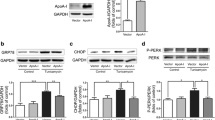
TUDCA reduced PA-induced ER stress as manifested by decreased eIF2α phosphorylation, XBP1 splicing and expression of BiP, ATF4, and CHOP in HuH-Ntcp cells. TUDCA also decreased PA-induced JNK phosphorylation, Puma up-regulation and Bax activation, which in turn suppressed caspase-dependent hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. Mice given TUDCA did not show a significant decrease in the intrahepatic triglyceride contents and steatosis. However, TUDCA treatment significantly reduced hepatic damage compared to controls for both early and late treatment groups. TUDCA treatment reduced the expression of ER stress markers and pro-apoptotic proteins, leading to decreased apoptosis and oxidative stress. Finally, TUDCA reduced histological fibrosis along with the down-regulation of pro-fibrotic gene expression in both early and late treatment groups.
Conclusions
These results show that TUDCA attenuates the progression of MCD diet-induced steatohepatitis by reducing ER stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fabbrini E, Sullivan S, Klein S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: biochemical, metabolic, and clinical implications. Hepatology. 2010;51:679–689.
Neuschwander-Tetri BA. Hepatic lipotoxicity and the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: the central role of nontriglyceride fatty acid metabolites. Hepatology. 2010;52:774–788.
Malhi H, Kaufman RJ. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol. 2011;54:795–809.
Gentile CL, Frye M, Pagliassotti MJ. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15:505–521.
Malhi H, Bronk SF, Werneburg NW, Gores GJ. Free fatty acids induce JNK-dependent hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:12093–12101.
Cazanave SC, Elmi NA, Akazawa Y, Bronk SF, Mott JL, Gores GJ. CHOP and AP-1 cooperatively mediate PUMA expression during lipoapoptosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010;299:G236–G243.
Kusminski CM, Shetty S, Orci L, Unger RH, Scherer PE. Diabetes and apoptosis: lipotoxicity. Apoptosis Int J Progr Cell Death. 2009;14:1484–1495.
Xie Q, Khaoustov VI, Chung CC, et al. Effect of tauroursodeoxycholic acid on endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced caspase-12 activation. Hepatology. 2002;36:592–601.
Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, et al. Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science. 2006;313:1137–1140.
Yang JS, Kim JT, Jeon J, et al. Changes in hepatic gene expression upon oral administration of taurine-conjugated ursodeoxycholic acid in ob/ob mice. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e13858.
Leclercq IA, Farrell GC, Schriemer R, Robertson GR. Leptin is essential for the hepatic fibrogenic response to chronic liver injury. J Hepatol. 2002;37:206–213.
Takahashi Y, Soejima Y, Fukusato T. Animal models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:2300–2308.
Rinella ME, Elias MS, Smolak RR, Fu T, Borensztajn J, Green RM. Mechanisms of hepatic steatosis in mice fed a lipogenic methionine choline-deficient diet. J Lipid Res. 2008;49:1068–1076.
Higuchi H, Bronk SF, Takikawa Y, et al. The bile acid glycochenodeoxycholate induces trail-receptor 2/DR5 expression and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:38610–38618.
Cogger VC, Muller M, Fraser R, McLean AJ, Khan J, Le Couteur DG. The effects of oxidative stress on the liver sieve. J Hepatol. 2004;41:370–376.
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313–1321.
Henkel AS, Dewey AM, Anderson KA, Olivares S, Green RM. Reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress does not improve steatohepatitis in mice fed a methionine- and choline-deficient diet. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;303:G54–G59.
Berger E, Haller D. Structure-function analysis of the tertiary bile acid TUDCA for the resolution of endoplasmic reticulum stress in intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;409:610–615.
Ceylan-Isik AF, Sreejayan N, Ren J. Endoplasmic reticulum chaperon tauroursodeoxycholic acid alleviates obesity-induced myocardial contractile dysfunction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;50:107–116.
Tu BP, Weissman JS. Oxidative protein folding in eukaryotes: mechanisms and consequences. J Cell Biol. 2004;164:341–346.
Malhotra JD, Miao H, Zhang K, et al. Antioxidants reduce endoplasmic reticulum stress and improve protein secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:18525–18530.
Rolo AP, Teodoro JS, Palmeira CM. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;52:59–69.
Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Vandenabeele P, Krysko DV, Agostinis P. ER stress-induced inflammation: does it aid or impede disease progression? Trends Mol Med. 2012;18:589–598.
Vizzutti F, Provenzano A, Galastri S, et al. Curcumin limits the fibrogenic evolution of experimental steatohepatitis. Lab Investig J Tech Met Pathol. 2010;90:104–115.
Schiff ER, Sorrell MF, Maddrey WC. Schiff’s Diseases of the Liver. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007.
Sanyal AJ, Brunt EM, Kleiner DE, et al. Endpoints and clinical trial design for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2011;54:344–353.
Rudolph G, Kloeters-Plachky P, Sauer P, Stiehl A. Intestinal absorption and biliary secretion of ursodeoxycholic acid and its taurine conjugate. Eur J Clin Invest. 2002;32:575–580.
Anstee QM, Goldin RD. Mouse models in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis research. Int J Exp Pathol. 2006;87:1–16.
Hofmann AF. Biliary secretion and excretion in health and disease: current concepts. Ann Hepatol. 2007;6:15–27.
Tanaka N, Matsubara T, Krausz KW, Patterson AD, Gonzalez FJ. Disruption of phospholipid and bile acid homeostasis in mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2012;56:118–129.
Plösch T, van der Veen JN, Havinga R, Huijkman NC, Bloks VW, Kuipers F. Abcg5/Abcg8-independent pathways contribute to hepatobiliary cholesterol secretion in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;291:G414–G423.
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M, Ahmad N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008;22:659–661.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the SNUH Research Fund (No. 03-2012-0220), and in part by Daewoong research fund (No. 06-2011-0070).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, EJ., Yoon, JH., Kwak, MS. et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Attenuates Progression of Steatohepatitis in Mice Fed a Methionine–Choline-Deficient Diet. Dig Dis Sci 59, 1461–1474 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3217-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3217-0