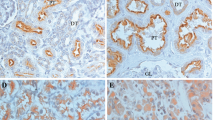
Abstract
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is an aggressive disease with unpredictable behaviour. Clinical parameters are not always accurate for prognosis prediction. The integration of molecular markers to prognostic models can significantly improve prognostic assessment and consequently patient management. We assessed the expression of alpha-enolase (ENO1) protein by immunohistochemistry in 360 patients with primary ccRCC and correlated its expression with multiple clinicopathological parameters including stage, grade, tumor size, disease-free and overall survival. Cox proportional hazard regression models adjusted for clinicopathological factors were used to test for a link between ENO1 expression and both disease-free and overall survival. We correlated ENO1 mRNA expression with overall survival in an independent set of 428 ccRCC cases from The Cancer Genome Atlas. ENO1 showed cytoplasmic, membranous and nuclear staining patterns. There is a statistically significant negative correlation between ENO1 expression, tumor stage, and grade. ENO1 expression also shows a statistically significant direct correlation with disease-free survival (p = 0.011) and overall survival (p = 0.030) in ccRCC. Patients with higher ENO1 expression had lower hazard ratio of recurrence, although this was not statistically significant (HR = 0.330, p = 0.060). These findings were validated at the mRNA level in an independent set of 428 ccRCC cases which also showed that low ENO1 expression is associated with significantly shorter overall survival. Down-regulation of ENO1 can be a predictor of poor prognosis in ccRCC, and it can be a potential prognostic marker.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ENO1:
-
Alpha-enolase
- ccRCC:
-
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
References
Chow WH, Dong LM, Devesa SS (2010) Epidemiology and risk factors for kidney cancer. Nat Rev Urol 7(5):245–257
Lipworth L, Tarone RE, McLaughlin JK (2006) The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 176(6 Pt 1):2353–2358
Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Zincke H, Weaver AL, Blute ML (2003) Comparisons of outcome and prognostic features among histologic subtypes of renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 27(5):612–624
Srigley JR, Delahunt B, Eble JN, Egevad L, Epstein JI, Grignon D, Hes O, Moch H, Montironi R, Tickoo SK et al (2013) The international society of urological pathology (ISUP) vancouver classification of renal neoplasia. Am J Surg Pathol 37(10):1469–1489
Feldstein MS, Rhodes DJ, Parker AS, Orford RR, Castle EP (2009) The haphazard approach to the early detection of asymptomatic renal cancer: results from a contemporary executive health programme. BJU Int 104(1):53–56
Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, Harshman LC, Bjarnason GA, Vaishampayan UN, Mackenzie M, Wood L, Donskov F, Tan MH et al (2013) External validation and comparison with other models of the international metastatic renal-cell carcinoma database consortium prognostic model: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 14(2):141–148
Pasic MD, Samaan S, Yousef GM (2013) Genomic medicine: new frontiers and new challenges. Clin Chem 59(1):158–167
Zhai W, Xu YF, Liu M, Zheng JH (2012) Transcriptome network analysis reveals candidate genes for renal cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther 8(1):28–33
Siu KW, DeSouza LV, Scorilas A, Romaschin AD, Honey RJ, Stewart R, Pace K, Youssef Y, Chow TF, Yousef GM (2009) Differential protein expressions in renal cell carcinoma: new biomarker discovery by mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 8(8):3797–3807
Sato Y, Yoshizato T, Shiraishi Y, Maekawa S, Okuno Y, Kamura T, Shimamura T, Sato-Otsubo A, Nagae G, Suzuki H et al (2013) Integrated molecular analysis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat Genet 45(8):860–867
White NM, Masui O, Newsted D, Scorilas A, Romaschin AD, Bjarnason GA, Siu KW, Yousef GM (2014) Galectin-1 has potential prognostic significance and is implicated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression through the HIF/mTOR signaling axis. Br J Cancer 110(5):1250–1259
Metzger GJ, Dankbar SC, Henriksen J, Rizzardi AE, Rosener NK, Schmechel SC (2012) Development of multigene expression signature maps at the protein level from digitized immunohistochemistry slides. PLoS One 7(3):e33520
Girgis AH, Iakovlev VV, Beheshti B, Bayani J, Squire JA, Bui A, Mankaruos M, Youssef Y, Khalil B, Khella H et al (2012) Multilevel whole-genome analysis reveals candidate biomarkers in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 72(20):5273–5284
