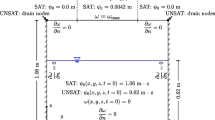
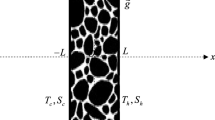
Abstract
In this paper, we follow a similar procedure as proposed by Koval (SPE J 3(2):145–154, 1963) to analytically model CO2 transfer between the overriding carbon dioxide layer and the brine layer below it. We show that a very thin diffusive layer on top separates the interface from a gravitationally unstable convective flow layer below it. Flow in the gravitationally unstable layer is described by the theory of Koval, a theory that is widely used and which describes miscible displacement as a pseudo two-phase flow problem. The pseudo two-phase flow problem provides the average concentration of CO2 in the brine as a function of distance. We find that downstream of the diffusive layer, the solution of the convective part of the model, is a rarefaction solution that starts at the saturation corresponding to the highest value of the fractional-flow function. The model uses two free parameters, viz., a dilution factor and a gravity fingering index. A comparison of the Koval model with the horizontally averaged concentrations obtained from 2-D numerical simulations provides a correlation for the two parameters with the Rayleigh number. The obtained scaling relations can be used in numerical simulators to account for the density-driven natural convection, which cannot be currently captured because the grid cells are typically orders of magnitude larger than the wavelength of the initial fingers. The method can be applied both for storage of greenhouse gases in aquifers and for EOR processes using carbon dioxide or other solvents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bando, S., Takemura, F., Nishio, M., Hihara, E., Makoto Akai, M.: Viscosity of aqueous NaCl solutions with dissolved CO2 at (30 to 60) °C and (10 to 20) MPa. J. Chem. Eng. Data 49, 1328–1332 (2004)
Bedrikovetsky, P., De Deus, J., Eurico Altoé, J.: Secondary migration of oil: analytical model. SPE 69411. In: 2001 SPE Latin American and Caribbean Petroleum Engineering Conference. Buenos Aires, Argentina, SPE (2001)
Blackwell, R.J., Rayne, I.R., Terry, W.M.: Factors influencing the efficiency of miscible displacement. Petrol. Trans., AIME 217, 1–4 (1959)
Booth, R.J.S.: On the growth of the mixing zone in miscible viscous fingering. J. Fluid Mech. 655, 527–539 (2010)
Booth, R.J.S.: Miscible flow through porous media. PhD dissertation, University of Oxford (2008)
Dake, L.P.: Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering, p. 365. Elsevier, New York (1978)
Dake, L.P.: The Practice of Reservoir Engineering, pp. 370–371. Elsevier, New York (1994)
Dougherty, E.L.: Mathematical model of an unstable miscible displacement. SPE J. 3, 155–163 (1963), SPE 509
Enick, R.M., Klara, S.M.: CO2 solubility in water and brine under reservoir conditions. Chem. Eng. Commun. 90(1), 23–33 (1990)
Ennis-King, J., Paterson, L.: Role of convective mixing in the long-term storage of carbon dioxide in deep saline aquifers. SPE J. 10(4), 349 (2005)
Farajzadeh, R., Salimi, H., Zitha, P.L.J., Bruining, J.: Numerical simulation of density-driven natural convection in porous media with application for CO2 injection projects. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 50(25–26), 5054–5064 (2007a)
Farajzadeh, R., Barati, A., Delil, H.A., Bruining, J., Zitha, P.L.J.: Enhanced mass transfer of CO2 into water and surfactant solutions. Pet. Sci. Technol. 25(13), 1493–1511 (2007b)
Farajzadeh, R., Farshbaf Zinati, F., Zitha, P.L.J., Bruining, J.: Density-driven natural convection in dual layered and anisotropic porous media with application for CO2 injection projects. A40 ECMOR XI. 8–11 September 2008, 11th European Conference on the Mathematics of Oil Recovery. Bergen, Norway (2008)
Farajzadeh, R., Bruining, J., Zitha, P.L.J.: Enhanced mass transfer of CO2 into water: experiment and modeling. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 48(10), 4542–4455 (2009)
Farajzadeh, R., Meulenbroek, B., Bruining, J.: An analytical method for predicting the performance of gravitationally unstable flow in porous media. SPE 143420. Presented at SPE EUROPEC/EAGE Annual Conference and Exhibition, 23–26 May 2011a, Vienna, Austria (2011a)
Farajzadeh, R., Ranganathan, P., Zitha, P.L.J., Bruining, J.: The effect of heterogeneity on the character of density-driven natural convection of CO2 overlying a brine layer. Adv. Water Resour. 34(4), 327–339 (2011b)
Fayers, F.J.: An approximate model with physically interpretable parameters for representing miscible viscous fingering. SPE Reserv. Eng. 3, 551–558 (1988)
Fayers, F.J., Newley, T.M.J.: Detailed validation of an empirical model for viscous fingering with gravity effects. SPE Reserv. Eng. 3, 542–550 (1988)
Fayers, F.J., Blunt, M.J., Christie, M.A.: Comparisons of empirical viscous-fingering models and their calibration for heterogeneous problems. SPE Reserv. Eng. 7(2), 195–203 (1992)
Gelhar, L.W.: Stochastic Subsurface Hydrology. 390 pp, ISBN 0138467676. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1993)
Gmelin L.: Gmelin Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie, 8. Auflage. Kohlenstoff, Teil C3, Verbindungen, pp. 64–75 (1973)
Guo, T., Neale, G.H.: Effects of buoyancy forces on miscible liquid–liquid displacement processes in a porous medium. Powder Technol. 86, 265–273 (1996)
