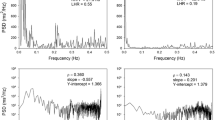
Autonomic dysfunction is a recognized complication of end-stage liver disease (ESLD) associated with a poor prognosis. The corrected QT interval (QTc) on electrocardiogram is a marker of autonomic function. A few small studies have suggested that QTc may normalize with the return of liver function after orthotopic liver transplantation. We sought to determine how transplantation affects the QTc in patients with ESLD. The QTc from the pretransplantation evaluation of 46 patients with ESLD was compared with the QTc at 4-month posttransplantation follow-up. Other factors that can influence autonomic function also were evaluated. Most patients with ESLD (54%) showed a prolonged QTc (≥440 msec) at the pretransplantation evaluation (451± 45 msec) that improved to within the normal range at posttransplantation follow-up (418± 18 msec; P < 0.001). There was no relationship between QTc prolongation and Child–Turcotte–Pugh score, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score, diabetes mellitus, age, or etiology of liver disease. Most patients with ESLD and a prolonged QTc will have a significant improvement in QTc after transplantation; however, 6.5% of patients in our study had a worsening of QTc after transplantation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thuluvath PJ, Triger DR: Autonomic neuropathy and chronic liver disease. Q J Med 72:737–747, 1989
MacGilchrist AJ, Reid JL: Impairment of autonomic reflexes in cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 85:288–292, 1990
Bernardi M, Calandra S, Colantoni A, et al.: Q-T interval prolongation in cirrhosis: Prevalence, relationship with severity, and etiology of the disease and possible pathogenetic factors. Hepatology 27:28–34, 1998
Trevisani F, Sica G, Mainquà P, et al.: Autonomic dysfunction and hyperdynamic circulation in cirrhosis with ascites. Hepatology 30:1387–1392, 1999
Hendrickse MT, Triger DR: Peripheral and cardiovascular autonomic impairment in chronic liver disease: Prevalence and relation to hepatic function. J Hepatol 16:177–183, 1992
Hendrickse MT, Thuluvath PJ, Triger DR: Natural history of autonomic neuropathy in chronic liver disease. Lancet 339:1462–1464, 1992
Puthumana L, Chaudhry V, Thuluvath PJ: Prolonged QTc interval and its relationship to autonomic cardiovascular reflexes in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol 35:733–738, 2001
Mohamed R, Forsey PR, Davies MK, Neuberger JM: Effect of liver transplantation on QT interval prolongation and autonomic dysfunction in end-stage liver disease. Hepatology 23:1128–1134, 1996
Trevisani F, Sica G, Mainquà P, et al.: Normalization of prolonged QT interval after liver transplantation (LTx) in cirrhosis. Hepatology 24 (Suppl):179A, 1996 (abstr)
Finucci G, Lunardi F, Sacerdoti D, et al.: Q-T interval prolongation in liver cirrhosis: Reversibility after orthotopic liver transplantation. Jpn Heart J 39:321–329, 1998
Garcia Gonzalez M, Hernandez-Madrid A, Lopez-Sanroman A, Candela A, Nuno J, Barcena R: Reversal of QT interval electrocardiographic alterations in cirrhotic patients undergoing liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 31:2366–2367, 1999
Bal JS, Thuluvath PJ: Prolongation of QTc interval: Relationship with etiology and severity of liver disease, mortality and liver transplantation. Liver Int 23:243–248, 2003
Fleckenstein JF, Frank S, Thuluvath PJ: Presence of autonomic neuropathy is a poor prognostic indicator in patients with advanced liver disease. Hepatology 23:471–475, 1996
Oliver MI, Miralles R, Rubies-Prat J, et al.: Autonomic dysfunction in patients with non-alcoholic chronic liver disease. J Hepatol 26:1242–1248, 1997
Trevisani F, Sica G, Mainquà P, et al.: Improvement of autonomic neuropathy after successful liver transplantation (LTx) in cirrhosis (abstract). Hepatology 24 (Suppl):179A, 1996
Suhr OB, Wiklund U, Ando Y, Ando E, Olofsson BO: Impact of liver transplantation on autonomic neuropathy in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: An evaluation by spectral analysis of heart rate variability. J Intern Med 242:225–229, 1997
Hodak SP, Moubarak JB, Rodriguez I, Gelfand MC, Alijani MR, Tracy CM: QT prolongation and near fatal cardiac arrhythmia after intravenous tacrolimus administration: a case report. Transplantation 66:535–537, 1998
Johnson MC, So S, Marsh JW, Murphy AM: QT prolongation and torsades de pointes after administration of FK506. Transplantation 53:929–930, 1992
Khazan M, Mathis AS: Probable case of torsades de points induced by fluconazole. Pharmacotherapy 22:1632–1637, 2002
Tallgren M, Hockerstedt K, Makinen J, Kirvela M, Lindgren L: Cardiac evaluation of liver transplant recipients: QT dispersion in electrocardiogram. Clin Transplantation 10:408–413, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carey, E.J., Douglas, D.D. Effects of Orthotopic Liver Transplantation on the Corrected QT Interval in Patients with End-Stage Liver Disease. Dig Dis Sci 50, 320–323 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-1603-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-1603-3