Arai E, Kanai Y (2010) Genetic and epigenetic alterations during renal carcinogenesis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 4(1):58–73
Kroeger N, Klatte T, Chamie K, Rao PN, Birkhauser FD, Sonn GA, Riss J, Kabbinavar FF, Belldegrun AS, Pantuck AJ (2013) Deletions of chromosomes 3p and 14q molecularly subclassify clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 119(8):1547–1554
Monzon FA, Alvarez K, Peterson L, Truong L, Amato RJ, Hernandez-McClain J, Tannir N, Parwani AV, Jonasch E (2011) Chromosome 14q loss defines a molecular subtype of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma associated with poor prognosis. Mod Pathol 24(11):1470–1479
Beroukhim R, Brunet JP, Di Napoli A, Mertz KD, Seeley A, Pires MM, Linhart D, Worrell RA, Moch H, Rubin MA et al (2009) Patterns of gene expression and copy-number alterations in von-hippel lindau disease-associated and sporadic clear cell carcinoma of the kidney. Cancer Res 69(11):4674–4681
Arai E, Ushijima S, Tsuda H, Fujimoto H, Hosoda F, Shibata T, Kondo T, Imoto I, Inazawa J, Hirohashi S et al (2008) Genetic clustering of clear cell renal cell carcinoma based on array-comparative genomic hybridization: its association with DNA methylation alteration and patient outcome. Clin Cancer Res 14(17):5531–5539
Moore LE, Jaeger E, Nickerson ML, Brennan P, De Vries S, Roy R, Toro J, Li H, Karami S, Lenz P et al (2012) Genomic copy number alterations in clear cell renal carcinoma: associations with case characteristics and mechanisms of VHL gene inactivation. Oncogenesis 1:e14
Yokomizo A, Yamamoto K, Furuno K, Shiota M, Tatsugami K, Kuroiwa K, Naito S (2010) Histopathologic subtype-specific genomic profiles of renal cell carcinomas identified by high-resolution whole-genome single nucleotide polymorphism array analysis. Oncol Lett 1(6):1073–1078
Chang YS, Wu W, Walsh G, Hong WK, Mao L (2003) Enolase-alpha is frequently down-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer and predicts aggressive biological behavior. Clin Cancer Res 9(10 Pt 1):3641–3644
Muller FL, Colla S, Aquilanti E, Manzo VE, Genovese G, Lee J, Eisenson D, Narurkar R, Deng P, Nezi L et al (2012) Passenger deletions generate therapeutic vulnerabilities in cancer. Nature 488(7411):337–342
Gao J, Zhao R, Xue Y, Niu Z, Cui K, Yu F, Zhang B, Li S (2013) Role of enolase-1 in response to hypoxia in breast cancer: exploring the mechanisms of action. Oncol Rep 29(4):1322–1332
Song Y, Luo Q, Long H, Hu Z, Que T, Zhang X, Li Z, Wang G, Yi L, Liu Z et al (2014) Alpha-enolase as a potential cancer prognostic marker promotes cell growth, migration, and invasion in glioma. Mol Cancer 13:65
Hsu KW, Hsieh RH, Lee YH, Chao CH, Wu KJ, Tseng MJ, Yeh TS (2008) The activated Notch1 receptor cooperates with alpha-enolase and MBP-1 in modulating c-myc activity. Mol Cell Biol 28(15):4829–4842
Feo S, Arcuri D, Piddini E, Passantino R, Giallongo A (2000) ENO1 gene product binds to the c-myc promoter and acts as a transcriptional repressor: relationship with Myc promoter-binding protein 1 (MBP-1). FEBS Lett 473(1):47–52
Lomnytska MI, Becker S, Gemoll T, Lundgren C, Habermann J, Olsson A, Bodin I, Engstrom U, Hellman U, Hellman K et al (2012) Impact of genomic stability on protein expression in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Br J Cancer 106(7):1297–1305
White NM, Masui O, Desouza LV, Krakovska O, Metias S, Romaschin AD, Honey RJ, Stewart R, Pace K, Lee J et al (2014) Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals potential diagnostic markers and pathways involved in pathogenesis of renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 5(2):506–518
White NM, Newsted DW, Masui O, Romaschin AD, Siu KW, Yousef GM (2014) Identification and validation of dysregulated metabolic pathways in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol 35(3):1833–1846
Khella HW, White NM, Faragalla H, Gabril M, Boazak M, Dorian D, Khalil B, Antonios H, Bao TT, Pasic MD et al (2012) Exploring the role of miRNAs in renal cell carcinoma progression and metastasis through bioinformatic and experimental analyses. Tumour Biol 33(1):131–140
Khella HW, Bakhet M, Allo G, Jewett MA, Girgis AH, Latif A, Girgis H, Von Both I, Bjarnason GA, Yousef GM (2013) miR-192, miR-194 and miR-215: a convergent microRNA network suppressing tumor progression in renal cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 34(10):2231–2239
Caramel J, Quignon F, Delattre O (2008) RhoA-dependent regulation of cell migration by the tumor suppressor hSNF5/INI1. Cancer Res 68(15):6154–6161
Shuch B, Amin A, Armstrong AJ, Eble JN, Ficarra V, Lopez-Beltran A, Martignoni G, Rini BI, Kutikov A (2014) Understanding pathologic variants of renal cell carcinoma: distilling therapeutic opportunities from biologic complexity. Eur Urol 67(1):85–97
