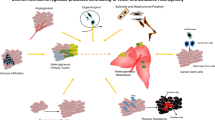
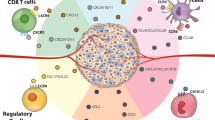
Abstract
Cancer metastasis results from a non-random process, in which organ selectivity by the tumor cells is largely determined by factors that are expressed at the remote organs that eventually turn into preferred sites of metastasis formation. These factors support the consecutive steps required for metastasis formation, including tumor cell adhesion to microvessel walls, extravasation into target tissue and migration. Of the different components that regulate organ selectivity, instrumental roles were recently attributed to chemokines and their receptors. The present review presents the rationale standing behind the first studies looking at the potential involvement of chemokine-related components in organ selectivity. Based on these studies and many others that followed, the current paradigm is that chemokines that are expressed at specific organs determine to large extent organ specificity by promoting tumor cell adhesion to microvessel walls, by facilitating processes of extravasation into the target tissue and by inducing tumor cell migration. Moreover, chemokines can possibly support additional steps that are required for “successful” establishment of metastases, such as tumor cell proliferation and survival. The review focuses on the CXCL12–CXCR4 pair as the role model in our current understanding of chemokine involvement in organ selectivity. This review also describes the prominent roles played by CCR7 and its corresponding chemokine ligands (CCL21, CCL19) in lymph node metastasis, and of the CCR10–CCL27 axis in melanoma skin survival and metastasis. Overall, the present discussion describes chemokines as important constituents of the tumor microenvironment at metastatic sites, dictating directionality of chemokine receptor-expressing tumor cells, facilitating their adhesion and extravasation, and eventually contributing to organ selectivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fidler IJ (2002) Critical determinants of metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol 12:89–96
Fidler IJ (2002) The organ microenvironment and cancer metastasis. Differentiation 70:498–505
Liotta LA (2001) An attractive force in metastasis. Nature 410:24–25
Park CC, Bissell MJ, Barcellos-Hoff MH (2000) The influence of the microenvironment on the malignant phenotype. Mol Med Today 6:324–329
Liotta LA, Kohn EC (2001) The microenvironment of the tumour-host interface. Nature 411:375–379
Witz IP (2001) Presence and functions of immune components in the tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol 495:317–324
Witz IP, Levy-Nissenbaum O (2006) The tumor microenvironment in the post-PAGET era. Cancer Lett 242:1–10
Ben-Baruch A (2006) The multifaceted roles of chemokines in malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25:357–371
Ben-Baruch A (2006) Inflammation-associated immune suppression in cancer: the roles played by cytokines, chemokines and additional mediators. Semin Cancer Biol 16:38–52
Balkwill F (2004) The significance of cancer cell expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Semin Cancer Biol 14:171–179
Balkwill F (2004) Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer 4:540–550
Craig MJ, Loberg RD (2006) CCL2 (Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1) in cancer bone metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25:611–619
Ben-Baruch A (2006) Pro-malignancy and putative anti-malignancy chemokines in the regulation of breast cancer progression. Nova Science Publishers
Kakinuma T, Hwang ST (2006) Chemokines, chemokine receptors, and cancer metastasis. J Leukoc Biol 79:639–651
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sozzani S, Vecchi A, Locati M, Sica A (2004) Chemokines in the recruitment and shaping of the leukocyte infiltrate of tumors. Semin Cancer Biol 14:155–160
Conti I, Rollins BJ (2004) CCL2 (monocyte chemoattractant protein-1) and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 14:149–154
