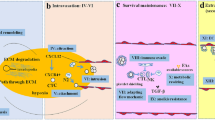
Abstract
Metastatic lesions are the leading cause of death among cancer patients. These lesions usually originate from clonal proliferation of single tumor cells dispersed from the primary tumor into the circulation which finally arrest in the capillary bed of distant organs. The microenvironment within the circulation of potential metastatic target organs provides a variety of pro- and anti- metastatic stimuli regulating the onset of organ colonisation by metastatic tumor cells. Mechanical shear stress, anoikis and cell mediated cytotoxicity within the microcirculation probably clear most circulating tumor cells. Adhesion, and eventually extravasation, are essential initial interactions of circulating tumor cells with distant organs and can provide escape from the cytotoxic environment within the circulation. Adhesion to the capillary wall is mostly controlled by the organ-specific availability of adhesion molecules on tumor cells, the endothelium, and the composition of the underlying extracellular matrix. The availability of pro-adhesive and pro-migratory paracrine signals provided by the organ specific microenvironment can further initiate the onset of metastatic organ colonisation. Tumor cell and microenvironment factors regulating survival within the microcirculation, adhesion and extravasation of tumor cells are highlighted in the review.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morris M, Iacopetta B, Platell C (2007) Comparing survival outcomes for patients with colorectal cancer treated in public and private hospitals. Med J Aust 186:296–300
Garcia-Closas M, Brinton LA, Lissowska J et al (2006) Established breast cancer risk factors by clinically important tumour characteristics. Br J Cancer 95:123–129
Wolfle U, Muller V, Pantel K (2006) Disseminated tumor cells in breast cancer: detection, characterization and clinical relevance. Future Oncol 2:553–561
Nicolson GL (1988) Cancer metastasis: TC and host organ properties important in metastasis to specific secondary sites. Biochem Biophys Acta 948:175–224
Weiss L (1992) Comments on hematogenous metastatic patterns in humans as revealed by autopsy. Clin Exp Metastasis 10:191–199
Fidler IJ (2003) The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the seed and soil hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer 3:1–6
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Thompson EW, Newgreen DF (2005) Carcinoma invasion and metastasis: a role for epithelial-mesenchymal transition? Cancer Res 65:5991–5995
Guarino M, Rubino B, Ballabio G (2007) The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology. Pathology 39:305–318
Tse JC, Kalluri R (2007) Mechanisms of metastasis: epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and contribution of tumor microenvironment. J Cell Biochem. 101:816–829
Grünert S, Jechlinger M, Beug H (2003) Diverse cellular and molecular mechanisms contribute to epithelial plasticity and metastasis. Nature Rev/Mol Cell Biol 4:657–665
Timmers M, Vekemans K, Vermijlen D et al (2004) Interactions between rat colon carcinoma cells and Kupffer cells during the onset of hepatic metastasis. Int J Cancer 112:793–802
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC (2002) Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer 2:563–572
Ewing J (1928) Neoplastic diseases, 6th edn. W. B. Sanders, Philadelphia
Paget S (1889) The distribution of secondary growth in cancer of the breast. Lancet 1:571–573
Weiss L, Voit A, Lane WW (1984) Metastatic patterns in patients with carcinoma of the lower esophagus and upper rectum. Invasion Metastasis 4:47–60
Tarin D, Price JE, Kettlewell MG et al (1984) Clinicopathological observations on metastasis in man studied in patients treated with peritoneovenous shunts. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 288:749–751