Klatte T, Kroeger N, Rampersaud EN, Birkhauser FD, Logan JE, Sonn G, Riss J, Rao PN, Kabbinavar FF, Belldegrun AS et al (2012) Gain of chromosome 8q is associated with metastases and poor survival of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 118(23):5777–5782
Klatte T, Rao PN, de Martino M, LaRochelle J, Shuch B, Zomorodian N, Said J, Kabbinavar FF, Belldegrun AS, Pantuck AJ (2009) Cytogenetic profile predicts prognosis of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 27(5):746–753
La Rochelle J, Klatte T, Dastane A, Rao N, Seligson D, Said J, Shuch B, Zomorodian N, Kabbinavar F, Belldegrun A et al (2010) Chromosome 9p deletions identify an aggressive phenotype of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 116(20):4696–4702
Baloglu H, Cannizzaro LA, Jones J, Koss LG (2001) Atypical endometrial hyperplasia shares genomic abnormalities with endometrioid carcinoma by comparative genomic hybridization. Hum Pathol 32(6):615–622
Yu L, Shi J, Cheng S, Zhu Y, Zhao X, Yang K, Du X, Klocker H, Yang X, Zhang J (2012) Estrogen promotes prostate cancer cell migration via paracrine release of ENO1 from stromal cells. Mol Endocrinol 26(9):1521–1530
Zhou W, Capello M, Fredolini C, Piemonti L, Liotta LA, Novelli F, Petricoin EF (2010) Mass spectrometry analysis of the post-translational modifications of alpha-enolase from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. J Proteome Res 9(6):2929–2936
Morgan TM, Seeley EH, Fadare O, Caprioli RM, Clark PE (2013) Imaging the clear cell renal cell carcinoma proteome. J Urol 189(3):1097–1103
Tang SW, Chang WH, Su YC, Chen YC, Lai YH, Wu PT, Hsu CI, Lin WC, Lai MK, Lin JY (2009) MYC pathway is activated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and essential for proliferation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 273(1):35–43
Gordan JD, Lal P, Dondeti VR, Letrero R, Parekh KN, Oquendo CE, Greenberg RA, Flaherty KT, Rathmell WK, Keith B et al (2008) HIF-alpha effects on c-Myc distinguish two subtypes of sporadic VHL-deficient clear cell renal carcinoma. Cancer Cell 14(6):435–446
Metias SM, Lianidou E, Yousef GM (2009) MicroRNAs in clinical oncology: at the crossroads between promises and problems. J Clin Pathol 62(9):771–776
Chen WC, Lin MS, Ye YL, Gao HJ, Song ZY, Shen XY (2012) microRNA expression pattern and its alteration following celecoxib intervention in human colorectal cancer. Exp Ther Med 3(6):1039–1048
Beggs AD, Domingo E, McGregor M, Presz M, Johnstone E, Midgley R, Kerr D, Oukrif D, Novelli M, Abulafi M et al (2012) Loss of expression of the double strand break repair protein ATM is associated with worse prognosis in colorectal cancer and loss of Ku70 expression is associated with CIN. Oncotarget 3(11):1348–1355
Wuttig D, Zastrow S, Fussel S, Toma MI, Meinhardt M, Kalman K, Junker K, Sanjmyatav J, Boll K, Hackermuller J et al (2012) CD31, EDNRB and TSPAN7 are promising prognostic markers in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma revealed by genome-wide expression analyses of primary tumors and metastases. Int J Cancer 131(5):693–704
Stillebroer AB, Mulders PF, Boerman OC, Oyen WJ, Oosterwijk E (2010) Carbonic anhydrase IX in renal cell carcinoma: implications for prognosis, diagnosis, and therapy. Eur Urol 58(1):75–83
Gossage L, Eisen T (2010) Alterations in VHL as potential biomarkers in renal-cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 7(5):277–288
Lichner Z, Scorilas A, White NM, Girgis AH, Rotstein L, Wiegand KC, Latif A, Chow C, Huntsman D, Yousef GM (2013) The chromatin remodeling gene ARID1A is a new prognostic marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol 182(4):1163–1170
Kroeze SG, Vermaat JS, van Brussel A, van Melick HH, Voest EE, Jonges TG, van Diest PJ, Hinrichs J, Bosch JL, Jans JJ (2010) Expression of nuclear FIH independently predicts overall survival of clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Eur J Cancer 46(18):3375–3382
Faragalla H, Youssef YM, Scorilas A, Khalil B, White NM, Mejia-Guerrero S, Khella H, Jewett MA, Evans A, Lichner Z et al (2012) The clinical utility of miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for renal cell carcinoma. J Mol Diagn 14(4):385–392
Iakovlev VV, Gabril M, Dubinski W, Scorilas A, Youssef YM, Faragalla H, Kovacs K, Rotondo F, Metias S, Arsanious A et al (2012) Microvascular density as an independent predictor of clinical outcome in renal cell carcinoma: an automated image analysis study. Lab Invest 92(1):46–56
Acknowledgments
GMY is supported by grants from the Canadian Institute of Health Research (MOP 119606), Kidney Foundation of Canada (KFOC130030), Kidney Cancer Research Network of Canada, and Prostate Cancer Canada Movember Discovery Grants (D2013-39).
