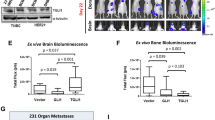
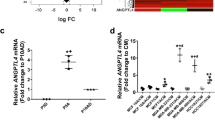
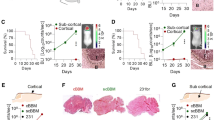
Abstract
Breast cancer metastasis to the brain develops after a clinical latency of years to even decades, suggesting that colonization of the brain is the most challenging step of the metastatic cascade. However, the underlying mechanisms used by breast cancer cells to successfully colonize the brain’s microenvironment remain elusive. Reelin is an archetypal extracellular glycoprotein that regulates migration, proliferation, and lamination of neurons. It is epigenetically silenced in various cancers, and its expression in multiple myelomas is linked to poor patient survival. We found that Reelin expression was low in primary breast cancer tissue. However, its expression was significantly higher in Her2+ breast cancers metastasizing to the brain. In particular, Reelin was highly expressed in the tumor periphery adjacent to surrounding astrocytes. This augmented Reelin expression was seen in Her2+ metastases, but not in triple negative (TN) primary tumors or in TN breast to brain metastasis cells co-cultured with astrocytes. Furthermore, the elevated expression was sustained in Her2+ cells grown in the presence of the DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-azacytidine, indicating epigenetic regulation of Reelin expression. The relative growth and rate of spheroids formation derived from Her2+ primary and BBM cells co-cultured with astrocytes were higher than those of TN primary and BBM cells, and knockdown of both Reelin and Her2 suppressed the astrocyte-induced growth and spheroid forming ability of Her2+ cells. Collectively, our results indicate that within the neural niche, astrocytes epigenetically regulate Reelin expression and its interaction with Her2 leading to increased proliferation and survival fitness.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kondziolka D, Kalkanis SN, Mehta MP, Ahluwalia M, Loeffler JS (2014) It is time to reevaluate the management of patients with brain metastases. Neurosurgery 75:1–9
Honda Y, Goto R, Idera N, Horiguchi K, Kitagawa D, et al. (2014) Prognostic significance of subtypes and Gpa (Graded Prognostic Assessment) in brain metastases from breast cancer. Ann Oncol
Pestalozzi BC (2009) Brain metastases and subtypes of breast cancer. Ann Oncol 20:803–805
Percy DB, Ribot EJ, Chen Y, McFadden C, Simedrea C et al (2011) In vivo characterization of changing blood-tumor barrier permeability in a mouse model of breast cancer metastasis: a complementary magnetic resonance imaging approach. Invest Radiol 46:718–725
Piccirilli M, Sassun TE, Brogna C, Giangaspero F, Salvati M (2007) Late brain metastases from breast cancer: clinical remarks on 11 patients and review of the literature. Tumori 93:150–154
Termini J, Neman J, Jandial R (2014) Role of the neural niche in brain metastatic cancer. Cancer Res 74:4011–4015
Jandial R, Anderson A, Choy C, Levy ML (2012) Bidirectional microevnironmental cues between neoplastic and stromal cells drive metastasis formation and efficiency. Neurosurgery 70:N12–N13.
Paget G (1889) Remarks on a case of alternate partial anaesthesia. Br Med J 1:1–3
Langley RR, Fidler IJ (2011) The seed and soil hypothesis revisited-The role of tumor-stroma interactions in metastasis to different organs. Int J Cancer 128:2527–2535
Curran T, D’Arcangelo G (1998) Role of Reelin in the control of brain development. Brain Res Rev 26:285–294
Rice DS, Curran T (2001) Role of the Reelin signaling pathway in central nervous system development. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1005–1039
Zhou Q, Obana EA, Radomski KL, Sukumar G, Wynder C et al (2016) Inhibition of the histone demethylase Kdm5b promotes neurogenesis and derepresses Reln (reelin) in neural stem cells from the adult subventricular zone of mice. Mol Biol Cell 27:627–639
Mitchell CP, Chen Y, Kundakovic M, Costa E, Grayson DR (2005) Histone deacetylase inhibitors decrease reelin promoter methylation in vitro. J Neurochem 93:483–492
Stein T, Cosimo E, Yu X, Smith PR, Simon R et al (2010) Loss of reelin expression in breast cancer is epigenetically controlled and associated with poor prognosis. Am J Pathol 177:2323–2333
Neman J, Termini J, Wilczynski S, Vaidehi N, Choy C et al (2014) Human breast cancer metastases to the brain display GABAergic properties in the neural niche. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:984–989
Zhang Y, Sloan SA, Clarke LE, Caneda C, Plaza CA et al (2016) Purification and characterization of progenitor and mature human astrocytes reveals transcriptional and functional differences with mouse. Neuron 89:37–53
Raposo G, Nijman HW, Stoorvogel W, Leijendekker R, Harding CV et al (1996) B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med 183:1161–1172
Bronisz A, Wang Y, Nowicki MO, Peruzzi P, Ansari KI et al (2014) Extracellular vesicles modulate the glioblastoma microenvironment via a tumor suppression signaling network directed by miR-1. Cancer Res 74:738–750
Neman J, Choy C, Kowolik CM, Anderson A, Duenas VJ et al (2013) Co-evolution of breast-to-brain metastasis and neural progenitor cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 30:753–768
Massalini S, Pellegatta S, Pisati F, Finocchiaro G, Farace MG et al (2009) Reelin affects chain-migration and differentiation of neural precursor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 42:341–349
Becker J, Frohlich J, Perske C, Pavlakovic H, Wilting J (2012) Reelin signalling in neuroblastoma: migratory switch in metastatic stages. Int J Oncol 41:681–689
Jossin Y, Cooper JA (2011) Reelin, Rap1 and N-cadherin orient the migration of multipolar neurons in the developing neocortex. Nat Neurosci 14:697–703
D’Arcangelo G (2014) Reelin in the years: controlling neuronal migration and maturation in the mammalian brain. Adv Neurosci 2014:19
Biamonte F, Scicchitano BB, Lama G (2015) Evaluation of the Reelin signaling in cancer stem cells isolated from tumor and peritumor tissue of glioblastoma. Ital J Anat Embriol 120(1):89.
