Abstract
Background
MicroRNAs play important roles in the development and progression of various cancers. Recent studies have shown that miR-638 was downregulated in several tumors; however, its role in gastric cancer (GC) has not been investigated in detail.
Aims
The purpose of this study was to determine the role of miR-638 and to elucidate its regulatory mechanism in GC.
Methods
The expression levels of miR-638 and specificity protein 2 (Sp2) were detected by real-time PCR and Western blotting in GC. After pcDNA6.2-GW/EmGFP-miR-638 vector, miR-638 inhibitor and Sp2-siRNA transfection, the AGS cell proliferation was investigated by MTT assay and cell cycle, and apoptosis was detected using the Annexin V/PI. In addition, the regulation of Sp2 by miR-638 was evaluated by real-time RT-PCR, Western blot and luciferase reporter assays; cyclin D1 expression was measured by Western blotting.
Results
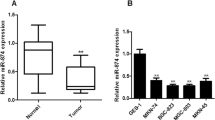
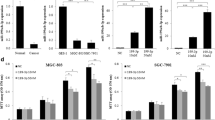
The expression of miR-638 is dramatically down-regulated and Sp2 expression is remarkably up-regulated in GC tissues. Luciferase assays revealed that miR-638 inhibited Sp2 expression by targeting the 3′-UTR of Sp2 mRNA. Overexpression of miR-638 and Sp2-siRNA reduced Sp2 expression at both the mRNA and protein levels in vitro, and inhibition of miR-638 increased Sp2 expression. Moreover, we found that miR-638 overexpression and Sp2-siRNA markedly suppressed cell proliferation with decreasing expression of cyclin D1 and inducing G1-phase cell-cycle arrest in vitro; inhibition of miR-638 significantly promoted cell proliferation by increasing expression of cyclin D1 and leading more cells into the S and G2/M phase.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrated that miR-638 suppressed GC cell proliferation by targeting Sp2 with influence on the expression of cyclin D1. We suggest that miR-638 might be a candidate predictor or an anticancer therapeutic target for GC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu H, Zhu L, Liu B, et al. RGenome-wide microRNA profiles identify miR-378 as a serum biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2012;316:196–203.
Parkin DM, Bray FI, Devesa SS. Cancer burden in the year 2000, the global picture. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37:S4–S66.
Yuasa Y. Control of gut differentiation and intestinal-type gastric carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:592–600.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–269.
Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, et al. E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGF beta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:272–286.
Kim YK, Yu J, Han TS, et al. Functional links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:1672–1681.
Yao Y, Suo AL, Li ZF, et al. MicroRNA profiling of human gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep. 2009;2:963–970.
Black AR, Black JD, Azizkhan-Clifford J. Sp1 and Kruppel-like factor family of transcription factors in cell growth regulation and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2001;188:143–160.
Kim TH, Chiera SL, Linder KE, et al. Overexpression of transcription factor sp2 inhibits epidermal differentiation and increases susceptibility towoundand carcinogen-induced tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2010;70:8507–8516.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–838.
Zhang F, Yang Z, Cao M, et al. MiR-203 suppresses tumor growth and invasion and down-regulates MiR-21 expression through repressing Ran in esophageal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014;342:121–129.
Wada R, Akiyama Y, Hashimoto Y, et al. miR-212 is downregulated and suppresses methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 in human gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:1106–1114.
Xia Y, Chen Q, Zhong Z, et al. Down-regulation of miR-30c promotes the invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting MTA1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32:476–485.
Gopalan V, Pillai S, Ebrahimi F, et al. Regulation of microRNA-1288 in colorectal cancer : Altered expression and its clinicopathological significance. Mol Carcinog. 2013;53:E36–E44.
Lang Q, Ling C. MiR-124 suppresses cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting PIK3CA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;426:247–252.
Poudel S, Song J, Jin EJ, et al. Sulfuretin-induced miR-30C selectively downregulates cyclin D1 and D2 and triggers cell death in human cancer cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;431:572–578.
Budhu A, Jia HL, Forgues M, et al. Identification of metastasis related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2008;47:897–907.
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ, Cressman EN. Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2008;48:2047–2063.
Rossi JJ. New hope for a microRNA therapy for liver cancer. Cell. 2009;137:990–992.
Li D, Wang Q, Liu C, et al. Aberrant expression of miR-638 contributes to benzo(a)pyrene-induced human cell transformation. Toxicol Sci. 2012;125:382–391.
Safe S, Abdelrahim M. Sp transcription factor family and its role in cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:2438–2448.
Wang L, Wei D, Huang S, et al. Transcription factor Sp1 expression is a significant predictor of survival in human gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:6371–6380.
Stoner M, Wormke M, Saville B, et al. Estrogen regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression in ZR-75 breast cancer cells through interaction of estrogen receptor a and Sp proteins. Oncogene. 2004;23:1052–1063.
Abdelrahim M, Smith R III, Burghardt R, et al. Role of Sp proteins in regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6740–6749.
Phan D, Cheng CJ, Galfione M, et al. Identification of Sp2 as a transcriptional repressor of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 in tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64:072–078.
Kozar K, Ciemerych MA, Rebel VI, et al. Mouse development and cell proliferation in the absence of D-cyclins. Cell. 2004;118:477–491.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from China Postdoctoral Science Foundation grant (No. 2013M542358) and a fund from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ling Yu Zhao and Yu Yao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L.Y., Yao, Y., Han, J. et al. miR-638 Suppresses Cell Proliferation in Gastric Cancer by Targeting Sp2. Dig Dis Sci 59, 1743–1753 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3087-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3087-5