Conflict of interest
The author’s declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10585_2015_9725_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 1 Correlation between cytoplasmic and nuclear intensity and frequency in cancerous kidney tissues. Both cytoplasmic and nuclear staining patterns showed significant positive correlation in cancerous kidney tissues. rs = spearman correlation coefficient (DOCX 50 kb)
10585_2015_9725_MOESM2_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 2 Correlation between cytoplasmic and membrane intensity and frequency in cancerous kidney tissues. Both cytoplasmic and membranous staining patterns showed significant positive correlation in cancerous kidney tissues. rs = spearman correlation coefficient (DOCX 44 kb)
10585_2015_9725_MOESM3_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 3 Correlation between cytoplasmic and nuclear intensity and frequency in kidney papillomas. Both cytoplasmic and nuclear staining patterns showed significant positive correlation in kidney papillomas. rs = spearman correlation coefficient (DOCX 41 kb)
10585_2015_9725_MOESM4_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 4 Correlation between cytoplasmic and membrane intensity and frequency in kidney papillomas. Both cytoplasmic and membranous staining patterns showed significant positive correlation in kidney papillomas. rs = spearman correlation coefficient (DOCX 41 kb)
10585_2015_9725_MOESM5_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 5 Kaplan–Meier survival curve for (a) DFS time and (b) OS time of patients with high and low cytoplasmic expression of alpha-enolase protein. a When using alpha-enolase as a dichotomous variable, patients with low alpha-enolase expression have a statistically significant decrease in disease free survival (p = 0.046) compared to those with high expression. b Patients with low alpha-enolase expression have a statistically significant decrease in overall survival (p = 0.048) compared to patients with high expression(DOCX 132 kb)
10585_2015_9725_MOESM6_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 6 Homozygous and heterozygous copy number loss at the ENO1 locus (ch1p36) was observed in 69 of 436 cases of ccRCC, indicating that chromosomal alterations are responsible, at least in part, of ENO1 dysregulation in kidney cancer. Blue indicates a copy number loss (TIFF 196 kb)
10585_2015_9725_MOESM7_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 7 miR-22 transfection. 786-O cells were successfully transfected with miR-22 mimic as there was a significant increase in the relative expression of miR-22 compared with untransfected and control cells. Untransfected cells display low endogenous expression of miR-22. Similar results were obtained for ACHN RCC cells (data not shown). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 versus control. NC negative control, siPORT transfection agent (DOCX 76 kb)
10585_2015_9725_MOESM8_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 8 Endogenous miR-22 and ENO1 expression in two kidney cancer cell lines (786-O and ACHN) and a pool of normal kidney tissues (n = 5). Expression levels of miR-22 and ENO1 are inversely correlated. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (DOCX 79 kb)
10585_2015_9725_MOESM13_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary material 13 Target prediction analysis showing a list of miRNAs that are predicted to target alpha-enolase. A value of 1 indicates that the miRNA was predicted to target alpha-enolase using the corresponding search algorithm. A value of 0 indicates that the miRNA was not predicted to target alpha-enolase using the corresponding search algorithm (XLSX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
White-Al Habeeb, N.M., Di Meo, A., Scorilas, A. et al. Alpha-enolase is a potential prognostic marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 32, 531–541 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9725-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9725-2