Abstract
Background
MicroRNAs (miRs) are small non-coding RNAs that play important roles in cancer development where they can act as oncogenes or as tumor-suppressors. MiR-34a is a tumor suppressor that is frequently downregulated in a number of tumor types. However, little is known about the role of miR-34a in colorectal cancer (CRC).
Aim
This study aims to show the dysregulation of miR-34a in CRC and to characterize the function and mechanism of miR-34a in CRC cell lines.
Methods
The expression of miR-34a was detected using real-time PCR on CRC tissues and adjacent non-tumorous tissues. The ELISA was used to assess vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and phosphorylated FAK Y397 (pY397FAK) were measured by Western blot. The functions of miR-34a in vivo were measured by migration, invasion, CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry.
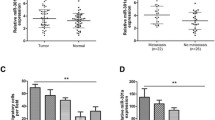
Results
MiR-34a was significantly downregulated and pY397FAK was upregulated in CRC cancer tissues. It plays an important role in inhibiting migration and invasion and in increasing apoptosis of CRC cells. Bioinformatic analysis suggested that VEGF may be a target of miR-34a, and this hypothesis was proved by ELISA and RT-PCR. The level of pY397FAK that could be activated by VEGF was downregulated in miR-34a overexpression CRC cell lines. The phosphorylation of FAK at 397 sites in miR-34a-stable cell lines was completely rescued by extra VEGF treatment.
Conclusion
MiR-34a is frequently downregulated in CRC and modulates the phosphorylation of FAK by negatively regulating VEGF.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29.
Pellegrino L, Jacob J, Roca-Alonso L, Krell J, Castellano L, et al. Altered expression of the miRNA processing endoribonuclease Dicer has prognostic significance in human cancers. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2013;13:21–27.
Pereira DM, Rodrigues PM, Borralho PM, Rodrigues CM. Delivering the promise of miRNA cancer therapeutics. Drug Discov Today. 2013;18:282–289.
Akbari Moqadam F, Pieters R, den Boer ML. The hunting of targets: challenge in miRNA research. Leukemia. 2013;27:16–23.
Pagliuca A, Valvo C, Fabrizi E, di Martino S, Biffoni M, et al. Analysis of the combined action of miR-143 and miR-145 on oncogenic pathways in colorectal cancer cells reveals a coordinate program of gene repression. Oncogene. 2013;32:4806–4813.
Takahashi M, Sung B, Shen Y, Hur K, Link A, et al. Boswellic acid exerts antitumor effects in colorectal cancer cells by modulating expression of the let-7 and miR-200 microRNA family. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33:2441–2449.
de Krijger I, Mekenkamp LJ, Punt CJ, Nagtegaal ID. MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer metastasis. J Pathol. 2011;224:438–447.
Stratmann J, Wang CJ, Gnosa S, Wallin A, Hinselwood D, et al. Dicer and miRNA in relation to clinicopathological variables in colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:345.
Bensen JT, Tse CK, Nyante SJ, Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Cole SR, et al. Association of germline microRNA SNPs in pre-miRNA flanking region and breast cancer risk and survival: the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. Cancer Causes Control. 2013;24:1099–1109.
Bandi N, Vassella E. miR-34a and miR-15a/16 are co-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer and control cell cycle progression in a synergistic and Rb-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 2011;10:55.
Xu X, Fan Z, Kang L, Han J, Jiang C, et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein represses miRNA-148a to enhance tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:630–645.
Yue X, Wang P, Xu J, Zhu Y, Sun G, et al. MicroRNA-205 functions as a tumor suppressor in human glioblastoma cells by targeting VEGF-A. Oncol Rep. 2012;27:1200–1206.
Volkomorov V, Grigoryeva E, Krasnov G, Litviakov N, Tsyganov M, et al. Search for potential gastric cancer markers using miRNA databases and gene expression analysis. Exp Oncol. 2013;35:2–7.
Ji X, Wang Z, Geamanu A, Goja A, Sarkar FH, et al. Delta-tocotrienol suppresses Notch-1 pathway by upregulating miR-34a in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2012;131:2668–2677.
