Abstract
Background and Aims
Although active inflammatory changes in chronic Crohn’s disease (CD) can be detected with serum inflammatory markers, these have low specificity and sensitivity. Stool markers of inflammation, such as M2-pyruvate kinase (M2-PK), permit more direct assessment of mucosal inflammation. The aim of this study was to assess levels of M2-PK in children with active CD and to compare to levels in healthy control children.
Methods
Fecal levels of M2-PK were measured by immunoassay using stored stool samples from children with untreated (active) CD and healthy control children. Correlations between M2-PK levels and disease activity scores and serum inflammatory markers were performed. Comparison was also made between M2PK and a second fecal inflammatory marker, S100A12.
Results
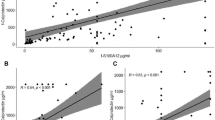
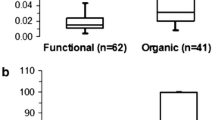
Mean fecal M2-PK levels were higher in the 17 patients with active CD than in the 21 healthy controls (p = 0.0007). M2-PK levels did not correlate with disease activity scores or serum inflammatory markers. There was a trend for children with ileocolonic disease to have higher levels of M2-PK in their stool compared to those with colonic disease or isolated ileal disease. Fecal M2PK did not correlate with fecal S100A12 in children with active CD.
Conclusion
Fecal M2-PK is increased in children with active CD, indicating that this marker may be a useful non-invasive marker for gut inflammation. Further studies of M2PK are required in additional settings with larger cohorts of children with CD and with comparison to other stool markers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beattie RM, Croft NM, Fell JM, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease. Arch Dis Child. 2006;91:426–432.
Griffiths AM, Buller HB. Inflammatory bowel diseases. In: Walker WA, Hamilton JR, et al., eds. Pediatric Gastrointestinal Disease, Chapter 41. Hamilton: BC Decker; 2000:613–652.
Mack DR, Langton C, Markowitz J, et al. Laboratory values for children with newly diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease. Pediatrics. 2007;119:1113–1119.
Judd TA, Day AS, Lemberg DA, Turner D, Leach ST. An update of faecal markers of inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26:1493–1499.
Langhorst J, Elsenbruch S, Mueller T, et al. Comparison of 4 neutrophil-derived proteins in feces as indicators of disease activity in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2005;11:1085–1091.
Sidler MA, Leach ST, Day AS. Fecal S100A12 and fecal calprotectin as noninvasive markers for inflammatory bowel disease in children. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:359–366.
Chung-Faye G, Hayee B, Maestranzi S, Donaldson N, Forgacs I, Sherwood R. Fecal M2-pyruvate kinase (M2-PK): a novel marker of intestinal inflammation. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007;13:1374–1378.
Czub E, Herzig K-H, Szaflarska-Popawska A, et al. Fecal pyruvate kinase: a potential new marker for intestinal inflammation in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:1147–1150.
Walkowiak J, Banasiewicz T, Krokowicz P, Hansdorfer-Korzon R, Drews M, Herzig K-H. Fecal pyruvate kinase (M2-PK): a new predictor for inflammation and severity of pouchitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:1493–1494.
Haug U, Wente MN, Seiler CM, et al. Tumor M2 pyruvate kinase as a stool marker for colorectal cancer: stability at room temperature and implications for application in the screening setting. Clin Chem. 2006;52:782–784.
Hardt PD, Mazurek S, Toepler M, et al. Faecal tumour M2 pyruvate kinase: a new, sensitive screening tool for colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:980–984.
Turner D, Leach ST, Mack D, et al. Faecal calprotectin, lactoferrin, M2-pyruvate kinase and S100A12 in severe ulcerative colitis: a prospective multicentre comparison of predicting outcomes and monitoring response. Gut. 2010;59:1207–1212.
Silverberg MS, Satsangi J, Ahmad T, et al. Toward an integrated clinical, molecular and serological classification of inflammatory bowel disease: Report of a Working Party of the 2005 Montreal World Congress of Gastroenterology. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005;19:5–36.
Hyams J, Ferry GD, Mandel FS, et al. Development and validation of a pediatric Crohn’s disease activity index. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1991;12:439–447.
de Jong NSH, Leach ST, Day AS. Faecal S100A12: a novel non-invasive marker of gastrointestinal inflammation in children. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2006;12:566–572.
Arnott ID, Watts D, Ghosh S. Review article: is clinical remission the optimum therapeutic goal in the treatment of Crohn’s disease? Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16:857–867.
Jeffrey J, Lewis SJ, Ayling RM. Fecal dimeric M2-pyruvate kinase (Tumor M2-PK) in the differential diagnosis of functional and organic bowel disorders. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15:1630–1634.
Joshi S, Lewis SJ, Creanor S, Ayling RM. Age-related faecal calprotectin, lactoferrin and tumour M2-PK concentrations in healthy volunteers. Ann Clin Biochem. 2010;47:259–263.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Day, A.S., Judd, T., Lemberg, D.A. et al. Fecal M2-PK in Children with Crohn’s Disease: A Preliminary Report. Dig Dis Sci 57, 2166–2170 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2215-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2215-3