Abstract
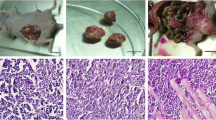
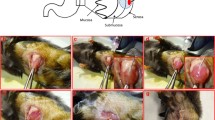
The aim of this study was to establish an orthotopic implantation model with high metastasis of gastric cancer to the peritoneum which is more faithful to clinical metastasis. A human gastric carcinoma cell line, GC9811, was injected as a single-cell suspension into the stomach of nude mice. The cells from some peritoneum metastatic foci were expanded in vitro and subsequently implanted to the stomach wall of nude mice. By repeating the in vivo stepwise selection method for four rounds and cloning culture, we obtained a cell line designated GC9811-P, which developed peritoneal metastasis in 13 of 13 (100%) of mice, compared with only 20% of those implanted with parental GC9811. The metastatic foci in the peritoneum showed essentially the same histological appearance as those induced by parental cells. Tumor cell growth of GC9811-P in vitro was faster than that of GC9811. Motility assays demonstrated higher motility of GC9811-P than of GC9811. The adhesive ability of GC9811-P cells to laminin was lower than that of GC9811 cells, whereas the ability of GC9811-P cells to adhere to fibronectin was significantly higher than that of parental cells. Differences between GC9811-P and their parental GC9811 cells were found in expression levels of various molecules by flow cytometric and western blot. The findings indicated that up-regulation in the expressions of CD155, VEGF, syndecan-1, and syndecan-2 or down-regulation in the expressions of IL-6 and E-cadherin play an important role in the peritoneal metastasis of human gastric carcinoma cells. The high-metastatic cell line appears to be useful for investigating the mechanisms of peritoneal metastasis and preventing peritoneal metastasis of human gastric cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sporn MB (1996) The war on cancer. Lancet 347:1377–1381
Nagasako Y, Misawa K, Kohashi S, Hasegawa K, Okawa Y, Sano H, Takada A, Sato H (2003) Evaluation of malignancy using Ki-67 labeling index for gastric stromal tumor. Gastric Cancer 6:168–172
Maehara Y, Hasuda S, Koga T, Tokunaga E, Kakeji Y, Sugimachi K (2000) Postoperative outcome and sites of recurrence in patients following curative resection of gastric cancer. Br J Surg 87:353–357
Shono M, Sato N, Mizumoto K, Maehara N, Nakamura M, Nagai E, Tanaka M (2001) Stepwise progression of centrosome defects associated with local tumor growth and metastatic process of human pancreatic carcinoma cells transplanted orthotopically into nude mice. Lab Invest 81:945–952
Yao X, Hu JF, Daniels M, Yien H, Lu H, Sharan H, Zhou X, Zeng Z, Li T, Yang Y, Hoffman AR (2003) A novel orthotopic tumor model to study growth factors and oncogenes in hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 9:2719–2726
Yashiro M, Chung YS, Nishimura S, Inoue T, Sowa M (1996) Peritoneal metastatic model for human scirrhous gastric carcinoma in nude mice. Clin Exp Metastasis 14:43–54
Yanagihara K, Takigahira M, Tanaka H, Komatsu T, Fukumoto H, Koizumi F, Nishio K, Ochiya T, Ino Y, Hirohashi S (2005) Development and biological analysis of peritoneal metastasis mouse models for human scirrhous stomach cancer. Cancer Sci 96:323–332
Hu S, Guo X, Xie H, Du Y, Pan Y, Shi Y, Wang J, Hong L, Han S, Zhang D, Huang D, Zhang K, Bai F, Jiang H, Zhai H, Nie Y, Wu K, Fan D (2006) Phage display selection of peptides that inhibit metastasis ability of gastric cancer cells with high liver-metastatic potential. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341:964–972
FH Bai, Guo XN, Yang L, Zhai HH, Wu KC, Fan DM (2003) Establishment of transplantation of human gastric tumor metastasis model in nude mice. J Fourth Mil Med Univ 24:873–875
Yamaguchi K, Ura H, Yasoshima T, Shishido T, Denno R, Hirata K (2001) Liver metastatic Model for human gastric cancer established by orthotopic tumor cell implantation. World J Surg 25:131–137
Wang J, Wu K, Zhang D, Tang H, Xie H, Hong L, Pan Y, Lan M, Hu S, Ning X, Fan D (2005) Expressions and clinical significances of angiopoietin-1, -2 and Tie2 in human gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 337:386–393
Hippo Y, Yashiro M, Ishii M, Taniguchi H, Tsutsumi S, Hirakawa K, Kodama T, Aburatani H (2001) Differential gene expression profiles of scirrhous gastric cancer cells with high metastatic potential to peritoneum or lymph nodes. Cancer Res 61:889–895