Zlotnik A (2006) Involvement of chemokine receptors in organ-specific metastasis. Contrib Microbiol 13:191–199
Zlotnik A (2004) Chemokines in neoplastic progression. Semin Cancer Biol 14:181–185
Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Mestas J, Gomperts B, Keane MP, Belperio JA (2006) Cancer CXC chemokine networks and tumour angiogenesis. Eur J Cancer 42:768–778
Homey B, Muller A, Zlotnik A (2002) Chemokines: agents for the immunotherapy of cancer? Nat Rev Immunol 2:175–184
Salcedo R, Oppenheim JJ (2003) Role of chemokines in angiogenesis: CXCL12/SDF-1 and CXCR4 interaction, a key regulator of endothelial cell responses. Microcirculation 10:359–370
Vicari AP, Caux C (2002) Chemokines in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13:143–154
Murphy PM, Baggiolini M, Charo IF, Hebert CA, Horuk R, Matsushima K, Miller LH, Oppenheim JJ, Power CA (2000) International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for chemokine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 52:145–176
Locati M, Otero K, Schioppa T, Signorelli P, Perrier P, Baviera S, Sozzani S, Mantovani A (2002) The chemokine system: tuning and shaping by regulation of receptor expression and coupling in polarized responses. Allergy 57:972–982
Rot A, von Andrian UH (2004) Chemokines in innate and adaptive host defense: basic chemokinese grammar for immune cells. Annu Rev Immunol 22:891–928
Zlotnik A, Yoshie O (2000) Chemokines: a new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity 12:121–127
Belperio JA, Keane MP, Arenberg DA, Addison CL, Ehlert JE, Burdick MD, Strieter RM (2000) CXC chemokines in angiogenesis. J Leukoc Biol 68:1–8
Strieter RM, Belperio JA, Phillips RJ, Keane MP (2004) CXC chemokines in angiogenesis of cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 14:195–200
Zlotnik A, Yoshie O, Nomiyama H (2006) The chemokine and chemokine receptor superfamilies and their molecular evolution. Genome Biol 7:243
Sallusto F, Mackay CR, Lanzavecchia A (2000) The role of chemokine receptors in primary, effector, and memory immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 18:593–620
Cyster JG (2000) Leukocyte migration: scent of the T zone. Curr Biol 10:R30–R33
Kim CH, Broxmeyer HE (1999) Chemokines: signal lamps for trafficking of T and B cells for development and effector function. J Leukoc Biol 65:6–15
Bacon K, Baggiolini M, Broxmeyer H, Horuk R, Lindley I, Mantovani A, Maysushima K, Murphy P, Nomiyama H, Oppenheim J, Rot A, Schall T, Tsang M, Thorpe R, Van Damme J, Wadhwa M, Yoshie O, Zlotnik A, Zoon K (2002) Chemokine/chemokine receptor nomenclature. J Interferon Cytokine Res 22:1067–1068
Devalaraja MN, Richmond A (1999) Multiple chemotactic factors: fine control or redundancy?. Trends Pharmacol Sci 20:151–156
Mantovani A (1999) The chemokine system: redundancy for robust outputs. Immunol Today 20:254–257
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME, McClanahan T, Murphy E, Yuan W, Wagner SN, Barrera JL, Mohar A, Verastegui E, Zlotnik A (2001) Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 410:50–56
Lapidot T (2001) Mechanism of human stem cell migration and repopulation of NOD/SCID and B2mnull NOD/SCID mice. The role of SDF-1/CXCR4 interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 938:83–95
Nagasawa T (2000) A chemokine, SDF-1/PBSF, and its receptor, CXC chemokine receptor 4, as mediators of hematopoiesis. Int J Hematol 72:408–411
Zou YR, Kottmann AH, Kuroda M, Taniuchi I, Littman DR (1998) Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in haematopoiesis and in cerebellar development. Nature 393:595–599
Mohle R, Bautz F, Rafii S, Moore MA, Brugger W, Kanz L (1998) The chemokine receptor CXCR-4 is expressed on CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors and leukemic cells and mediates transendothelial migration induced by stromal cell-derived factor-1. Blood 91:4523–4530
Peled A, Petit I, Kollet O, Magid M, Ponomaryov T, Byk T, Nagler A, Ben-Hur H, Many A, Shultz L, Lider O, Alon R, Zipori D, Lapidot T (1999) Dependence of human stem cell engraftment and repopulation of NOD/SCID mice on CXCR4. Science 283:845–848
