Abstract
Background
Claudins are tight junction (TJ) proteins, and the relationship between the level of expression and localization of TJ protein, and tumor aggressiveness in early gastric cancer (GC) is still far from clear.
Aims
To investigate the expression of claudins and Ki-67 in early GC cells and surrounding normal gastric mucosa.
Methods
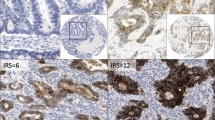
A total of 53 early GC lesions removed via endoscopic mucosal resection or endoscopic submucosal resection were evaluated. All of the GCs were characterized as well to moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma. The labeling index (LI) of Ki-67 was calculated for each sample. To assess the prevalence of epithelial TJs, immunofluorescent staining for claudin-3, claudin-4, and claudin-7 was performed. The immunoreactivity was graded according to the percentage of stained cells.
Results
Claudin-3, claudin-4, and claudin-7 expression at TJs in GC and intestinal metaplasia were significantly higher than that in gastric mucosa with no intestinal metaplasia. The Ki-67 LI of GC specimens was inversely correlated with claudin-3 expression, but not with claudin-4 or claudin-7 expression. Claudin-3 expression was significantly lower at the submucosal invasive front of GCs.
Conclusions
The down-regulation of claudin-3 was associated with the proliferative potential of GC cells, indicating that claudins may have a pivotal role in the progression of GC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM. Epidemiology of cancer: global patterns and trends. Toxicol Lett. 1998;102–103:227–234.
Park YM, Cho E, Kang HY, Kim JM. The effectiveness and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Surg Endosc. 2011;25:2666–2677.
Tsukita S, Furuse M. Pores in the wall: claudins constitute tight junction strands containing aqueous pores. J Cell Biol. 2000;149:13–16.
Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Natl Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:285–293.
Oshima T, Miwa H, Joh T. Changes in the expression of claudins in active ulcerative colitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:S146–S150.
Soini Y, Tommola S, Helin H, Martikainen P. Claudins 1, 3, 4 and 5 in gastric carcinoma, loss of claudin expression associates with the diffuse subtype. Virchows Arch. 2006;448:52–58.
Johnson AH, Frierson HF, Zaika A, et al. Expression of tight-junction protein claudin-7 is an early event in gastric tumorigenesis. Am J Pathol. 2005;167:577–584.
Resnick MB, Gavilanez M, Newton E, et al. Claudin expression in gastric adenocarcinomas: a tissue microarray study with prognostic correlation. Hum Pathol. 2005;36:886–892.
Oliveira SS, Morgado-Díaz JA. Claudins: multifunctional players in epithelial tight junctions and their role in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007;64:17–28.
Satake S, Semba S, Matsuda Y, et al. Cdx2 transcription factor regulates claudin-3 and claudin-4 expression during intestinal differentiation of gastric carcinoma. Pathol Int. 2008;58:156–163.
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma—2nd English edition—response assessment of chemotherapy and radiotherapy for gastric carcinoma: clinical criteria. Gastric Cancer. 2001;4:1–8.
Ouban A, Ahmed AA. Claudins in human cancer: a review. Histol Histopathol. 2010;25:83–90.
Ohtani S, Terashima M, Satoh J, et al. Expression of tight-junction-associated proteins in human gastric cancer: downregulation of claudin-4 correlates with tumor aggressiveness and survival. Gastric Cancer. 2009;12:43–51.
Jalava P, Kuopio T, Juntti-Patinen L, Kotkansalo T, Kronqvist P, Collan Y. Ki67 immunohistochemistry: a valuable marker in prognostication but with a risk of misclassification: proliferation subgroups formed based on Ki67 immunoreactivity and standardized mitotic index. Histopathology. 2006;48:674–682.
Matsuda Y, Semba S, Ueda J, et al. Gastric and intestinal claudin expression at the invasive front of gastric carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:1014–1019.
Lee SK, Moon J, Park SW, Song SY, Chung JB, Kang JK. Loss of the tight junction protein claudin 4 correlates with histological growth-pattern and differentiation in advanced gastric adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2005;13:193–199.
Tan X, Tamori Y, Egami H, et al. Analysis of invasion-metastasis mechanism in pancreatic cancer: involvement of tight junction transmembrane protein occludin and MEK/ERK signal transduction pathway in cancer cell dissociation. Oncol Rep. 2004;11:993–998.
Kamata I, Ishikawa Y, Akishima-Fukasawa Y, et al. Significance of lymphatic invasion and cancer invasion-related proteins on lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:1527–1533.
Jung H, Jun KH, Jung JH, Chin HM, Park WB. The expression of claudin-1, claudin-2, claudin-3, and claudin-4 in gastric cancer tissue. J Surg Res. 2011;167:e185–e191.
Mima S, Tsutsumi S, Ushijima H, et al. Induction of claudin-4 by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and its contribution to their chemopreventive effect. Cancer Res. 2005;65:1868–1876.
Zavala-Zendejas VE, Torres-Martinez AC, Salas-Morales B, Fortoul TI, Montaño LF, Rendon-Huerta EP. Claudin-6, 7, or 9 overexpression in the human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line AGS increases its invasiveness, migration, and proliferation rate. Cancer Invest. 2011;29:1–11.
Takehara M, Nishimura T, Mima S, Hoshino T, Mizushima T. Effect of claudin expression on paracellular permeability, migration and invasion of colonic cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009;32:825–831.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Noriko Kamiya for the technical assistance. This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan through a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) 2010–2012 (no. 22590691).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okugawa, T., Oshima, T., Chen, X. et al. Down-Regulation of Claudin-3 Is Associated with Proliferative Potential in Early Gastric Cancers. Dig Dis Sci 57, 1562–1567 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2043-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2043-5