Abstract
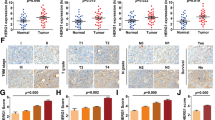
Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) is an inhibitor of Raf-mediated activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase (MEK)-MAP kinase and is considered as an important tumor suppressor. RKIP-expression was investigated retrospectively in 321 esophageal cancers [179 adenocarcinomas (ACs), 142 squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs)]. RKIP-expression was further investigated in 41 precursor lesions consisting of 14 cases of non-dysplastic Barrett’s mucosa, 5 low grade dysplasias (LGD), and 12 high grade dysplasias (HGD) as well as, 4 cases with low grade and 6 cases with high-grade squamous cell dysplasia. Corresponding lymph node metastases were investigated in 140 patients, distant metastases in 29, and local recurrences in 12. High RKIP-expression was significantly more common in Barrett’s mucosa without dysplasia and in LGD compared to HGD (p = 0.047, χ2 test) and invasive AC (p < 0.001, χ2 test). In 187 primary esophageal cancers (58.3 %) RKIP was downregulated (AC: 51.4 %; SCC: 66.9 %). RKIP status of primary tumors influenced RKIP expression in corresponding lymph node and distant metastases (p < 0.05, linear regression). Downregulation of RKIP was associated with shorter overall survival (OS) and disease free survival (DFS) in all tumors (p ≤ 0.05, Cox regression). In AC, downregulation of RKIP was an independent prognostic factor for OS and DFS (p ≤ 0.05, Cox regression), while in SCC it reached significance only in univariate analysis (p ≤ 0.05, log-rank test). In conclusion, downregulation of RKIP is associated with shorter survival in esophageal cancers, and RKIP status of tumor cells seems to be preserved at the formation of metastases. Inhibition of RKIP-downregulation might reduce the ability of esophageal cancers to establish disseminated disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones PA, Takai D (2001) The role of DNA methylation in mammalian epigenetics. Science 293(5532):1068–1070
Bird A (2002) DNA methylation patterns and epigenetic memory. Genes Dev 16(1):6–21
Yoo CB, Jones PA (2006) Epigenetic therapy of cancer: past, present and future. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(1):37–50
Yeung K et al (2000) Mechanism of suppression of the Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by the raf kinase inhibitor protein. Mol Cell Biol 20(9):3079–3085
Yeung K et al (1999) Suppression of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature 401(6749):173–177
Al-Mulla F et al (2008) Raf kinase inhibitor protein: mechanism of loss of expression and association with genomic instability. J Clin Pathol 61(4):524–529
Yeung KC et al (2001) Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol 21(21):7207–7217
Ku GY, Ilson DH (2010) Esophagogastric cancer: targeted agents. Cancer Treat Rev 36(3):235–248
Driessen A et al (2006) Expression of carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX), a hypoxia-related protein, rather than vascular-endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a pro-angiogenic factor, correlates with an extremely poor prognosis in esophageal and gastric adenocarcinomas. Ann Surg 243(3):334–340
Tanaka N et al (2008) Expression of carbonic anhydrase 9, a potential intrinsic marker of hypoxia, is associated with poor prognosis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 99(9):1468–1475
Beshir AB et al (2010) Raf kinase inhibitor protein suppresses nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent cancer cell invasion through negative regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression. Cancer Lett 299(2):137–149
Li TT et al (2009) Beta-arrestin/Ral signaling regulates lysophosphatidic acid-mediated migration and invasion of human breast tumor cells. Mol Cancer Res 7(7):1064–1077
Li HZ et al (2009) Effects of raf kinase inhibitor protein expression on metastasis and progression of human breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res 7(6):832–840
Li HZ et al (2008) Effects of raf kinase inhibitor protein expression on metastasis and progression of human epithelial ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Res 6(6):917–928
Schuierer MM et al (2004) Reduction in Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression is associated with increased Ras-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling in melanoma cell lines. Cancer Res 64(15):5186–5192
Chatterjee D et al (2004) RKIP sensitizes prostate and breast cancer cells to drug-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279(17):17515–17523
Woods Ignatoski KM et al (2008) Loss of Raf kinase inhibitory protein induces radioresistance in prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72(1):153–160
Zaravinos A et al (2009) BRAF and RKIP are significantly decreased in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Cycle 8(9):1402–1408
Paulson TG et al (2009) Chromosomal instability and copy number alterations in Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15(10):3305–3314
Ruan L et al (2010) Raf kinase inhibitor protein correlates with sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma to radiotherapy. J Cell Biochem 110(4):975–981
Zlobec I et al (2008) Two-marker protein profile predicts poor prognosis in patients with early rectal cancer. Br J Cancer 99(10):1712–1717
Minoo P et al (2007) Loss of raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein expression is associated with tumor progression and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 127(5):820–827
Hagan S et al (2005) Reduction of Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein expression correlates with breast cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 11(20):7392–7397
Fu Z et al (2006) Metastasis suppressor gene Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) is a novel prognostic marker in prostate cancer. Prostate 66(3):248–256
Chatterjee D et al (2008) Inverse association between Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma patients: implications for clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res 14(10):2994–3001
Conflict of interest
The authors indicate to have no financial disclosures, conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Birner, P., Jesch, B., Schultheis, A. et al. RAF-kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) downregulation in esophageal cancer and its metastases. Clin Exp Metastasis 29, 551–559 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-012-9470-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-012-9470-8