Ratajczak MZ, Zuba-Surma E, Kucia M, Reca R, Wojakowski W, Ratajczak J (2006) The pleiotropic effects of the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis in organogenesis, regeneration and tumorigenesis. Leukemia 20:1915–1924
Luker KE, Luker GD (2006) Functions of CXCL12 and CXCR4 in breast cancer. Cancer Lett 238:30–41
Wang J, Loberg R, Taichman RS (2006) The pivotal role of CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 axis in bone metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25:573–587
Dewan MZ, Ahmed S, Iwasaki Y, Ohba K, Toi M, Yamamoto N (2006) Stromal cell-derived factor-1 and CXCR4 receptor interaction in tumor growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 60:273–276
Burger JA, Kipps TJ (2006) CXCR4: a key receptor in the crosstalk between tumor cells and their microenvironment. Blood 107:1761–1767
Epstein RJ (2004) The CXCL12-CXCR4 chemotactic pathway as a target of adjuvant breast cancer therapies. Nat Rev Cancer 4:901–909
Su YC, Wu MT, Huang CJ, Hou MF, Yang SF, Chai CY (2006) Expression of CXCR4 is associated with axillary lymph node status in patients with early breast cancer. Breast 15:533–539
Cabioglu N, Sahin A, Doucet M, Yavuz E, Igci A, Engin OY, Aktas E, Bilgic S, Kiran B, Deniz G, Price JE (2005) Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in breast cancer as a potential predictive marker of isolated tumor cells in bone marrow. Clin Exp Metastasis 22:39–46
Salvucci O, Bouchard A, Baccarelli A, Deschenes J, Sauter G, Simon R, Bianchi R, Basik M (2006). The role of CXCR4 receptor expression in breast cancer: a large tissue microarray study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 97:275–283
Cabioglu N, Yazici MS, Arun B, Broglio KR, Hortobagyi GN, Price JE, Sahin A (2005) CCR7 and CXCR4 as novel biomarkers predicting axillary lymph node metastasis in T1 breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:5686–5693
Kato M, Kitayama J, Kazama S, Nagawa H (2003) Expression pattern of CXC chemokine receptor-4 is correlated with lymph node metastasis in human invasive ductal carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res 5:R144–R150
Hao L, Zhang C, Qiu Y, Wang L, Luo Y, Jin M, Zhang Y, Guo TB, Matsushima K (2007) Recombination of CXCR4, VEGF, and MMP-9 predicting lymph node metastasis in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett 253:34–42
Schmid BC, Rudas M, Rezniczek GA, Leodolter S, Zeillinger R (2004) CXCR4 is expressed in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast and in atypical ductal hyperplasia. Breast Cancer Res Treat 84:247–250
Kang H, Watkins G, Douglas-Jones A, Mansel RE, Jiang WG (2005) The elevated level of CXCR4 is correlated with nodal metastasis of human breast cancer. Breast 14:360–367
Liang Z, Wu T, Lou H, Yu X, Taichman RS, Lau SK, Nie S, Umbreit J, Shim H (2004) Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by selective synthetic polypeptide against CXCR4. Cancer Res 64:4302–4308
Shim H, Lau SK, Devi S, Yoon Y, Cho HT, Liang Z (2006) Lower expression of CXCR4 in lymph node metastases than in primary breast cancers: potential regulation by ligand-dependent degradation and HIF-1alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346:252–258
Andre F, Cabioglu N, Assi H, Sabourin JC, Delaloge S, Sahin A, Broglio K, Spano JP, Combadiere C, Bucana C, Soria JC, Cristofanilli M (2006) Expression of chemokine receptors predicts the site of metastatic relapse in patients with axillary node positive primary breast cancer. Ann Oncol 17:945–951
Tamamura H, Hori A, Kanzaki N, Hiramatsu K, Mizumoto M, Nakashima H, Yamamoto N, Otaka A, Fujii N (2003) T140 analogs as CXCR4 antagonists identified as anti-metastatic agents in the treatment of breast cancer. FEBS Lett 550:79–83
Lapteva N, Yang AG, Sanders DE, Strube RW, Chen SY (2005) CXCR4 knockdown by small interfering RNA abrogates breast tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther 12:84–89
Smith MC, Luker KE, Garbow JR, Prior JL, Jackson E, Piwnica-Worms D, Luker GD (2004) CXCR4 regulates growth of both primary and metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res 64:8604–8612
