Abstract
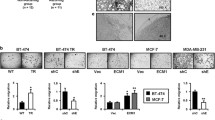
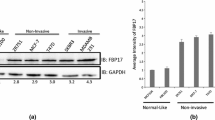
CAS proteins and Ezrin, Radixin, Moesin (ERM) family members act as intracellular scaffolds and are involved in interactions with the cytoskeleton, respectively. Both protein families have previously been associated with metastasis and poor prognosis in cancer. Our group recently reported on the overexpression of EZR/VIL2 and BCAR1 and their protein products in breast carcinoma effusions compared to primary breast carcinoma. In the present study, the role of these two proteins was studied in semi-normal MCF10A cells and metastatic MDA-MB-231 breast carcinoma cells cultured in tri-dimensional (3-D) conditions that were hypothesized to reproduce the in vivo conditions of breast cancer metastasis. MCF10A cells formed spheroid-shaped colonies without any Matrigel invasion, while MDA-MB-231 cells displayed an invasive phenotype and showed satellite projections that bridged multiple cell colonies in 3-D culture. E-cadherin was expressed in MCF10A, but not in MDA-MB-231 cells. The temporal expression of ezrin and BCAR1/p130Cas at the mRNA and protein level differed in the two cell lines upon 3-D culturing on Matrigel. Upregulation of BCAR1/p130cas was observed in the transition of MDA-MB-231 from attached to detached culture. Silencing of Ezrin and p130Cas in MDA-MB-231 cells by short hairpin RNA resulted in decreased invasive potential, and p130Cas silencing further resulted in smaller spheroid/colony formation. Our data show that MCF10A and MDA-MB-231 cells differ in their ability to form spheroids, in expression of E-cadherin and in the expression of Ezrin and BCAR1/p130Cas in 3-D cultures on Matrigel, suggesting a role in tumor progression in breast carcinoma.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Wilkes JD, Fidias P, Vaickus L, Perez RP (1995) Malignancy-related pericardial effusion. 127 cases from the Roswell Park Center Institute. Cancer (Phila) 76:1377–1387
Hausheer FH, Yarbro JW (1985) Diagnosis and treatment of malignant pleural effusion. Semin Oncol 12:54–75
Martinez-Moragon E, Aparicio J, Sanchis J, Menendez R, Cruz Rogado M, Sanchis F (1998) Malignant pleural effusion: prognostic factors for survival and response to chemical pleurodesis in a series of 120 cases. Respiration 65:108–113
Fentiman IS, Millis R, Sexton S, Hayward JL (1981) Pleural effusion in breast cancer: a review of 105 cases. Cancer 47:2087–2092
Dieterich M, Goodman SN, Rojas-Corona RR, Emralino AB, Jimenez-Joseph D, Sherman ME (1994) Multivariate analysis of prognostic features in malignant pleural effusions from breast cancer patients. Acta Cytol 38:945–952
Banerjee AK, Willetts I, Robertson JF, Blamey RW (1994) Pleural effusion in breast cancer: a review of the Nottingham experience. Eur J Surg Oncol 20:33–36
Davidson B, Konstantinovsky S, Nielsen S, Dong HP, Berner A, Vyberg M, Reich R (2004) Altered expression of metastasis-associated and regulatory molecules in effusions from breast cancer patients- a novel model for tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res 10:7335–7346
Davidson B, Reich R, Lazarovici P, Ann Flørenes V, Nielsen S, Nesland JM (2004) Altered expression and activation of the nerve growth factor receptors TrkA and p75 provides the first evidence of tumor progression to effusion in breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 83:119–128
Davidson B, Konstantinovsky S, Kleinberg L, Nguyen MTP, Bassarova A, Kvalheim G, Nesland JM, Reich R (2006) The mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) p38 and JNK are markers of tumor progression in breast carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 102:453–461
Konstantinovsky S, Smith Y, Zilber S, Tuft Stavnes H, Becker AM, Nesland JM, Reich R, Davidson B (2010) Breast carcinoma cells in primary tumors and effusions have different gene array profiles. J Oncol 2010:969084
Bissell MJ, Hall HG, Parry G (1982) How does the extracellular matrix direct gene expression? J Theor Biol 99:31–68
Schmeichel KL, Bissell MJ (2003) Modeling tissue-specific signaling and organ function in three dimensions. J Cell Sci 116:2377–2388
Defilippi P, Di Stefano P, Cabodi S (2006) p130Cas: a versatile scaffold in signaling networks. Trends Cell Biol 16:257–263
Tikhmyanova N, Little JL, Golemis EA (2010) CAS proteins in normal and pathological cell growth control. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:1025–1048
Fehon RG, McClatchey AI, Bretscher A (2010) Organizing the cell cortex: the role of ERM proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:276–287
Debnath J, Brugge JS (2005) Modelling glandular epithelial cancers in three-dimensional cultures. Nat Rev Cancer 5:675–688
Kenny PA, Lee GY, Myers CA, Neve RM, Semeiks JR, Spellman PT, Lorenz K, Lee EH, Barcellos-Hoff MH, Petersen OW, Gray JW, Bissell MJ (2007) The morphologies of breast cancer cell lines in three-dimensional assays correlate with their profiles of gene expression. Mol Oncol 1:84–96