Tarin D, Price JE, Kettlewell MG et al (1984) Mechanisms of human tumor metastasis studied in patients with peritoneovenous shunts. Cancer Res 44:3584–3592
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H et al (2001) Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 410:50–56
Glaves D, Huben RP, Weiss L (1988) Haematogeneous dissemination of cells from human renal adenocarcinomas. Br J Cancer 57:32–35
Glaves D, Ketch DA, Asch BB (1993) Conservation of epithelial cell phenotypes during hematogeneous metastasis from mammary carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst 76:933–938
Barbera-Guillem E, Weiss L (1993) Cancer-cell traffic in the liver. III Lethal deformation of B16 melanoma cells in liver sinusoids. Int J Cancer 54:880–884
Weiss L, Nannmark U, Johansson BR et al (1992) Lethal deformation of cancer cells in the microcirculation: a potential rate regulator of hematogenous metastasis. Int J Cancer 50:103–107
Weiss L (1991) Deformation-driven, lethal damage to cancer cells. Its contribution to metastatic inefficiency. Cell Biophys 18:73–79
Weiss L, Harlos JP, Elkin G (1990) Mechanisms for the biomechanical destruction of L1210 leukemia cells: a rate regulator for metastasis. Cell Biophys 16:149–159
Weiss L (1988) Biomechanical destruction of cancer cells in the heart: a rate regulator for hematogenous metastasis. Invasion Metastasis 8:228–237
Weiss L (1989) Biomechanical destruction of cancer cells in skeletal muscle: a rate-regulator for hematogenous metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 7:483–491
Haier J, Nicolson GL (2001) Tumor cell adhesion under hydrodynamic conditions of fluid flow. APMIS 109:241–262
Kucik DF, Dustin ML, Miller JM (1996) Adhesion-activating phorbol ester increases the mobility of leukocyte integrin LFA-1 in cultured lymphocytes. J Clin Invest 97:2139–2144
Ni N, Kevil CG, Bullard DC et al (2003) Avidity modulation activates adhesion under flow and requires cooperativity among adhesion receptors. Biophys J 85:4122–4133
Korb T, Schlüter K, Enns A et al (2004) Integrity of actin fibres and microtubules influences metastatic tumor cell adhesion. Exp Cell Res 299:236–247
McIntire LV (1994) 1992 ALZA distinguished lecture: bioengineering and vascular biology. Ann Biomed Eng 22:2–13
Galbraith CG, Sheetz MP (1998) Forces on adhesive contacts affect cell function. Curr Opin Cell Biol 10:566–571
von Sengbusch A, Gassmann P, Fisch K et al (2005) Focal Adhesion Kinase regulates dynamic adhesion of carcinoma cells to collagens. Am J Pathol 166:585–593
Okuyama M, Ohta Y, Kambayashi J et al (1996) Fluid shear stress induces actin polymerization in human neutrophils. J Cell Biochem 63:432–441
Haier J, Nicolson GL (2000) Tumor cell adhesion of human colon carcinoma cells with different metastatic properties to extracellular matrix under dynamic conditions of laminar flow. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 126:699–706
Glinskii OV, Huxley VH, Glinsky GV et al (2005) Mechanical entrapment is insufficient and intercellular adhesion is essential for metastatic cell arrest in distant organs. Neoplasia 7:522–527
Mook OR, Van Marle J, Vreeling-Sindelarova H et al (2003) Visualization of early events in tumor formation of eGFP-transfected rat colon cancer cells in liver. Hepatology 38:295–304
Steinbauer M, Guba M, Cernaianu G et al (2003) GFP-transfected tumor cells are useful in examining early metastasis in vivo, but immune reaction precludes long-term tumor development studies in immunocompetent mice. Clin Exp Metastasis 20:135–141
Ding L, Sunamura M, Kodama T et al (2001) In vivo evaluation of the early events associated with liver metastasis of circulating cancer cells. Br J Cancer 85:431–438
Enns A, Gassmann P, Schluter K et al (2004) Integrins can directly mediate metastatic tumor cell adhesion within the liver sinusoids. J Gastrointest Surg 8:1049–1059
Enns A, Korb T, Schluter K et al (2005) Alphavbeta5-integrins mediate early steps of metastasis formation. Eur J Cancer 41:1065–1072