Hassanzadeh, H., Pooladi-Darvish, M., Keith, D.: Scaling behavior of convective mixing, with application to CO2 geological storage. AIChE J. 53(6), 1121–1131 (2007)
Hearn, C.L.: Simulation of stratified waterflooding by pseudo relative permeability curves. JPT 805–13 (1971)
Hebach, A., Oberhof, A., Dahmen, N.: Density of water + carbon dioxide at elevated pressures: measurements and correlation. J. Chem. Eng. Data 49(5), 950–953 (2004)
Hill, S.: Chanelling in packed columns. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1, 247–253 (1952)
Khosrokhavar, R., Elsinga, G., Mojaddam, A., Farajzadeh, R., Bruining, J.: Visualization of natural convection flow of (sub-) and (super-) critical CO2 in aqueous and oleic systems by applying Schlieren method. 73rd EAGE Conference and Exhibition Incorporating SPE EUROPEC 2011, SPE 143264 (2011)
Koval, E.J.: A method for predicting the performance of unstable miscible displacement in heterogeneous media. SPE J. 3(2), 145–154 (1963)
Kumagai, A., Yokoyama, C.: Viscosities of aqueous NaCl solutions containing CO2 at high pressures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 44, 227–229 (1999)
Lake, L.W.: Enhanced Oil Recovery. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1989)
Landau, L.D., Lifshitz, E.M.: Course of theoretical physics. Fluid Mechanics. Series in Advanced Physics, vol. 6. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1959)
Lu, C., Lichtner, P.C.: High resolution numerical investigation on the effect of convective instability on long-term CO2 storage in saline aquifers. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 78, 12042 (2007)
Neufeld, J.A., Hesse, M.A., Riaz, A., Hallworth, M.A., Tchelepi, H.A., Huppert, H.E.: Convective dissolution of carbon dioxide in saline aquifers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37(23) (2010) art. no. L22404
Pau, G.S.H., Bell, J.B., Pruess, K., Almgren, A.S., Lijewski, M.J., Zhang, K.: High-resolution simulation and characterization of density-driven flow in CO2 storage in saline aquifers. Adv. Water Resour. 33(5), 443–455 (2010)
Peaceman, D.W., Rachford Jr., H.H.: Numerical calculation of multi-dimensional miscible displacement. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 2, 327–339 (1962)
Perrine, R. L. : The development of stability theory for miscible liquid–liquid displacement. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1(1), 17–25 (1961)
Ranganathan, P., Farajzadeh, R., Bruining, J., Zitha, P.L.J.: Numerical simulation of natural convection in heterogeneous porous media for CO2 geological storage. Transp. Porous Med. 95, 25–54 (2012)
Riaz, A., Tchelepi, H.A.: Dynamics of vertical displacement in porous media associated with CO2 sequestration. Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition 6, pp. 4298–309 (2006)
Riaz, A., Hesse, M., Tchelepi, A., Orr, F.M.: Onset of convection in a gravitationally unstable diffusive boundary layer in porous medium. J. Fluid Mech. 548, 87–111 (2006b)
Siddiqui, F.I., Lake, L.W.: A comprehensive dynamic theory of hydrocarbon migration and trapping. SPE 38682. In: 1997 72nd Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio, TX, SPE (1997)
Silin, D., Patzek, T., Benson, S.M.: A model of buoyancy-driven two-phase countercurrent fluid flow. Transp. Porous Med. 76, 449–469 (2009)
Sharp, D.H.: An overview of Rayleigh–Taylor instability. Physica 12D, 3–18 (1984)
Taylor, G.I.: The instability of liquid surfaces when accelerated in a direction perpendicular to their planes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond., A 201, 192–196 (1950)
Todd, M.R., Longstaff, W.J.: The development, testing, and application of a numerical simulator for predicting miscible flood performance. J. Pet. Technol. 24, 874–882 (1972)
Van Dyke, M.: Perturbation Methods in Fluid Mechanics. The Parabolic Press, Stanford (1975)
Verhulst, F.: Methods and Applications of Singular Perturbations. Springer, New York (2000)
Waggoner, J.R., Zapata, V.J., Lake, L.W.: Viscous mixing in unstable miscible displacements. SPE 22235-MS (1991)
Waggoner, J.R., Castillo, J.L., Lake, L.W.: Simulation of EOR processes in stochastically generated permeable media. SPE Form. Eval. 7(2), 173–180 (1992)
Willhite, P.G.: Waterflooding, pp. 151–153. Society of Petroleum Engineers Inc., Richardson (1986), SPE textbook series
Wooding, R.A.: Growth of fingers at an unstable diffusing interface in a porous medium or Hele–Shaw cell. J. Fluid Mech. 39, 477–495 (1969)
Yang, C., Gu, Y.: Accelerated mass transfer of CO2 in reservoir brine due to density-driven natural convection at high pressures and elevated temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45, 2430–2436 (2006)
Yortsos, Y.C., Salin, D.: On the selection principle for viscous fingering in porous media. J. Fluid Mech. 557, 225–236 (2006)
Zimmerman, W.B., Homsy, G.M.: Viscous fingering in miscible displacements: Unification of effects of viscosity contrast, anisotropic dispersion, and velocity dependence of dispersion on nonlinear finger propagation. Phys. Fluid A 4, 2348–2359 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farajzadeh, R., Meulenbroek, B., Daniel, D. et al. An empirical theory for gravitationally unstable flow in porous media. Comput Geosci 17, 515–527 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-012-9336-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-012-9336-9