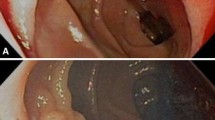
Abstract
Background Small bowel mass lesions (SBML) are a relatively common cause of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding (OGIB). Their detection has been limited by the inability to endoscopically examine the entire small intestine. This has changed with the introduction of capsule endoscopy (CE) and double balloon enteroscopy (DBE) into clinical practice. Study Aim To evaluate the detection of SBML by DBE and CE in patients with OGIB who were found to have SBML by DBE and underwent both procedures. Methods A retrospective review of a prospectively collected database of all patients undergoing DBE for OGIB at seven North American tertiary centers was performed. Those patients who were found to have SBML as a cause of their OGIB were further analyzed. Results During an 18 month period, 183 patients underwent DBE for OGIB. A small bowel mass lesion was identified in 18 patients. Of these, 15 patients had prior CE. Capsule endoscopy identified the mass lesion in five patients; fresh luminal blood with no underlying lesion in seven patients, and non-specific erythema in three patients. Capsule endoscopy failed to identify all four cases of primary small bowel adenocarcinoma. Conclusions Double balloon enteroscopy detects small bowel mass lesions responsible for OGIB that are missed by CE. Additional endoscopic evaluation of the small bowel by DBE or intraoperative enteroscopy should be performed in patients with ongoing OGIB and negative or non-specific findings on CE.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ciresi DL, Scholten DJ (1995) The continuing clinical dilemma of primary tumors of the small intestine. Am Surg 61:698–702, discussion 702–3
Lewis BS (1994) Small intestinal bleeding. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 23:67–91
Kariv R, Arber N (2003) Malignant tumors of the small intestine—new insights into a rare disease. Isr Med Assoc J 5:188–192
Lewis BS, Eisen GM, Friedman S (2005) A pooled analysis to evaluate results of capsule endoscopy trials. Endoscopy 37:960–965
Gong F, Swain P, Mills T (2000) Wireless endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 51:725–729
Iddan G, Meron G, Glukhovsky A, Swain P (2000) Wireless capsule endoscopy. Nature 405:417
Lewis BS, Swain P (2002) Capsule endoscopy in the evaluation of patients with suspected small intestinal bleeding: results of a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc 56:349–353
Pennazio M, Santucci R, Rondonotti E, Abbiati C, Beccari G, Rossini FP, De Franchis R (2004) Outcome of patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding after capsule endoscopy: report of 100 consecutive cases. Gastroenterology 126:643–653
Triester SL, Leighton JA, Leontiadis GI, Fleischer DE, Hara AK, Heigh RI, Shiff AD, Sharma VK (2005) A meta-analysis of the yield of capsule endoscopy compared to other diagnostic modalities in patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol 100:2407–2418
Yamamoto H, Sekine Y, Sato Y, Higashizawa T, Miyata T, Iino S, Ido K, Sugano K (2001) Total enteroscopy with a nonsurgical steerable double-balloon method. Gastrointest Endosc 53:216–220
Yamamoto H, Sugano K (2003) A new method of enteroscopy—the double-balloon method. Can J Gastroenterol 17:273–274
Heine GD, Hadithi M, Groenen MJ, Kuipers EJ, Jacobs MA, Mulder CJ (2006) Double-balloon enteroscopy: indications, diagnostic yield, and complications in a series of 275 patients with suspected small-bowel disease. Endoscopy 38:42–48
May A, Nachbar L, Ell C (2005) Double-balloon enteroscopy (push-and-pull enteroscopy) of the small bowel: feasibility and diagnostic and therapeutic yield in patients with suspected small bowel disease. Gastrointest Endosc 62:62–70
May A, Nachbar L, Schneider M, Neumann M, Ell C (2005) Push-and-pull enteroscopy using the double-balloon technique: method of assessing depth of insertion and training of the enteroscopy technique using the Erlangen Endo-Trainer. Endoscopy 37:66–70
May A, Nachbar L, Wardak A, Yamamoto H, Ell C (2003) Double-balloon enteroscopy: preliminary experience in patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding or chronic abdominal pain. Endoscopy 35:985–991
Yamamoto H (2005) Double-balloon endoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:S27–S29
Yamamoto H, Yano T, Kita H, Sunada K, Ido K, Sugano K (2003) New system of double-balloon enteroscopy for diagnosis and treatment of small intestinal disorders. Gastroenterology 125:1556, author reply 1556-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ross, A., Mehdizadeh, S., Tokar, J. et al. Double Balloon Enteroscopy Detects Small Bowel Mass Lesions Missed by Capsule Endoscopy. Dig Dis Sci 53, 2140–2143 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0110-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0110-0