Haier J, Korb T, Hotz B et al (2003) An intravital model to monitor steps of metastatic tumor cell adhesion within the hepatic microcirculation. J Gastrointest Surg 7:507–514
Wang H, Fu W, Im JH et al (2004) Tumor cell alpha3beta1 integrin and vascular laminin-5 mediate pulmonary arrest and metastasis. J Cell Biol 164:935–941
Al-Mehdi AB, Tozawa K, Fisher AB et al (2000) Intravascular origin of metastasis from the proliferation of endothelium-attached tumor cells: a new model for metastasis. Nat Med 6:100–102
MacDonald IC, Schmidt EE, Morris VL et al (1992) Intravital videomicroscopy of the chorioallantoic microcirculation: a model system for studying metastasis. Microvasc Res 44:185–199
Naumov GN, Wilson SM, MacDonald IC et al (1992) Cellular expression of green fluorescent protein, coupled with high-resolution in vivo videomicroscopy, to monitor steps in tumor metastasis. J Cell Sci 112:1835–1842
Karpatkin S, Pearlstein E (1981) Role of platelets in tumor cell metastases. Ann Intern Med 95:636–641
Palumbo JS, Talmage KE, Massari JV et al (2005) Platelets and fibrin(ogen) increase metastatic potential by impeding natural killer cell-mediated elimination of tumor cells. Blood 105:178–185
Nakamori S, Kameyama M, Imaoka S et al (1993) Increased expression of sialyl Lewisx antigen correlates with poor survival in patients with colorectal carcinoma: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study. Cancer Res 53:3632–3637
Amado M, Carneiro F, Seixas M et al (1998) Dimeric sialyl-Le(x) expression in gastric carcinoma correlates with venous invasion and poor outcome. Gastroenterology 114:462–470
Steinert BW, Tang DG, Grossi IM et al (1993) Studies on the role of platelet eicosanoid metabolism and integrin alpha IIb beta 3 in tumor-cell-induced platelet aggregation. Int J Cancer 54:92–101
Borsig L, Wong R, Hynes RO et al (2002) Synergistic effects of L- and P-selectin in facilitating tumor metastasis can involve non-mucin ligands and implicate leukocytes as enhancers of metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:2193–2198
Camerer E, Qazi AA, Duong DN et al (2004) Platelets, protease-activated receptors, and fibrinogen in hematogenous metastasis. Blood 104:397–401
Amirkhosravi A, Mousa SA, Amaya M et al (2003) Inhibition of tumor cell-induced platelet aggregation and lung metastasis by the oral GpIIb/IIIa antagonist XV454. Thromb Haemost 90:549–554
Klepfish A, Greco MA, Karpatkin S (1993) Thrombin stimulates melanoma tumor-cell binding to endothelial cells and subendothelial matrix. Int J Cancer 53:978–982
Dardik R, Savion N, Kaufmann Y et al (1998) Thrombin promotes platelet-mediated melanoma cell adhesion to endothelial cells under flow conditions: role of platelet glycoproteins P-selectin and GPIIb-IIIA. Br J Cancer 77:2069–2075
Honn KV, Tang DG, Grossi IM et al (1994) Enhanced endothelial cell retraction mediated by 12(S)-HETE: a proposed mechanism for the role of platelets in tumor cell metastasis. Exp Cell Res 210:1–9
Liotta LA (1992) Cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Sci Am 266:54–59, 62–63
Dong C, Slattery MJ, Rank BM (2002) In vitro characterization and micromechanics of tumor cell chemotactic protrusion, locomotion, and extravasation. Ann Biomed Eng 30:344–355
Slattery MJ, Dong C (2003) Neutrophils influence melanoma adhesion and migration under flow conditions. Int J Cancer 106:713–722
Slattery MJ, Liang S, Dong C (2005) Distinct role of hydrodynamic shear in leukocyte-facilitated tumor cell extravasation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C831–C839
Wu QD, Wang JH, Condron C et al (2001) Human neutrophils facilitate tumor cell transendothelial migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280:C814–C822
Khatib AM, Fallavollita L, Wancewicz EV et al (2002) Inhibition of hepatic endothelial E-selectin expression by C-raf antisense oligonucleotides blocks colorectal carcinoma liver metastasis. Cancer Res 62:5393–5398
