Abstract
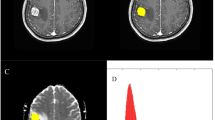
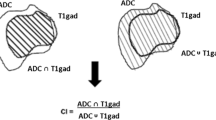
To investigate the predictive capacity of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) as a biomarker of radiation response in brain metastases. Seventy brain metastases from 42 patients treated with either stereotactic radiosurgery or whole brain radiotherapy were imaged at baseline, 1 week, and 1 month post-treatment using diffusion-weighted MRI. Mean and median relative ADC for metastases was calculated by normalizing ADC measurements to baseline ADC. At 1 year post-treatment, or last available follow-up MRI, volume criteria determined final tumour response status. Uni- and multivariate analysis was used to account for factors associated with tumour response at 1 week and 1 month. A generalized estimating equations model took into consideration multiple tumours per subject. Optimal thresholds that distinguished responders from non-responders, as well as sensitivity and specificity were determined by receiver operator characteristic analysis and Youden’s index. Lower relative ADC values distinguished responders from non-responders at 1 week and 1 month (P < 0.05). Optimal cut-off values for response were 1.060 at 1 week with a sensitivity and specificity of 75.0 and 56.3 %, respectively. At 1 month, the cut-off was 0.971 with a sensitivity and specificity of 70.0 and 68.8 %, respectively. A multivariate general estimating equations analysis identified no prior radiation [odds ratio (OR) 0.211 and 0.137, P = 0.033 and 0.0177], and a lower median relative ADC at 1 week and 1 month (OR 0.619 and 0.694, P = 0.0036 and 0.005), as predictors of tumour response. Lower relative ADC values at 1 week and 1 month following radiation distinguished responders from non-responders and may be a promising biomarker of early radiation response.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schüttrumpf LH, Niyazi M, Nachbichler SB, Manapov F, Jansen N, Siefert A et al (2014) Prognostic factors for survival and radiation necrosis after stereotactic radiosurgery alone or in combination with whole brain radiation therapy for 1–3 cerebral metastases. Radiat Oncol 9:105. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-9-105
Patchell RA (2003) The management of brain metastases. Cancer Treat Rev 29:533–540. doi:10.1016/S0305-7372(03)00105-1
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Assoc 295:2483–2491. doi:10.1001/jama.295.21.2483
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG et al (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:1037–1044. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70263-3
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villà S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG et al (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1655
Tsao M, Xu W, Sahgal A (2012) A meta-analysis evaluating stereotactic radiosurgery, whole-brain radiotherapy, or both for patients presenting with a limited number of brain metastases. Cancer 118:2486–2493. doi:10.1002/cncr.26515
Sahgal A, Aoyama H, Kocher M, Neupane B, Collette S, Tago M et al (2015) Phase 3 trials of stereotactic radiosurgery with or without whole-brain radiation therapy for 1 to 4 brain metastases: individual patient data meta-analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 91:710–717. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.10.024
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC et al (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16250-8
Chang EL, Shiu AS, Lii M-F, Rhines LD, Mendel E, Mahajan A et al (2004) Phase I clinical evaluation of near-simultaneous computed tomographic image-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy for spinal metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:1288–1294. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.04.025
Sahgal A (2015) Point/counterpoint: Stereotactic radiosurgery without whole-brain radiotherapy for patients with a limited number of brain metastases: the current standard of care? Neuro-Oncology. 17(7):916–918
Chao ST, Ahluwalia MS, Barnett GH, Stevens GHJ, Murphy ES, Stockham AL et al (2013) Challenges with the diagnosis and treatment of cerebral radiation necrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87:449–457. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.05.015
El Kady RM, Choudhary AK, Tappouni R (2011) Accuracy of apparent diffusion coefficient value measurement on PACS workstation: a comparative analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:W280–W284. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.4706
Nagane M, Kobayashi K, Tanaka M, Tsuchiya K, Shishido-Hara Y, Shimizu S et al (2014) Predictive significance of mean apparent diffusion coefficient value for responsiveness of temozolomide-refractory malignant glioma to bevacizumab: preliminary report. Int J Clin Oncol 19:16–23. doi:10.1007/s10147-013-0517-x
Pope WB, Lai A, Mehta R, Kim HJ, Qiao J, Young JR et al (2011) Apparent diffusion coefficient histogram analysis stratifies progression-free survival in newly diagnosed bevacizumab-treated glioblastoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:882–889. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2385