Liang Z, Yoon Y, Votaw J, Goodman MM, Williams L, Shim H (2005) Silencing of CXCR4 blocks breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 65:967–971
Li YM, Pan Y, Wei Y, Cheng X, Zhou BP, Tan M, Zhou X, Xia W, Hortobagyi GN, Yu D, Hung MC (2004) Upregulation of CXCR4 is essential for HER2-mediated tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell 6:459–469
Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, Carey VJ, Richardson AL, Weinberg RA (2005) Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell 121:335–348
Helbig G, Christopherson KW 2nd, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Kumar S, Kishimoto H, Miller KD, Broxmeyer HE, Nakshatri H (2003) NF-kappaB promotes breast cancer cell migration and metastasis by inducing the expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. J Biol Chem 278:21631–21638
Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, Drobnjak M, Kakonen SM, Cordon-Cardo C, Guise TA, Massague J (2003) A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell 3:537–549
Rahman KM, Sarkar FH, Banerjee S, Wang Z, Liao DJ, Hong X, Sarkar NH (2006) Therapeutic intervention of experimental breast cancer bone metastasis by indole-3-carbinol in SCID-human mouse model. Mol Cancer Ther 5:2747–2756
Chen Y, Stamatoyannopoulos G, Song CZ (2003) Down-regulation of CXCR4 by inducible small interfering RNA inhibits breast cancer cell invasion in vitro. Cancer Res 63:4801–4804
Sun R, Gao P, Chen L, Ma D, Wang J, Oppenheim JJ, Zhang N (2005) Protein kinase C zeta is required for epidermal growth factor-induced chemotaxis of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 65:1433–1441
Lechertier T, Berard M, Vassy R, Herve MA, Crepin M (2004) Transendothelial migration of two metastatic breast carcinoma cells depend on the SDF-lalpha-CXCR4 complexes. Anticancer Res 24:4011–4017
Lee BC, Lee TH, Avraham S, Avraham HK (2004) Involvement of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its ligand stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha in breast cancer cell migration through human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res 2:327–338
Bachelder RE, Wendt MA, Mercurio AM (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes breast carcinoma invasion in an autocrine manner by regulating the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Cancer Res 62:7203–7206
Chen X, Beutler JA, McCloud TG, Loehfelm A, Yang L, Dong HF, Chertov OY, Salcedo R, Oppenheim JJ, Howard OM (2003) Tannic acid is an inhibitor of CXCL12 (SDF-1alpha)/CXCR4 with antiangiogenic activity. Clin Cancer Res 9:3115–3123
Prasad A, Fernandis AZ, Rao Y, Ganju RK (2004) Slit protein-mediated inhibition of CXCR4-induced chemotactic and chemoinvasive signaling pathways in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 279:9115–9124
Fernandis AZ, Prasad A, Band H, Klosel R, Ganju RK (2004) Regulation of CXCR4-mediated chemotaxis and chemoinvasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 23:157–167
Denoyelle C, Hong L, Vannier JP, Soria J, Soria C (2003) New insights into the actions of bisphosphonate zoledronic acid in breast cancer cells by dual RhoA-dependent and -independent effects. Br J Cancer 88:1631–1640
Grimshaw MJ, Hagemann T, Ayhan A, Gillett CE, Binder C, Balkwill FR (2004) A role for endothelin-2 and its receptors in breast tumor cell invasion. Cancer Res 64:2461–2468
Kang H, Watkins G, Parr C, Douglas-Jones A, Mansel RE, Jiang WG (2005) Stromal cell derived factor-1: its influence on invasiveness and migration of breast cancer cells in vitro, and its association with prognosis and survival in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 7:R402–R410
Lee BC, Lee TH, Zagozdzon R, Avraham S, Usheva A, Avraham HK (2005) Carboxyl-terminal Src kinase homologous kinase negatively regulates the chemokine receptor CXCR4 through YY1 and impairs CXCR4/CXCL12 (SDF-1alpha)-mediated breast cancer cell migration. Cancer Res 65:2840–2845