Kim YJ, Borsig L, Han HL et al (1999) Distinct selectin ligands on colon carcinoma mucins can mediate pathological interactions among platelets, leukocytes, and endothelium. Am J Pathol 155:461–472
Wisse E, van’t Noordende JM, van der Meulen J et al (1976) The pit cell: description of a new type of cell occurring in rat liver sinusoids and peripheral blood. Cell Tissue Res 173:423–435
Grundy MA, Zhang T, Sentmann CL (2007) NK cells remove B16F10 tumor cells in a perforin and interferon-gamma independent manner in vivo. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56:1153–1161
Wiltrout RH (2000) Regulation and antimetastatic functions of liver-associated natural killer cells. Immunol Rev 174:63–76
Vermijlen D, Luo D, Robaye B et al (1999) Pit cells (Hepatic natural killer cells) of the rat induce apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells by the perforin/granzyme pathway. Hepatology 29:51–56
Shresta S, MacIvor DM, Heusel JW et al (1995) Natural killer and lymphokine-activated killer cells require granzyme B for the rapid induction of apoptosis in susceptible target cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5679–5683
Oshimi Y, Oda S, Honda Y et al (1996) Involvement of Fas ligand and Fas-mediated pathway in the cytotoxicity of human natural killer cells. J Immunol 157:2909–2915
Wiltrout RH, Herberman RB, Zhang SR et al (1985) Role of organ-associated NK cells in decreased formation of experimental metastases in lung and liver. J Immunol 134:4267–4275
Smyth MJ, Thia KY, Street SE et al (2000) Differential tumor surveillance by natural killer (NK) and NKT cells. J Exp Med 191:661–668
Smyth MJ, Taniguchi M, Street SE (2000) The anti-tumor activity of IL-12: mechanisms of innate immunity that are model and dose dependent. J Immunol 165:2665–2670
Gardner CR, Wasserman AJ, Laskin DL (1987) Differential sensitivity of tumor targets to liver macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity. Cancer Res 47:6686–6691
Decker T, Kiderlen AF, Lohmann-Matthes ML (1985) Liver macrophages (Kupffer cells) as cytotoxic effector cells in extracellular and intracellular cytotoxicity. Infect Immun 50:358–364
Sturm JW, Magdeburg R, Berger K (2003) Influence of TNFA on the formation of liver metastases in a syngenic mouse model. Int J Cancer 107:11–21
Fingar VH, Taber SW, Buschemeyer WC (1997) Constitutive and stimulated expression of ICAM-1 protein on pulmonary endothelial cells in vivo. Microvasc Res 54:135–144
Heimburg J, Yan J, Morey S et al (2006) Inhibition of spontaneous breast cancer metastasis by anti-Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen monoclonal antibody JAA-F11. Neoplasia 8:939–948
Ito S, Nakanishi H, Ikehara Y (2001) Real-time observation of micrometastasis formation in the living mouse liver using a green fluorescent protein gene-tagged rat tongue carcinoma cell line. Int J Cancer 93:212–217
Shimizu S, Yamada N, Sawada T et al (2001) Ultrastructure of early phase hepatic metastasis of human colon carcinoma cells with special reference to desmosomal junctions with hepatocytes. Pathol Int 50:953–959
Khatib AM, Kontogiannea M, Fallavollita L et al. (1999). Rapid induction of cytokine and E-selectin expression in the liver in response to metastatic tumor cells. Cancer Res 59:1356–1361
Wang HH, McIntosh AR, Hasinoff BB et al (2002) Regulation of B16F1 melanoma cell metastasis by inducible functions of the hepatic microvasculature. Eur J Cancer 38:1261–1270
Orr FW, Wang HH, Lafrenie RM et al (2000) Interactions between cancer cells and the endothelium in metastasis. J Pathol 190:310–329
Eble JA, Haier J (2006) Integrins in cancer treatment. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 6:89–105
Meyer T, Hart IR (1998) Mechanisms of tumour metastasis. Eur J Cancer 34:214–221
Gooding JM, Yap KL, Ikura M (2004) The cadherin–catenin complex as a focal point of cell adhesion and signalling: new insights from three-dimensional structures. Bioessays 26:497–511
