Abstract
Background
The chronic disease eosinophilic esophagitis may be mediated by the innate immune system. Activation of toll-like receptors (TLRs) in other tissues is known to initiate eosinophil infiltration, thus TLRs may be a potential mediator of esophageal eosinophilia. Little is known about TLRs in the esophagus.
Aims
The purpose of this study was to identify the presence and activation of TLR2 and TLR3 on esophageal epithelial cell lines, primary epithelial cells and mucosal esophageal biopsies.
Methods
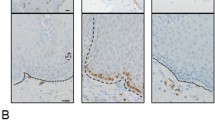
TLR2 and TLR3 were identified by immunocytochemistry and immunoblot. PCR assessed alterations to gene expression by activation of TLR2 and TLR3. Immunohistochemistry co-localized eosinophils and TLR2/TLR3 on esophageal biopsies.
Results
TLR2 and TLR3 were expressed on the esophageal adenocarcinoma cell lines TE-1 and TE-7, but only TLR3 was present on the esophageal epithelial cell line HET-1A. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin gene expression was altered in response to ligands zymosan and polyI:C, demonstrating activation. Primary esophageal epithelial cells did not express TLR2 or TLR3. In esophageal biopsies, TLR2 and TLR3 expression was limited to eosinophils and other immune cells during esophagitis.
Conclusions
TLR2 and TLR3 expression on cultured esophageal epithelial cells differs from TLR2 and TLR3 expression in esophageal biopsies, which is limited to immune cells during esophagitis.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EDN:
-
Eosinophil derived neurotoxin
- EoE:
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis
- HPF:
-
High power field
- PAMP:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular pattern
- PRR:
-
Pattern recognition receptor
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
References
Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1342–1363.
Mulder DJ, Justinich CJ. Understanding eosinophilic esophagitis: the cellular and molecular mechanisms of an emerging disease. Mucosal Immunol. 2011;4:139–147.
Rothenberg ME. Biology and treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:1238–1249.
Terhorst D, Kalali BN, Ollert M, Ring J, Mempel M. The role of toll-like receptors in host defenses and their relevance to dermatologic diseases. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010;11:1–10.
Albert EJ, Duplisea J, Dawicki W, Haidl ID, Marshall JS. Tissue eosinophilia in a mouse model of colitis is highly dependent on TLR2 and independent of mast cells. Am J Pathol. 2011;178:150–160.
Yang D, Chen Q, Su SB, et al. Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin acts as an alarmin to activate the TLR2-MyD88 signal pathway in dendritic cells and enhances Th2 immune responses. J Exp Med. 2008;205:79–90.
Uehara A, Fujimoto Y, Fukase K, Takada H. Various human epithelial cells express functional toll-like receptors, NOD1 and NOD2 to produce anti-microbial peptides, but not proinflammatory cytokines. Mol Immunol. 2007;44:3100–3111.
Zhu X, Wang M, Mavi P, et al. Interleukin-15 expression is increased in human eosinophilic esophagitis and mediates pathogenesis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:182–193.
Buckland KF, O’Connor E, Murray LA, Hogaboam CM. Toll like receptor-2 modulates both innate and adaptive immune responses during chronic fungal asthma in mice. Inflamm Res. 2008;57:379–387.
Schroder M, Bowie AG. TLR3 in antiviral immunity: key player or bystander? Trends Immunol. 2005;26:462–468.
Lim DM, Narasimhan S, Michaylira CZ, Wang ML. TLR3-mediated NF-{kappa}B signaling in human esophageal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009;297:G1172–G1180.
Tsuji K, Yamamoto S, Ou W, et al. dsRNA enhances eotaxin-3 production through interleukin-4 receptor upregulation in airway epithelial cells. Eur Respir J. 2005;26:795–803.
Pei Z, Bini EJ, Yang L, Zhou M, Francois F, Blaser MJ. Bacterial biota in the human distal esophagus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:4250–4255.
Francois F, Roper J, Goodman AJ, et al. The association of gastric leptin with oesophageal inflammation and metaplasia. Gut. 2008;57:16–24.
Yang L, Lu X, Nossa CW, Francois F, Peek RM, Pei Z. Inflammation and intestinal metaplasia of the distal esophagus are associated with alterations in the microbiome. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:588–597.
Moqbel R, Lacy P. Molecular mechanisms in eosinophil activation. Chem Immunol. 2000;78:189–198.
Rothenberg ME, Spergel JM, Sherrill JD, et al. Common variants at 5q22 associate with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Nat Genet. 2010;42:289–291.