Kishimoto H, Wang Z, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Chang D, Clarke R, Nakshatri H (2005) The p160 family coactivators regulate breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion through autocrine/paracrine activity of SDF-1alpha/CXCL12. Carcinogenesis 26:1706–1715
Cabioglu N, Summy J, Miller C, Parikh NU, Sahin AA, Tuzlali S, Pumiglia K, Gallick GE, Price JE (2005) CXCL-12/stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha transactivates HER2-neu in breast cancer cells by a novel pathway involving Src kinase activation. Cancer Res 65:6493–6497
Matteucci E, Locati M, Desiderio MA (2005) Hepatocyte growth factor enhances CXCR4 expression favoring breast cancer cell invasiveness. Exp Cell Res 310:176–185
Akekawatchai C, Holland JD, Kochetkova M, Wallace JC, McColl SR (2005) Transactivation of CXCR4 by the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) in human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 280:39701–39708
Schabath H, Runz SR, Joumaa S, Altevogt P (2006) CD24 affects CXCR4 function in pre-B lymphocytes and breast carcinoma cells. J Cell Sci 119:314–325
Ueda Y, Neel NF, Schutyser E, Raman D, Richmond A (2006) Deletion of the COOH-terminal domain of CXC chemokine receptor 4 leads to the down-regulation of cell-to-cell contact, enhanced motility and proliferation in breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 66:5665–5675
Mehta SA, Christopherson KW, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Goulet RJ Jr, Broxmeyer HE, Kopelovich L, Nakshatri H (2007) Negative regulation of chemokine receptor CXCR4 by tumor suppressor p53 in breast cancer cells: implications of p53 mutation or isoform expression on breast cancer cell invasion. Oncogene 26:3329–3337
Hsu EL, Yoon D, Choi HH, Wang F, Taylor RT, Chen N, Zhang R, Hankinson O (2007) A proposed mechanism for the protective effect of dioxin against breast cancer. Toxicol Sci 98:436–444
Janowska-Wieczorek A, Marquez-Curtis LA, Wysoczynski M, Ratajczak MZ (2006) Enhancing effect of platelet-derived microvesicles on the invasive potential of breast cancer cells. Transfusion 46:1199–1209
Hall JM, Korach KS (2003) Stromal cell-derived factor 1, a novel target of estrogen receptor action, mediates the mitogenic effects of estradiol in ovarian and breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 17:792–803
Kang H, Mansel RE, Jiang WG (2005) Genetic manipulation of stromal cell-derived factor-1 attests the pivotal role of the autocrine SDF-1-CXCR4 pathway in the aggressiveness of breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol 26:1429–1434
Hartmann TN, Burger JA, Glodek A, Fujii N, Burger M (2005) CXCR4 chemokine receptor and integrin signaling co-operate in mediating adhesion and chemoresistance in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cells. Oncogene 24:4462–4471
Holland JD, Kochetkova M, Akekawatchai C, Dottore M, Lopez A, McColl SR (2006) Differential functional activation of chemokine receptor CXCR4 is mediated by G proteins in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:4117–4124
Zhu ZB, Makhija SK, Lu B, Wang M, Kaliberova L, Liu B, Rivera AA, Nettelbeck DM, Mahasreshti PJ, Leath CA 3rd, Yamaoto M, Alvarez RD, Curiel DT (2004) Transcriptional targeting of adenoviral vector through the CXCR4 tumor-specific promoter. Gene Ther 11:645–648
Stoff-Khalili MA, Stoff A, Rivera AA, Banerjee NS, Everts M, Young S, Siegal GP, Richter DF, Wang M, Dall P, Mathis JM, Zhu ZB, Curiel DT (2005) Preclinical evaluation of transcriptional targeting strategies for carcinoma of the breast in a tissue slice model system. Breast Cancer Res 7:R1141–R1152
Maroni P, Bendinelli P, Matteucci E, Desiderio MA (2007) HGF induces CXCR4 and CXCL12-mediated tumor invasion through Ets1 and NF-kappaB. Carcinogenesis 28:267–279
Moskovits N, Kalinkovich A, Bar J, Lapidot T, Oren M (2006) p53 Attenuates cancer cell migration and invasion through repression of SDF-1/CXCL12 expression in stromal fibroblasts. Cancer Res 66:10671–10676