Dorssers LC, Grebenchtchikov N, Brinkman A, Look MP, van Broekhoven SP, de Jong D, Peters HA, Portengen H, Meijer-van Gelder ME, Klijn JG, van Tienoven DT, Geurts-Moespot A, Span PN, Foekens JA, Sweep FC (2004) The prognostic value of BCAR1 in patients with primary breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:6194–6202
Bruce B, Khanna G, Ren L, Landberg G, Jirström K, Powell C, Borczuk A, Keller ET, Wojno KJ, Meltzer P, Baird K, McClatchey A, Bretscher A, Hewitt SM, Khanna C (2007) Expression of the cytoskeleton linker protein ezrin in human cancers. Clin Exp Metastasis 24:69–78
Tait L, Soule HD, Russo J (1990) Ultrastructural and immunocytochemical characterization of an immortalized human breast epithelial cell line, MCF-10. Cancer Res 50:6087–6094
Brinkley BR, Beall PT, Wible LJ, Mace ML, Turner DS, Cailleau RM (1980) Variations in cell form and cytoskeleton in human breast carcinoma cells in vitro. Cancer Res 40:3118–3129
Barcellos-Hoff MH, Aggeler J, Ram TG, Bissell MJ (1989) Functional differentiation and alveolar morphogenesis of primary mammary cultures on reconstituted basement membrane. Development 105:223–235
Roskelley CD, Desprez PY, Bissell MJ (1994) Extracellular matrix-dependent tissue-specific gene expression in mammary epithelial cells requires both physical and biochemical signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:12378–12382
Nelson CM, Bissell MJ (2006) Of extracellular matrix, scaffolds, and signaling: Tissue architecture regulates development, homeostasis, and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:287–309
Petersen OW, Ronnov-Jessen L, Howlett AR, Bissell MJ (1992) Interaction with basement membrane serves to rapidly distinguish growth and differentiation pattern of normal and malignant human breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9064–9068
Muthuswamy SK, Li D, Lelievre S, Bissell MJ, Brugge JS (2001) ErbB2, but not ErbB1, reinitiates proliferation and induces luminal repopulation in epithelial acini. Nat Cell Biol 3:785–792
Park CC, Zhang H, Pallavicini M, Gray JW, Baehner F, Park CJ, Bissell MJ (2006) Beta1 integrin inhibitory antibody induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells, inhibits growth, and distinguishes malignant from normal phenotype in three dimensional cultures and in vivo. Cancer Res 66:1526–1535
Gautreau A, Louvard D, Arpin M (2002) ERM proteins and NF2 tumor suppressor: the Yin and Yang of cortical actin organization and cell growth signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol 14:104–109
Gautreau A, Poullet P, Louvard D, Arpin M (1999) Ezrin, a plasma membrane-microfilament linker, signals cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7300–7305
Pujuguet P, Del Maestro L, Gautreau A, Louvard D, Arpin M (2003) Ezrin regulates E-cadherin-dependent adherens junction assembly through Rac1 activation. Mol Biol Cell 14:2181–2191
Akisawa N, Nishimori I, Iwamura T, Onishi S, Hollingsworth MA (1999) High levels of ezrin expressed by human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines with high metastatic potential. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 258:395–400
Nestl A, Von Stein OD, Zatloukal K, Thies WG, Herrlich P, Hofmann M, Sleeman JP (2001) Gene expression patterns associated with the metastatic phenotype in rodent and human tumors. Cancer Res 61:1569–1577
Khanna C, Khan J, Nguyen P, Prehn J, Caylor J, Yeung C, Trepel J, Meltzer P, Helman L (2001) Metastasis-associated differences in gene expression in a murine model of osteosarcoma. Cancer Res 61:3750–3759
O’Neill GM, Fashena SJ, Golemis EA (2000) Integrin signalling: a new Cas(t) of characters enters the stage. Trends Cell Biol 10:111–119
Giancotti FG (2003) A structural view of integrin activation and signaling. Dev Cell 4:149–151
Wei L, Yang Y, Zhang X, Yu Q (2002) Anchorage-independent phosphorylation of p130(Cas) protects lung adenocarcinoma cells from anoikis. J Cell Biochem 87:439–449
Radisky D, Hagios C, Bissell MJ (2001) Tumors are unique organs defined by abnormal signaling and context. Semin Cancer Biol 11:87–95
Weigelt B, Bissell MJ (2008) Unraveling the microenvironmental influences on the normal mammary gland and breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 18:311–321
Krishnan K, Bruce B, Hewitt S, Thomas D, Khanna C, Helman LJ (2006) Ezrin mediates growth and survival in Ewing’s sarcoma through the AKT/mTOR, but not the MAPK, signaling pathway. Clin Exp Metastasis 23:227–236
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Norwegian Cancer Society and the Research Fund at the Norwegian Radium Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konstantinovsky, S., Davidson, B. & Reich, R. Ezrin and BCAR1/p130Cas mediate breast cancer growth as 3-D spheroids. Clin Exp Metastasis 29, 527–540 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-012-9468-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-012-9468-2