Abstract
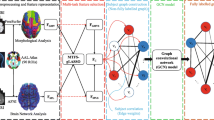
Currently, it is still a great challenge in clinical practice to accurately detect the early state of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), i.e., mild cognitive impairment (MCI) including early MCI (EMCI) and late MCI (LMCI). To address this challenge, we propose a new MCI detection framework based on multi-atlas multi-view hybrid graph convolutional networks and ensemble learning. We first construct nine different graphs based on three brain atlases and three morphological measurements using both imaging and non-imaging data of each subject. Then, in order to integrate the information of different graphs and obtain more discriminative feature representations for detecting MCI, we propose a hybrid graph convolutional network method. Finally, a new ensemble learning method is proposed to perform MCI detection tasks. An evaluation of our proposed framework has been conducted with 369 subjects with cognitively normal (CN), 779 subjects with MCI including 310 subjects with EMCI and 469 subjects with LMCI, and 301 subjects with AD on three classification tasks. Experimental results show that our proposed framework can get an accuracy of 90.8% and an AUC of 0.932 for MCI/CN classification, an accuracy of 88.6% and an AUC of 0.908 for MCI/AD classification, and an accuracy of 83.5% and an AUC of 0.851 for EMCI/LMCI classification, respectively. Compared with some state-of-the-art methods about MCI detection, our proposed framework can get better performance. Overall, our proposed framework is effective and promising for MCI detection in clinical practice.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anirudh, R., Thiagarajan, J.J.: Bootstrapping graph convolutional neural networks for autism spectrum disorder classification. In: ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 3197–3201. IEEE (2019)
Association, A., et al.: 2018 alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 14(3), 367–429 (2018)
Augustinack, J.C., Huber, K.E., Stevens, A.A., Roy, M., Frosch, M.P., van der Kouwe, A.J., Wald, L.L., Van Leemput, K., McKee, A.C., Fischl, B., et al.: Predicting the location of human perirhinal cortex, brodmann’s area 35, from mri. Neuroimage 64, 32–42 (2013)
Banerjee, C., Mukherjee, T., Pasiliao, E.: Feature representations using the reflected rectified linear unit (rrelu) activation. Big Data Mining and Analytics 3(2), 102–120 (2020)
Carrillo, M.C., Bain, L.J., Frisoni, G.B., Weiner, M.W.: Worldwide alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 8(4), 337–342 (2012)
Defferrard, M., Bresson, X., Vandergheynst, P.: Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp. 3844–3852 (2016)
Desikan, R.S., Ségonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B.T., Dickerson, B.C., Blacker, D., Buckner, R.L., Dale, A.M., Maguire, R.P., Hyman, B.T., et al.: An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on mri scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 31(3), 968–980 (2006)
Destrieux, C., Fischl, B., Dale, A., Halgren, E.: Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. Neuroimage 53(1), 1–15 (2010)
Farias, S.T., Mungas, D., Reed, B.R., Harvey, D., DeCarli, C.: Progression of mild cognitive impairment to dementia in clinic-vs community-based cohorts. Archives of neurology 66(9), 1151–1157 (2009)
Fischl, B.: Freesurfer. Neuroimage 62(2), 774–781 (2012)
Fischl, B., Rajendran, N., Busa, E., Augustinack, J., Hinds, O., Yeo, B.T., Mohlberg, H., Amunts, K., Zilles, K.: Cortical folding patterns and predicting cytoarchitecture. Cerebral cortex 18(8), 1973–1980 (2008)
Fischl, B., Stevens, A.A., Rajendran, N., Yeo, B.T., Greve, D.N., Van Leemput, K., Polimeni, J.R., Kakunoori, S., Buckner, R.L., Pacheco, J., et al.: Predicting the location of entorhinal cortex from mri. Neuroimage 47(1), 8–17 (2009)
Fischl, B., Van Der Kouwe, A., Destrieux, C., Halgren, E., Ségonne, F., Salat, D.H., Busa, E., Seidman, L.J., Goldstein, J., Kennedy, D., et al.: Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cerebral cortex 14(1), 11–22 (2004)
Fleisher, A., Sun, S., Taylor, C., Ward, C., Gamst, A., Petersen, R.C., Jack, C., Aisen, P., Thal, L., et al.: Volumetric mri vs clinical predictors of alzheimer disease in mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 70(3), 191–199 (2008)
Guo, Y., Nejati, H., Cheung, N.M.: Deep neural networks on graph signals for brain imaging analysis. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3295–3299. IEEE (2017)
He, X., Chen, L., Li, X., Fu, H.: Brain image feature recognition method for alzheimer’s disease. Cluster Computing 22(4), 8109–8117 (2019)
Jack Jr, C.R., Bernstein, M.A., Fox, N.C., Thompson, P., Alexander, G., Harvey, D., Borowski, B., Britson, P.J., L Whitwell, J., Ward, C., et al.: The alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (adni): Mri methods. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 27(4), 685–691 (2008)
Kong, Y., Gao, J., Xu, Y., Pan, Y., Wang, J., Liu, J.: Classification of autism spectrum disorder by combining brain connectivity and deep neural network classifier. Neurocomputing 324(9), 63–68 (2019)
Ktena, S.I., Parisot, S., Ferrante, E., Rajchl, M., Lee, M., Glocker, B., Rueckert, D.: Metric learning with spectral graph convolutions on brain connectivity networks. Neuroimage 169, 431–442 (2018)
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015)
Lian, C., Liu, M., Zhang, J., Shen, D.: Hierarchical fully convolutional network for joint atrophy localization and alzheimer’s disease diagnosis using structural mri. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 42(4), 880–893 (2020)