Dallol A, Da Silva NF, Viacava P, Minna JD, Bieche I, Maher ER, Latif F (2002) SLIT2, a human homologue of the Drosophila Slit2 gene, has tumor suppressor activity and is frequently inactivated in lung and breast cancers. Cancer Res 62:5874–5880
Grimshaw MJ, Naylor S, Balkwill FR (2002) Endothelin-2 is a hypoxia-induced autocrine survival factor for breast tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther 1:1273–1281
Gunn MD, Tangemann K, Tam C, Cyster JG, Rosen SD, Williams LT (1998) A chemokine expressed in lymphoid high endothelial venules promotes the adhesion and chemotaxis of naive T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:258–263
Saeki H, Moore AM, Brown MJ, Hwang ST (1999) Cutting edge: secondary lymphoid-tissue chemokine (SLC) and CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) participate in the emigration pathway of mature dendritic cells from the skin to regional lymph nodes. J Immunol 162:2472–2475
Gunn MD (2003) Chemokine mediated control of dendritic cell migration and function. Semin Immunol 15:271–276
Cabioglu N, Gong Y, Islam R, Broglio K, Sneige N, Sahin A, Gonzalez-Angulo A, Morandi P, Bucana C, Hortobagyi G, Cristofanilli M (2007) Expression of growth factor and chemokine receptors: new insights in the biology of inflammatory breast cancer. Ann Oncol 18:1021–1029
Kodama J, Hasengaowa, Kusumoto T, Seki N, Matsuo T, Ojima Y, Nakamura K, Hongo A, Hiramatsu Y (2007) Association of CXCR4 and CCR7 chemokine receptor expression and lymph node metastasis in human cervical cancer. Ann Oncol 18:70–76
Wilson JL, Burchell J, Grimshaw MJ (2006) Endothelins induce CCR7 expression by breast tumor cells via endothelin receptor A and hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Cancer Res 66:11802–11807
Takeuchi H, Fujimoto A, Tanaka M, Yamano T, Hsueh E, Hoon DS (2004) CCL21 chemokine regulates chemokine receptor CCR7 bearing malignant melanoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 10:2351–2358
Gunther K, Leier J, Henning G, Dimmler A, Weissbach R, Hohenberger W, Forster R (2005) Prediction of lymph node metastasis in colorectal carcinoma by expressionof chemokine receptor CCR7. Int J Cancer 116:726–733
Yan C, Zhu ZG, Yu YY, Ji J, Zhang Y, Ji YB, Yan M, Chen J, Liu BY, Yin HR, Lin YZ (2004) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor C and chemokine receptor CCR7 in gastric carcinoma and their values in predicting lymph node metastasis. World J Gastroenterol 10:783–790
Mashino K, Sadanaga N, Yamaguchi H, Tanaka F, Ohta M, Shibuta K, Inoue H, Mori M (2002) Expression of chemokine receptor CCR7 is associated with lymph node metastasis of gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res 62:2937–2941
Tsuzuki H, Takahashi N, Kojima A, Narita N, Sunaga H, Takabayashi T, Fujieda S (2006) Oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas expressing CCR7 have poor prognoses. Auris Nasus Larynx 33:37–42
Ding Y, Shimada Y, Maeda M, Kawabe A, Kaganoi J, Komoto I, Hashimoto Y, Miyake M, Hashida H, Imamura M (2003) Association of CC chemokine receptor 7 with lymph node metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 9:3406–3412
Takanami I (2003) Overexpression of CCR7 mRNA in nonsmall cell lung cancer: correlation with lymph node metastasis. Int J Cancer 105:186–189
Hasegawa H, Nomura T, Kohno M, Tateishi N, Suzuki Y, Maeda N, Fujisawa R, Yoshie O, Fujita S (2000) Increased chemokine receptor CCR7/EBI1 expression enhances the infiltration of lymphoid organs by adult T-cell leukemia cells. Blood 95:30–38
Till KJ, Lin K, Zuzel M, Cawley JC (2002) The chemokine receptor CCR7 and alpha4 integrin are important for migration of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells into lymph nodes. Blood 99:2977–2984
Wiley HE, Gonzalez EB, Maki W, Wu MT, Hwang ST (2001) Expression of CC chemokine receptor-7 and regional lymph node metastasis of B16 murine melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:1638–1643
Wang J, Xi L, Hunt JL, Gooding W, Whiteside TL, Chen Z, Godfrey TE, Ferris RL (2004) Expression pattern of chemokine receptor 6 (CCR6) and CCR7 in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck identifies a novel metastatic phenotype. Cancer Res 64:1861–1866