Silbert JE, Sugumaran G (2003) A starting place for the road to function. Glycoconj 19:227–237
Haier J, Nasralla M, Nicolson GL (2000) Cell surface molecules and their prognostic values in assessing colorectal carcinomas. Ann Surg 231:11–24
Juliano RL, Varner JA (1993) Adhesion molecules in cancer: the role of integrins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5:812–818
Hulleman E, Boonstra J (2001) Regulation of G1 phase progression by growth factors and the extracellular matrix. Cell Mol Life Sci 58:80–93
Juliano RL, Varner JA (1993) Adhesion molecules in cancer: the role of integrins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5:812–818
Varner JA, Emerson DA, Juliano RL (1995) Integrin alpha5beta1 expression negatively regulate cell growth: reversal by attachment to fibronectin. Mol Biol Cell 6:725–740
Derksen PW, Liu X, Saridin F et al (2006) Somatic inactivation of E-cadherin and p53 in mice leads to metastatic lobular mammary carcinoma through induction of anoikis resistance and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 10:437–449
Owens DM, Watt FM (2001) Influence of beta1 integrins on epidermal squamous cell carcinoma formation in a transgenic mouse model: alpha3beta1, but not alpha2beta1, suppresses malignant conversion. Cancer Res 61:5248–5254
Zutter MM, Santoro SA, Staatz WD (1995) Re-expression of the alpha2beta1 integrin abrogates the malignant phenotype of breast carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7411–7415
Bogenrieder T, Herlyn M (2003) Axis of evil: molecular mechanisms of cancer metastasis. Oncogene 22:6524–6536
Woodhouse EC, Chuaqui RF, Liotta LA (1997) General mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer 80:1529–1537
Hood JD, Cheresh DA (2002) Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration. Nat Rev Cancer 2:91–100
Byers SW, Sommers CL, Hoxter B, Mercurio AM, Tozeren A (1995) Role of E-cadherin in the response of tumor cell aggregates to lymphatic, venous and arterial flow: measurement of cell–cell adhesion strength. J Cell Sci 108:2053–2064
Wolf K, Mazo I, Leung H (2003) Compensation mechanism in tumor cell migration: mesenchymal-amoeboid transition after blocking of pericellular proteolysis. J Cell Biol 160:267–277
Friedl P, Wolf K (2003) Tumour–cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer 3:362–374
Sahai E, Marschall CJ (2003) Differing modes of tumor cell invasion have distinct requirements for Rho/ROCK signalling and extracellular proteolysis. Nat Cell Biol 5:711–719
Fukumura D, Yuan F, Monsky WL (1997) Effect of host microenvironment on the microcirculation of human colon adenocarcinoma. Am J Pathol 151:679–688
Kikkawa H, Kaihou M, Horaguchi N (2002) Role of integrin alphavbeta3 in the early phase of liver metastasis: PET and IVM analyses. Clin Exp Metastasis 19:717–725
Nip J, Shibata H, Loskutoff DJ et al (1992) Human melanoma cells derived from lymphatic metastasis use the integrin alpha(V)beta(3) to adhere to lymph node vitronectin. J Clin Invest 90:1406–1413
Byzova TV, Kim W, Midura RJ et al (2000) Activation of integrin alpha(V)beta(3) regulates cell adhesion and migration to bone sialoprotein. Exp Cell Res 254:299–308
Liapsi H, Flath H, Kitazawa S (1996) Integrin alpha V beta 3 expression by bone-residing breast cancer metastasis. Diagn Mol Pathol 5:127–135
Sloan EK, Pouliot N, Stanley KL et al (2006) Tumor-specific expression of alphavbeta3 integrin promotes spontaneous metastasis of breast cancer to bone. Breast Cancer Res 8:R20
Bosman FT, Stamenkovic I (2003) Functional structure and composition of the extracellular matrix. J Pathol 200:423–428
Hayashi C, Rittling S, Hayata T et al (2007) Serum osteopontin, an enhancer of tumor metastasis to bone, promotes B16 melanoma cell migration. J Cell Biochem 27 [Epub ahead of print]
Desai B, Rogers MJ, Chellaiah MA (2007) Mechanisms of osteopontin and CD44 as metastatic principles in prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer 6:18