Litjens, G., Kooi, T., Bejnordi, B.E., Setio, A.A.A., Ciompi, F., Ghafoorian, M., Laak, J.V.D., Ginneken, B.V., Snchez, C.I.: A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Medical image analysis 42, 60–88 (2017)
Liu, J., Li, M., Lan, W., Wu, F.X., Pan, Y., Wang, J.: Classification of alzheimer’s disease using whole brain hierarchical network. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics 15(2), 624–632 (2018)
Liu, J., Pan, Y., Li, M., Chen, Z., Tang, L., Lu, C., Wang, J.: Applications of deep learning to mri images:a survey. Big Data Mining and Analytics 1(1), 1–18 (2018)
Liu, J., Pan, Y., Wu, F.X., Wang, J.: Enhancing the feature representation of multi-modal mri data by combining multi-view information for mci classification. Neurocomputing 400, 322–332 (2020)
Liu, J., Sheng, Y., Lan, W., Guo, R., Wang, Y., Wang, J.: Improved asd classification using dynamic functional connectivity and multi-task feature selection. Pattern Recognition Letters 138, 82–87 (2020)
Liu, J., Wang, J., Tang, Z., Hu, B., Wu, F.X., Pan, Y.: Improving alzheimeres disease classification by combining multiple measures. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics 15(5), 1649–1659 (2018)
Liu, J., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Pan, Y., Wang, X., Wang, J.: Mmm: classification of schizophrenia using multi-modality multi-atlas feature representation and multi-kernel learning. Multimedia Tools and Applications 77(22), 29651–29667 (2018)
Liu, L., Cheng, J., Quan, Q., Wu, F.X., Wang, Y.P., Wang, J.: A survey on u-shaped networks in medical image segmentations. Neurocomputing 409, 244–258 (2020)
Liu, L., Kurgan, L., Wu, F.X., Wang, J.: Attention convolutional neural network for accurate segmentation and quantification of lesions in ischemic stroke disease. Medical Image Analysis 65, 101791 (2020)
Liu, M., Zhang, J., Nie, D., Yap, P.T., Shen, D.: Anatomical landmark based deep feature representation for mr images in brain disease diagnosis. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 22(5), 1476–1485 (2018)
Mosconi, L., Brys, M., Glodzik-Sobanska, L., De Santi, S., Rusinek, H., De Leon, M.J.: Early detection of alzheimers disease using neuroimaging. Experimental gerontology 42(1–2), 129–138 (2007)
Parisot, S., Ktena, S.I., Ferrante, E., Lee, M., Guerrero, R., Glocker, B., Rueckert, D.: Disease prediction using graph convolutional networks: Application to autism spectrum disorder and alzheimers disease. Medical image analysis 48, 117–130 (2018)
Pennanen, C., Testa, C., Laakso, M., Hallikainen, M., Helkala, E., Hänninen, T., Kivipelto, M., Könönen, M., Nissinen, A., Tervo, S., et al.: A voxel based morphometry study on mild cognitive impairment. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 76(1), 11–14 (2005)
Saravanakumar, S., Thangaraj, P.: A voxel based morphometry approach for identifying alzheimer from mri images. Cluster Computing 22(6), 14081–14089 (2019)
Schmand, B., Huizenga, H., Van Gool, W.: Meta-analysis of csf and mri biomarkers for detecting preclinical alzheimer’s disease. Psychological medicine 40(1), 135–145 (2010)
Shuman, D., Narang, S., Frossard, P., Ortega, A., Vandergheynst, P.: The emerging field of signal processing on graphs: Extending high-dimensional data analysis to networks and other irregular domains. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 3(30), 83–98 (2013)
Su, H., Maji, S., Kalogerakis, E., Learned-Miller, E.: Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3d shape recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 945–953 (2015)
Tripathi, S., Nozadi, S.H., Shakeri, M., Kadoury, S.: Sub-cortical shape morphology and voxel-based features for alzheimer’s disease classification. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, pp. 991–994 (2017)
Wang, Y., Wang, J., Wu, F.X., Hayrat, R., Liu, J.: Aimafe: Autism spectrum disorder identification with multi-atlas deep feature representation and ensemble learning. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 343, 108840 (2020)
Xiang, Y., Wang, J., Tan, G., Wu, F.X., Liu, J.: Schizophrenia identification using multi-view graph measures of functional brain networks. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 7, 479 (2020)
Zhang, J., Zhan, J., Li, J., Jin, J., Qian, L.: Optimizing execution for pipelined-based distributed deep learning in a heterogeneously networked gpu cluster. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience p. e5923 (2020)
Zhang, Y., Schuff, N., Camacho, M., Chao, L.L., Fletcher, T.P., Yaffe, K., Woolley, S.C., Madison, C., Rosen, H.J., Miller, B.L., et al.: Mri markers for mild cognitive impairment: comparisons between white matter integrity and gray matter volume measurements. PloS one 8(6), e66367 (2013)
Zhang, Z., Cui, P., Zhu, W.: Deep learning on graphs: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.04202 (2018)
Zhong, W., Yu, N., Ai, C.: Applying big data based deep learning system to intrusion detection. Big Data Mining and Analytics 3(3), 181–195 (2020)
Zhou, J., Cui, G., Zhang, Z., Yang, C., Liu, Z., Maosong, S.: Graph neural networks: A review of methods and applications arXiv:1812.08434 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.61802442, No.61877059, the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province under Grant No.2019JJ50775, No.2018JJ2534, the 111 Project (No. B18059), and the Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Program (2018WK4001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zeng, D., Guo, R. et al. MMHGE: detecting mild cognitive impairment based on multi-atlas multi-view hybrid graph convolutional networks and ensemble learning. Cluster Comput 24, 103–113 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-020-03199-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-020-03199-8