Koizumi K, Kozawa Y, Ohashi Y, Nakamura ES, Aozuka Y, Sakurai H, Ichiki K, Doki Y, Misaki T, Saiki I (2007) CCL21 promotes the migration and adhesion of highly lymph node metastatic human non-small cell lung cancer Lu-99 in vitro. Oncol Rep 17:1511–1516
Sancho M, Vieira JM, Casalou C, Mesquita M, Pereira T, Cavaco BM, Dias S, Leite V (2006) Expression and function of the chemokine receptor CCR7 in thyroid carcinomas. J Endocrinol 191:229–238
Shields JD, Fleury ME, Yong C, Tomei AA, Randolph GJ, Swartz MA (2007) Autologous chemotaxis as a mechanism of tumor cell homing to lymphatics via interstitial flow and autocrine CCR7 signaling. Cancer Cell 11:526–538
Vicari AP, Treilleux I, Lebecque S (2004) Regulation of the trafficking of tumour-infiltrating dendritic cells by chemokines. Semin Cancer Biol 14:161–169
Homey B, Wang W, Soto H, Buchanan ME, Wiesenborn A, Catron D, Muller A, McClanahan TK, Dieu-Nosjean MC, Orozco R, Ruzicka T, Lehmann P, Oldham E, Zlotnik A (2000) Cutting edge: the orphan chemokine receptor G protein-coupled receptor-2 (GPR-2, CCR10) binds the skin-associated chemokine CCL27 (CTACK/ALP/ILC). J Immunol 164:3465–3470
Morales J, Homey B, Vicari AP, Hudak S, Oldham E, Hedrick J, Orozco R, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, McEvoy LM, Zlotnik A (1999) CTACK, a skin-associated chemokine that preferentially attracts skin-homing memory T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14470–14475
Simonetti O, Goteri G, Lucarini G, Filosa A, Pieramici T, Rubini C, Biagini G, Offidani A (2006) Potential role of CCL27 and CCR10 expression in melanoma progression and immune escape. Eur J Cancer 42:1181–1187
Murakami T, Cardones AR, Finkelstein SE, Restifo NP, Klaunberg BA, Nestle FO, Castillo SS, Dennis PA, Hwang ST (2003) Immune evasion by murine melanoma mediated through CC chemokine receptor-10. J Exp Med 198:1337–1347
Murakami T, Cardones AR, Hwang ST (2004) Chemokine receptors and melanoma metastasis. J Dermatol Sci 36:71–78
Dellacasagrande J, Schreurs OJ, Hofgaard PO, Omholt H, Steinsvoll S, Schenck K, Bogen B, Dembic Z (2003) Liver metastasis of cancer facilitated by chemokine receptor CCR6. Scand J Immunol 57:534–544
Bendre MS, Gaddy-Kurten D, Mon-Foote T, Akel NS, Skinner RA, Nicholas RW, Suva LJ (2002) Expression of interleukin 8 and not parathyroid hormone-related protein by human breast cancer cells correlates with bone metastasis in vivo. Cancer Res 62:5571–5579
Bendre MS, Montague DC, Peery T, Akel NS, Gaddy D, Suva LJ (2003) Interleukin-8 stimulation of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption is a mechanism for the increased osteolysis of metastatic bone disease. Bone 33:28–37
Valentin G, Haas P, Gilmour D (2007) The chemokine SDF1a coordinates tissue migration through the spatially restricted activation of Cxcr7 and Cxcr4b. Curr Biol 17:1026–1031
Burns JM, Summers BC, Wang Y, Melikian A, Berahovich R, Miao Z, Penfold ME, Sunshine MJ, Littman DR, Kuo CJ, Wei K, McMaster BE, Wright K, Howard MC, Schall TJ (2006) A novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in cell survival, cell adhesion, and tumor development. J Exp Med 203:2201–2213
Tachibana K, Hirota S, Iizasa H, Yoshida H, Kawabata K, Kataoka Y, Kitamura Y, Matsushima K, Yoshida K, Nishikawa S, Kishimoto T, Nagasawa T (1998) The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is essential for vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract. Nature 393:591–594
Lazarini F, Tham TN, Casanova P, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Dubois-Dalcq M (2003). Role of the alpha-chemokine stromal cell-derived factor (SDF-1) in the developing and mature central nervous system. Glia 42:139–148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Baruch, A. Organ selectivity in metastasis: regulation by chemokines and their receptors. Clin Exp Metastasis 25, 345–356 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-007-9097-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-007-9097-3