Stoner GD, Kaighn ME, Reddel RR, et al. Establishment and characterization of SV40 T-antigen immortalized human esophageal epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1991;51:365–371.
Andl CD, Mizushima T, Nakagawa H, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mediates increased cell proliferation, migration, and aggregation in esophageal keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:1824–1830.
Katayama M, Akaishi T, Nishihira T, Kasai M, Kan M, Yamane I. Primary culture of human esophageal epithelial cells. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1984;143:129–140.
Zboralske FF, Karasek MA. Growth characteristics of human esophageal epithelial cells in primary explant and serial culture. In Vitro. 1984;20:109–118.
Blanchard C, Mingler MK, Vicario M, et al. IL-13 involvement in eosinophilic esophagitis: transcriptome analysis and reversibility with glucocorticoids. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:1292–1300.
Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, et al. The montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1900–1920.
Sherman PM, Hassall E, Fagundes-Neto U, et al. A global, evidence-based consensus on the definition of gastroesophageal reflux disease in the pediatric population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:1278–1295.
Flo TH, Halaas O, Torp S, et al. Differential expression of toll-like receptor 2 in human cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2001;69:474–481.
Muzio M, Bosisio D, Polentarutti N, et al. Differential expression and regulation of toll-like receptors (TLR) in human leukocytes: selective expression of TLR3 in dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2000;164:5998–6004.
Sanghavi SK, Reinhart TA. Increased expression of TLR3 in lymph nodes during simian immunodeficiency virus infection: implications for inflammation and immunodeficiency. J Immunol. 2005;175:5314–5323.
Lane EB, Rugg EL, Navsaria H, et al. A mutation in the conserved helix termination peptide of keratin 5 in hereditary skin blistering. Nature. 1992;356:244–246.
Cario E, Podolsky DK. Differential alteration in intestinal epithelial cell expression of toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and TLR4 in inflammatory bowel disease. Infect Immun. 2000;68:7010–7017.
van Aubel RA, Keestra AM, Krooshoop DJ, van Eden W, van Putten JP. Ligand-induced differential cross-regulation of toll-like receptors 2, 4 and 5 in intestinal epithelial cells. Mol Immunol. 2007;44:3702–3714.
Mayer AK, Muehmer M, Mages J, et al. Differential recognition of TLR-dependent microbial ligands in human bronchial epithelial cells. J Immunol. 2007;178:3134–3142.
Wang Y, Devkota S, Musch MW, et al. Regional mucosa-associated microbiota determine physiological expression of TLR2 and TLR4 in murine colon. PLoS One. 2010;5:e13607.
Sherrill JD, Gao PS, Stucke EM, et al. Variants of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and its receptor associate with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126:160–165.
Kato A, Favoreto S Jr, Avila PC, Schleimer RP. TLR3- and Th2 cytokine-dependent production of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in human airway epithelial cells. J Immunol. 2007;179:1080–1087.
Lee KH, Cho KA, Kim JY, et al. Filaggrin knockdown and toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) stimulation enhanced the production of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) from epidermal layers. Exp Dermatol. 2011;20:149–151.
Vu AT, Baba T, Chen X, et al. Staphylococcus aureus membrane and diacylated lipopeptide induce thymic stromal lymphopoietin in keratinocytes through the toll-like receptor 2-toll-like receptor 6 pathway. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126:985–993.
Davicino R, Martinez C, Mattar MA, et al. Larrea divaricata Cav (jarilla): production of superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide and expression of zymosan receptors. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2008;30:489–501.
Mullaly SC, Kubes P. Mast cell-expressed complement receptor, not TLR2, is the main detector of zymosan in peritonitis. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:224–234.
Martinelli C, Reichhart JM. Evolution and integration of innate immune systems from fruit flies to man: lessons and questions. J Endotoxin Res. 2005;11:243–248.
Beutler B. Innate immune sensing of microbial infection: the mechanism and the therapeutic challenge. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2002;152:547–551.
Khailova L, Mount Patrick SK, Arganbright KM, Halpern MD, Kinouchi T, Dvorak B. Bifidobacterium bifidum reduces apoptosis in the intestinal epithelium in necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010;299:G1118–G1127.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support from Kingston General Hospital and the Queen’s University Gastrointestinal Diseases Research Unit. The research is funded by Physicians’ Services Incorporated (PSI) Grant: PAED-237-09.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mulder, D.J., Lobo, D., Mak, N. et al. Expression of Toll-Like Receptors 2 and 3 on Esophageal Epithelial Cell Lines and on Eosinophils During Esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci 57, 630–642 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1907-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-011-1907-4