Evangelisti C, Florian MC, Massimi I, Dominici C, Giannini G et al (2009) MiR-128 up-regulation inhibits Reelin and DCX expression and reduces neuroblastoma cell motility and invasiveness. FASEB J 23:4276–4287
Hu HL, Deng F, Liu Y, Chen MF, Zhang XL et al (2012) Characterization and retinal neuron differentiation of WERI-Rb1 cancer stem cells. Mol Vision 18:2388–2397
Seigel GM, Hackam AS, Ganguly A, Mandell LM, Gonzalez-Fernandez F (2007) Human embryonic and neuronal stem cell markers in retinoblastoma. Mol Vis 13:823–832
Lin L, Yan F, Zhao D, Lv M, Liang X et al (2016) Reelin promotes the adhesion and drug resistance of multiple myeloma cells via integrin beta1 signaling and STAT3. Oncotarget 7:9844–9858
Sui L, Wang Y, Ju LH, Chen M (2012) Epigenetic regulation of reelin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor genes in long-term potentiation in rat medial prefrontal cortex. Neurobiol Learn Mem 97:425–440
Dohi O, Takada H, Wakabayashi N, Yasui K, Sakakura C et al (2010) Epigenetic silencing of RELN in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol 36:85–92
Grayson DR, Chen Y, Costa E, Dong E, Guidotti A et al (2006) The human reelin gene: transcription factors (+), repressors (-) and the methylation switch (+/-) in schizophrenia. Pharmacol Ther 111:272–286
Biamonte F, Scicchitano BM, Lama G (2015) Evaluation of the Reelin signaling in cancer stem cells isolated from tumor and peritumor tissue of glioblastoma. Ital J Antomy Embryol 120:89
Basso M, Bonetto V (2016) Extracellular vesicles and a novel form of communication in the brain. Front Neurosci 10:127
Budnik V, Ruiz- Canada C, Wendler F (2016) Extracellular vesicles round off communication in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 17:160–172
Rajendran L, Bali J, Barr MM, Court FA, Kramer-Albers EM et al (2014) Emerging roles of extracellular vesicles in the nervous system. J Neurosci 34:15482–15489
Zhang L, Zhang S, Yao J, Lowery FJ, Zhang Q et al (2015) Microenvironment-induced PTEN loss by exosomal microRNA primes brain metastasis outgrowth. Nature 527:100–104
Liu HY, Huang CM, Hung YF, Hsueh YP (2015) The microRNAs Let7c and miR21 are recognized by neuronal Toll-like receptor 7 to restrict dendritic growth of neurons. Exp Neurol 269:202–212
Fong MY, Zhou W, Liu L, Alontaga AY, Chandra M et al (2015) Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 17:183–194
Lee SA, Lee H, Pinney JR, Khialeeva E, Bergsneider M et al (2011) Development of microfabricated magnetic actuators for removing cellular occlusion. J Micromech Microeng 21:54006
Khialeeva E, Lane TF, Carpenter EM (2011) Disruption of reelin signaling alters mammary gland morphogenesis. Development 138: 767–776
Yuan Y, Chen H, Ma G, Cao X, Liu Z (2012) Reelin is involved in transforming growth factor-beta1-induced cell migration in esophageal carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 7:e31802
Perrone G, Vincenzi B, Zagami M, Santini D, Panteri R et al (2007) Reelin expression in human prostate cancer: a marker of tumor aggressiveness based on correlation with grade. Mod Pathol 20:344–351
Khialeeva E, Chou JW, Carpenter EM (2015) Reelin signaling in tumor microenvironment is required for metastasis of mammary carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1538-7445
Khialeeva E, Chou JW, Carpenter EM (2015) Exploring the relationship between reelin signaling and breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1538-7445
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the flow cytometry core, pathology core, and microscopy cores, for their valuable assistance in this project. We also thank Anders Persson for his advice on the manuscript.
Funding
R.J. is supported by Department of Defense (DOD) Grant (BC142323), The Margaret E. Early Medical Research Trust, National Institutes of Health (NIH) Grant K12 CA001727-16A1. Additional project support was provided by National Cancer Institute Grant P30 CA033572.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jandial, R., Choy, C., Levy, D.M. et al. Astrocyte-induced Reelin expression drives proliferation of Her2+ breast cancer metastases. Clin Exp Metastasis 34, 185–196 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-017-9839-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-017-9839-9