Abstract
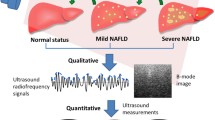
This study was designed to test whether ultrasound can be used to diagnose nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) utilizing a prototype. We collected 115 ultrasounds. A prototype was chosen that represented NAFLD; 5 features of NAFLD prototype were described. Ultrasounds were read blinded to diagnosis as matching prototype or not. A 20-minute teaching session was made to a group of 15 providers. Ten ultrasounds were presented for comparison to prototype with intraobserver reliability measured. Of 20 patients shown by liver biopsy to have NAFLD, 16 were successfully predicted by comparison to the prototype (sensitivity 80%). In 94 of 95 cases, ultrasound predicted those without NAFLD (specificity 99%). The positive predictive value was 94% and negative predictive value 96%. Training results showed substantial agreement with a kappa score of 0.76 with 95% of cases identified correctly. In conclusion, physicians can apply a bedside ultrasound to identify NAFLD when compared to prototype.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harrison SA, Torgerson S, Hayashi PH: The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a clinical histopathological study. Am J Gastroenterol 98:2042–2047, 2003
Sanyal AJ, Contos MJ, Sterling RK, et al.: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with hepatitis C is associated with features of the metabolic syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol 98:2064–2071, 2003
Angulo P, Keach JC, Batts KP, Lindor KD: Independent predictors of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 30:1356–1362, 1999
Lonardo A, Bellini M, Tondelli E, et al.: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and the “bright liver syndrome”: should a recently expanded clinical entity be further expanded?Am J Gastroenterololgy 90:2072–2074, 1995
Wilson LS, Robinson DE, Griffiths KA, Griffiths KA, Manoharan A, Doust BAD: Evaluation of ultrasonic attenuation in diffuse diseases of spleen and liver. Ultrasonic Imaging 9:236–247, 1994
Saverymuttu SH, Joseph AE, Maxwell JD: Ultrasound scanning in the detection of hepatic fibrosis and steatosis. Brit Med J 292:13–15, 1986
Sandford NL, Walsh P, Matis C, Baddeley H, Powell LW: Is ultrasonography useful in the assessment of diffuse parenchymal liver disease?Gastroenterology 89:186–191, 1985
Saadeh S, Younossi ZM, Remer EM, et al.: The utility of radiological imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 123:745–750, 2002
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Bacon BR: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol 94:2467–2474, 1999
Deems RO, Friedman LS, Friedman MI, Munoz SJ, Deems DA, Maddrey WC: Relationship between liver biochemical tests and dietary intake in patients with liver disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 18304–18308, 1994
Ueno T, Sugawara H, Sujaku K, et al.: Therapeutic effects of restricted diet and exercise in obese patients with fatty liver. J Hepatol 27:103–107, 1997
Riley TR, Khan A: Risk Factors and ultrasound can predict chronic hepatitis caused by non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis Sci (in press)
Riley TR: How often does ultrasound marking change the liver biopsy site?Am J Gastroenterol 94:3320–3322, 1999
Riley TR, Bruno MA: Sonographic measurement of the thickness of subcutaneous tissues in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease versus other chronic liver diseases. J Clin Ultrasound 2005 (in press)
Ahmad M, Riley TR: Can one predict when ultrasound will be useful with percutaneous liver biopsy?Am J Gastroenterol 96:547–549, 2001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riley, T.R., Mendoza, A. & Bruno, M.A. Bedside Ultrasound Can Predict Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in the Hands of Clinicians Using a Prototype Image. Dig Dis Sci 51, 982–985 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9343-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9343-6