Bouvet M, Wang J, Nardin SR, Nassirpour R, Yang M, Baranov E, Jiang P, Moossa AR, Hoffman RM (2002) Real-time optical imaging of primary tumor growth and multiple metastatic events in a pancreatic cancer orthotopic model. Cancer Res 62:1534–1540
Kondo K, Fujino H, Miyoshi T, Ishikura H, Sakiyama S, Monden Y (2004) Orthotopically implanted SCID mouse model of human lung cancer suitable for investigating metastatic potential and anticancer drug effects. Oncol Rep 12:991–999
Hofmann HS, Hansen G, Richter G, Taege C, Simm A, Silber RE, Burdach S (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase-12 expression correlates with local recurrence and metastatic disease in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 11:1086–1092
Agnantis NJ, Goussia AC, Batistatou A, Stefanou D (2004) Tumor markers in cancer patients. An update of their prognostic significance. Part II. In Vivo 18:481–488
Rodriguez-Rodriguez L, Sancho-Torres I, Mesonero C, Gibbon DG, Shih WJ, Zotalis G (2003) The CD44 receptor is a molecular predictor of survival in ovarian cancer. Med Oncol 20:255–263
Katsura M, Furumoto H, Nishimura M, Kamada M, Aono T (1998) Overexpression of CD44 variants 6 and 7 in human endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol 71:185–189
Kikkawa H, Kaihou M, Horaguchi N, Uchida T, Imafuku H, Takiguchi A, Yamazaki Y, Koike C, Kuruto R, Kakiuchi T, Tsukada H, Takada Y, Matsuura N, Oku N (2002) Role of integrin alpha (v) beta3 in the early phase of liver metastasis: PET and IVM analyses. Clin Exp Metastasis 19:717–725
Arboleda MJ, Lyons JF, Kabbinavar FF, Bray MR, Snow BE, Ayala R, Danino M, Karlan BY, Slamon DJ (2003) Overexpression of AKT2/protein kinase B beta leads to up-regulation of beta1 integrins, increased invasion, and metastasis of human breast and ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res 63:196–206
Merrill MK, Bernhardt G, Sampson JH, Wikstrand CJ, Bigner DD, Gromeier M (2004) Poliovirus receptor CD155-targeted oncolysis of glioma. Neuro-oncol 6:208–217
Sloan KE, Eustace BK, Stewart JK, Zehetmeier C, Torella C, Simeone M (2004) CD155/PVR plays a key role in cell motility during tumor cell invasion and migration. BMC Cancer 4:73
Ferrara N (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 25:581–611
McQuade KJ, Rapraeger AC (2003) Syndecan-1 transmembrane and extracellular domains have unique and distinct roles in cell spreading. J Biol Chem 278:46607–466015
Sanderson RD (2001) Heparan sulfate proteoglycans in invasion and metastasis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 12:89–98
Beauvais DM, Rapraeger AC (2004) Syndecans in tumor cell adhesion and signaling. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2:3
Barbareschi M, Maisonneuve P, Aldovini D, Cangi MG, Pecciarini L, Angelo Mauri F, Veronese S, Caffo O, Lucenti A, Palma PD, Galligioni E, Doglioni C (2003) High syndecan-1 expression in breast carcinoma is related to an aggressive phenotype and to poorer prognosis. Cancer 98:474–483
Burbach BJ, Friedl A, Mundhenke C, Rapraeger AC (2003) Syndecan-1 accumulates in lysosomes of poorly differentiated breast carcinoma cells. Matrix Biol 22:163–177
Matsuda K, Maruyama H, Guo F, Kleeff J, Itakura J, Matsumoto Y, Lander AD, Korc M (2001) Glypican-1 is overexpressed in human breast cancer and modulates the mitogenic effects of multiple heparin-binding growth factors in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 61:5562–5569
Keller ET, Wanagat J, Ershler WB (1996) Molecular and cellular biology of interleukin-6 and it receptor. Front Biosci 1: 340–357
Mayer B, Johnson JP, Leitl F, Jauch KW, Heiss MM, Schildberg FW, Birchmeier W, Funke I (1993) E-cadherin expression in primary and metastatic gastric cancer: down-regulation correlates with cellular dedifferentiation and glandular disintegration. Cancer Res 53:1690–1695
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grant 30160033 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China. We also thank Taidong Qiao for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, F., Guo, X., Yang, L. et al. Establishment and Characterization of a High Metastatic Potential in the Peritoneum for Human Gastric Cancer by Orthotopic Tumor Cell Implantation. Dig Dis Sci 52, 1571–1578 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9570-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9570-x