Abstract
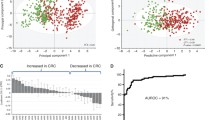
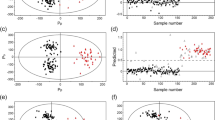
We report here the results of a pilot study in which ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight–mass spectrometry (UPLC/TOF–MS) and multivariate statistical analysis (supervised partial least squares discriminant analysis, PLS-DA) were applied for urinary metabolite profiling and data interpretation. The results of the PLS-DA indicated that the metabolic pattern as a whole was significantly different between the groups of preoperative colorectal cancer (CRC) patients, postoperative CRC patients, and healthy volunteers, respectively. The preoperative group of patients showed significantly increased levels of low-molecular weight compounds (LMC) MW 283 and MW 234 in comparison to the group of healthy volunteers group. After the operation, the levels of these two LMC significantly decreased. These preliminary results suggest that the UPLC–MS-based method coupled with pattern recognition will likely lead to procedures with the potential to be clinically applicable for the diagnosis of CRC and, consequently, to an improvement in patient prognosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hung KE, Chung DC. Colorectal cancer screening: today and tomorrow. South Med J. 2006;99(3):240–246. doi:10.1097/01.smj.0000203817.89741.29.
You WC, Jin F, Devesa S, et al. Rapid increase in colorectal cancer rates in urban Shanghai, 1972–97, in relation to dietary changes. J Cancer Epidemiol Prev. 2002;7(3):143–146.
Moller Sorensen N, Vejgaard Sorensen I, Ornbjerg Wurtz S, et al. Biology and potential clinical implications of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 in colorectal cancer treatment. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008;43(7):774–786. doi:10.1080/00365520701878163.
Lindon JC, Holmes E, Bollard ME, et al. Metabonomics technologies and their applications in physiological monitoring, drug safety assessment and disease diagnosis. Biomarkers. 2004;9(1):1–31. doi:10.1080/13547500410001668379.
Saghatelian A, Cravatt BF. Global strategies to integrate the proteome and metabolome. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005;9(1):62–68. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2004.12.004.
Griffin JL. Understanding mouse models of disease through metabolomics. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2006;10(4):309–315. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.06.027.
Nobeli I, Thornton JM. A bioinformatician’s view of the metabolome. Bioessays. 2006;28(5):534–545. doi:10.1002/bies.20414.
Griffin JL, Bollard ME. Metabonomics: its potential as a tool in toxicology for safety assessment and data integration. Curr Drug Metab. 2004;5(5):389–398. doi:10.2174/1389200043335432.
A J, Trygg J, Gullberg J, et al. Extraction and GC/MS analysis of the human blood plasma metabolome. Anal Chem. 2005;77(24):8086–8094.
Thysell E, Pohjanen E, Lindberg J, et al. Reliable profile detection in comparative metabolomics. OMICS. 2007;11(2):209–224. doi:10.1089/omi.2007.0006.
Nicholson K, Lindon JC, Holm E. Metabonomics: understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica. 1999;29(11):1181–1189. doi:10.1080/004982599238047.
Griffin JL, Kauppinen RA. Tumour metabolomics in animal models of human cancer. J Proteome Res. 2007;6(2):498–505. doi:10.1021/pr060464h.
Beckonert O, Keun HC, Ebbels TM, et al. Metabolic profiling, metabolomic and metabonomic procedures for NMR spectroscopy of urine, plasma, serum and tissue extracts. Nat Protocols. 2007;2(11):2692–2703. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.376.
Kind T, Tolstikov V, Fiehn O, et al. A comprehensive urinary metabolomic approach for identifying kidney cancerr. Anal Biochem. 2007;363(2):185–195. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2007.01.028.
Lu G, Wang JS, Zhao XJ, et al. Study on gender difference based metabolites in urine by ultra high performance liquid chromatography/time of flight mass spectrometry. Chin J Chromatogr. 2006;24(2):109–113. doi:10.1016/S1872-2059(06)60005-9.
Wilson ID, Nicholson JK, Castro-Perez J, et al. High resolution “ultra performance” liquid chromatography coupled to oa-TOF mass spectrometry as a tool for differential metabolic pathway profiling in functional genomic studies. J Proteome Res. 2005;4(2):591–598. doi:10.1021/pr049769r.
Stanley EG, Bailey NJ, Bollard ME, et al. Sexual dimorphism in urinary metabolite profiles of Han Wistar rats revealed by nuclear-magnetic-resonance-based metabonomics. Anal Biochem. 2005;343(2):195–202. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2005.01.024.
Plumb RS, Granger JH, Stumpf CL, et al. A rapid screening approach to metabonomics using UPLC and oa-TOF mass spectrometry: application to age, gender and diurnal variation in normal/Zucker obese rats and black, white and nude mice. Analyst (Lond). 2005;130(6):844–849. doi:10.1039/b501767j. PMID: 10598751.
Zheng YF, Xu GW, Liu DY, et al. Study of urinary nucleosides as biological marker in cancer patients analyzed by Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography. Electrophoresis. 2002;23:4104–4109. doi:10.1002/elps.200290027.
Perroud B, Lee J, Valkova N. Pathway analysis of kidney cancer using proteomics and metabolic profiling. Mol Cancer. 2006;5:64. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-5-64.
Schmidt C. Metabolomics takes its place as latest up-and-coming “omic” science. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96(10):732–734.
Dettmer K, Hammock BD. Metabolomics: A new exciting weld within the “omics” sciences. Environ Health Perspect. 2004;112:A396–A397.
Wren SA. Peak capacity in gradient ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC). J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2005;38(2):337–343. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2004.12.028.
Plumb R, Castro-Perez J, Granger J, et al. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole-orthogonal time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2004;18(19):2331–2337. doi:10.1002/rcm.1627.
Acknowledgments
We also would like to express our deep and sincere gratitude to the Professor M. Michael Wolf (Boston University School of Medicine, USA) for his advice on this manuscript when he came to Shanghai. This work was financially supported by grants from the Shanghai Science and Technology Development Fund (No.05DJ14010) and the Major Basic Research Program of Shanghai (No. 07DZ19505).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, YL., Qin, HL., Liu, WJ. et al. Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry for the Metabolomic Analysis of Urine in Colorectal Cancer. Dig Dis Sci 54, 2655–2662 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0665-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0665-4