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J et al (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Ostergaard L, Hochberg FH, Rabinov JD, Sorensen AG, Lev M, Kim L et al (1999) Early changes measured by magnetic resonance imaging in cerebral blood flow, blood volume, and blood-brain barrier permeability following dexamethasone treatment in patients with brain tumors. J Neurosurg 90:300–305. doi:10.3171/jns.1999.90.2.0300
Follwell MJ, Khu KJ, Cheng L, Xu W, Mikulis DJ, Millar B-A et al (2012) Volume specific response criteria for brain metastases following salvage stereotactic radiosurgery and associated predictors of response. Acta Oncol 51:629–635. doi:10.3109/0284186X.2012.681066
Tomura N, Narita K, Izumi J, Suzuki A, Anbai A, Otani T et al (2006) Diffusion changes in a tumor and peritumoral tissue after stereotactic irradiation for brain tumors: possible prediction of treatment response. J Comput Assist Tomogr 30:496–500
Lee C-C, Wintermark M, Xu Z, Yen C-P, Schlesinger D, Sheehan JP (2014) Application of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging to predict the intracranial metastatic tumor response to gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 118:351–361. doi:10.1007/s11060-014-1439-9
Hein PA, Kremser C, Judmaier W, Griebel J, Pfeiffer K-P, Kreczy A et al (2003) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring diffusion changes in rectal carcinoma during combined, preoperative chemoradiation: preliminary results of a prospective study. Eur J Radiol 45:214–222
Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG (2000) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 217:331–345. doi:10.1148/radiology.217.2.r00nv24331
Mintorovitch J, Yang GY, Shimizu H, Kucharczyk J, Chan PH, Weinstein PR (1994) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of acute focal cerebral ischemia: comparison of signal intensity with changes in brain water and Na+, K(+)-ATPase activity. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 14:332–336. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1994.40
Liang D, Bhatta S, Gerzanich V, Simard JM (2007) Cytotoxic edema: mechanisms of pathological cell swelling. Neurosurg Focus 22:E2. doi:10.3171/foc.2007.22.5.3
Farjam R, Tsien CI, Feng FY, Gomez-Hassan D, Hayman JA, Lawrence TS et al (2014) Investigation of the diffusion abnormality index as a new imaging biomarker for early assessment of brain tumor response to radiation therapy. Neuro Oncol 16:131–139. doi:10.1093/neuonc/not153
Asao C, Korogi Y, Kitajima M, Hirai T, Baba Y, Makino K et al (2005) Diffusion-weighted imaging of radiation-induced brain injury for differentiation from tumor recurrence. Am J Neuroradiol 26:1455–1460
Jakubovic R, Sahgal A, Soliman H, Milwid R, Zhang L, Eilaghi A et al (2014) Magnetic resonance imaging-based tumour perfusion parameters are biomarkers predicting response after radiation to brain metastases. Clin Oncol 26:704–712. doi:10.1016/j.clon.2014.06.010
Chung C, Jalali S, Foltz W, Burrell K, Wildgoose P, Lindsay P et al (2013) Imaging biomarker dynamics in an intracranial Murine Glioma study of radiation and antiangiogenic therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:805–812. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.07.005
Moffat BA, Chenevert TL, Lawrence TS, Meyer CR, Johnson TD, Dong Q et al (2005) Functional diffusion map: a noninvasive MRI biomarker for early stratification of clinical brain tumor response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5524–5529. doi:10.1073/pnas.0501532102
Long DM (1979) Capillary ultrastructure in human metastatic brain tumors. J Neurosurg 51:53–58. doi:10.3171/jns.1979.51.1.0053
Cha S (2009) Neuroimaging in neuro-oncology. Neurotherapeutics 6:465–477. doi:10.1016/j.nurt.2009.05.002
Deeken JF, Löscher W (2007) The blood-brain barrier and cancer: transporters, treatment, and trojan horses. Clin Cancer Res 13:1663–1674. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2854
Hein PA, Eskey CJ, Dunn JF, Hug EB (2004) Diffusion-weighted imaging in the follow-up of treated high-grade gliomas: tumor recurrence versus radiation injury. Am J Neuroradiol 25:201–209
Mahmood F, Johannesen HH, Geertsen P, Opheim GF, Hansen RH (2015) The effect of region of interest strategies on apparent diffusion coefficient assessment in patients treated with palliative radiation therapy to brain metastases. Acta Oncol 54:1529–1534. doi:10.3109/0284186X.2015.1061211
Hiwatashi A, Kinoshita T, Moritani T, Wang HZ, Shrier DA, Numaguchi Y et al (2003) Hypointensity on diffusion-weighted MRI of the brain related to T2 shortening and susceptibility effects. Am J Roentgenol 181:1705–1709. doi:10.2214/ajr.181.6.1811705
Duygulu G, Ovali GY, Çalli C, Kitis Ö, Yünten N, Akalin T et al (2010) Intracerebral metastasis showing restricted diffusion: correlation with histopathologic findings. Eur J Radiol 74:117–120. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.03.004
Acknowledgments
Raphael Jakubovic and Stephanie Zhou contributed equally as first author of this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have relevant disclosures.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jakubovic, R., Zhou, S., Heyn, C. et al. The predictive capacity of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in response assessment of brain metastases following radiation. Clin Exp Metastasis 33, 277–284 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-016-9778-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-016-9778-x