Paris S, Sesboue R, Chauzy C et al (2006) Hyaluronectin modulation of lung metastasis in nude mice. Eur J Cancer 42:3253–3259
Bauerle T, Peterschmitt J, Hilbig H et al (2006) Treatment of bone metastasis induced by MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells with an antibody against bone sialoprotein. Int J Oncol 28:573–583
Jacob K, Webber M, Benayahu D et al (1999) Osteonectin promotes prostate cancer cell migration and invasion: a positive mechanism for metastasis to bone. Cancer Res 59:4453–4457
Wang H, Fu W, Im JH et al (2004) Tumor cell alpha3beta1 integrin and vascular laminin-5 mediate pulmonary arrest and metastasis. J Cell Biol 164:935–941
Egeblad M, Werb Z (2002) New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:161–174
McCawley LJ, Matrisian LM (2001) Matrix metalloproteinases: they´re not just for matrix anymore. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:534–540
Mackay CR (2001) Chemokines: immunology’s high impact factors. Nat Immunol 2:95–101
Schier AF (2003) Chemokine signaling: rules of attraction. Curr Biol 13:R192–R194
Youngs SJ, Ali SA, Taub DD et al (1997) Chemokines induce migrational responses in human breast carcinoma cell lines. Int J Cancer 71:257–266
Zipin-Roitman A, Meshel T, Sagi-Assif O et al (2007) CXCL10 promotes invasion-related properties in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 67:3396–3405
Burger JA, Burger M, Kipps TJ (1999) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells express functional CXCR4 chemokine receptors that mediate spontaneous migration beneath bone marrow stromal cells. Blood 94:3658–3667
Burger M, Glodek A, Hartmann T et al (2003) Functional expression of CXCR4 (CD184) on small-cell lung cancer cells mediates migration, integrin activation, and adhesion to stromal cells. Oncogene 22:8093–8101
Zeelenberg IS, Ruuls-Van Stalle L, Roos E (2003) The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is required for outgrowth of colon carcinoma micrometastases. Cancer Res 63:3833–3839
Cardones AR, Murakami T, Hwang ST (2003) CXCR4 enhances adhesion of B16 tumor cells to endothelial cells In vitro and in vivo via beta(1) integrin. Cancer Res 63:6751–6757
Dellacasagrande J, Schreurs OJ, Hofgaard PO et al (2003) Liver metastasis of cancer facilitated by chemokine receptor CCR6. Scand J Immunol 57:534–544
Kucia M, Jankowski K, Reca R et al (2004) CXCR4-SDF-1 signalling, locomotion, chemotaxis and adhesion. J Mol Histol 35:233–245
Fernandis AZ, Prasad A, Band H et al (2004) Regulation of CXCR4-mediated chemotaxis and chemoinvasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 23:157–167
Wang J, Loberg R, Taichman RS (2006) The pivotal role of CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 axis in bone metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25:573–587
Wiley HE, Gonzalez EB, Maki W et al (2001) Expression of CC chemokine receptor-7 and regional lymph node metastasis of B16 murine melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:1638–1643
Pelletier AJ, van der Laan LJ, Hildbrand P et al (2000) Presentation of chemokine SDF-1 alpha by fibronectin mediates directed migration of T cells. Blood 96:2682–2690
McNeel DG, Eickhoff J, Lee FT et al (2005) Phase I trial of a monoclonal antibody specific for alphavbeta3 integrin (MEDI-522) in patients with advanced malignancies, including an assessment of effect on tumor perfusion. Clin Cancer Res 11:7851–7860
Ishida T, Ueda R (2006) CCR4 as a novel molecular target for immunotherapy of cancer. Cancer Sci 97:1139–1146
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gassmann, P., Haier, J. The tumor cell–host organ interface in the early onset of metastatic organ colonisation. Clin Exp Metastasis 25, 171–181 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-007-9130-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-007-9130-6