Fujita Y, Kojima K, Hamada N, Ohhashi R, Akao Y, et al. Effects of miR-34a on cell growth and chemoresistance in prostate cancer PC3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;377:114–119.
Duan W, Xu Y, Dong Y, Cao L, Tong J, et al. Ectopic expression of miR-34a enhances radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells, partly by suppressing the LyGDI signaling pathway. J Radiat Res. 2013;54:611–619.
Chang TC, Wentzel EA, Kent OA, Ramachandran K, Mullendore M, et al. Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol Cell. 2007;26:745–752.
Zhao H, Ma B, Wang Y, Han T, Zheng L, et al. miR-34a inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by repressing the expression of CD44. Oncol Rep. 2013;29:1027–1036.
Mackiewicz M, Huppi K, Pitt JJ, Dorsey TH, Ambs S, et al. Identification of the receptor tyrosine kinase AXL in breast cancer as a target for the human miR-34a microRNA. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;130:663–679.
Gallardo E, Navarro A, Vinolas N, Marrades RM, Diaz T, et al. miR-34a as a prognostic marker of relapse in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1903–1909.
Nalls D, Tang SN, Rodova M, Srivastava RK, Shankar S. Targeting epigenetic regulation of miR-34a for treatment of pancreatic cancer by inhibition of pancreatic cancer stem cells. PLoS One. 2011;6:e24099.
Roy S, Levi E, Majumdar AP, Sarkar FH. Expression of miR-34 is lost in colon cancer which can be re-expressed by a novel agent CDF. J Hematol Oncol. 2012;5:58.
Cho SG, Yi Z, Pang X, Yi T, Wang Y, et al. Kisspeptin-10, a KISS1-derived decapeptide, inhibits tumor angiogenesis by suppressing Sp1-mediated VEGF expression and FAK/Rho GTPase activation. Cancer Res. 2009;69:7062–7070.
Chen XL, Nam JO, Jean C, Lawson C, Walsh CT, et al. VEGF-induced vascular permeability is mediated by FAK. Dev Cell. 2012;22:146–157.
Schlaepfer DD, Hunter T. Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix—a role for the focal adhesion protein–tyrosine kinase FAK. Cell Struct Funct. 1996;21:445–450.
Pang X, Zhang L, Lai L, Chen J, Wu Y, et al. 1′-Acetoxychavicol acetate suppresses angiogenesis-mediated human prostate tumor growth by targeting VEGF-mediated Src-FAK-Rho GTPase-signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32:904–912.
He K, Cui B, Li G, et al. The effect of anti-VEGF drugs (bevacizumab and aflibercept) on the survival of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Onco Targets Ther. 2012;5:59–65.
Sun F, Fu H, Liu Q, Tie Y, Zhu J, et al. Downregulation of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a induces cell cycle arrest. FEBS Lett. 2008;582:1564–1568.
Hashimi ST, Fulcher JA, Chang MH, Gov L, Wang S, et al. MicroRNA profiling identifies miR-34a and miR-21 and their target genes JAG1 and WNT1 in the coordinate regulation of dendritic cell differentiation. Blood. 2009;114:404–414.
Yang P, Li QJ, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Markowitz GJ, et al. TGF-beta-miR-34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:291–303.
Mudduluru G, Ceppi P, Kumarswamy R, Scagliotti GV, Papotti M, et al. Regulation of Axl receptor tyrosine kinase expression by miR-34a and miR-199a/b in solid cancer. Oncogene. 2011;30:2888–2899.
Gilmore AP, Romer LH. Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling in focal adhesions decreases cell motility and proliferation. Mol Biol Cell. 1996;7:1209–1224.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants-in-aid for Special-Term Professor Scientific Research from the Educational Department of Liaoning Province, China (Liaocai Zhijiao no. 2012-512). All sources of financial support during the last 2 years are acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Zhou, J. & Dong, M. Dysregulation of MicroRNA-34a Expression in Colorectal Cancer Inhibits the Phosphorylation of FAK Via VEGF. Dig Dis Sci 59, 958–967 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2983-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2983-4