Abstract
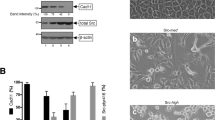
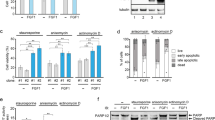
Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (RhoGDIs) regulate the activity of Rho family GTPases. RhoGDIβ (LyGDI/GDID4/RhoGDI2) has two caspase cleavage sites after Asp19 and Asp55. The resulting cleavage products, ΔN(1–19)RhoGDIβ and ΔN(1–55)RhoGDIβ, are expressed in cells under conditions that activate caspases. ΔN(1–19)RhoGDIβ, which can inhibit GDP dissociation, is implicated in the process of apoptosis, whereas the physiological roles for ΔN(1–55)RhoGDIβ, which lacks the ability to inhibit GDP dissociation, are largely unknown. To explore the roles of ΔN(1–55)RhoGDIβ, we examined the phenotypes of v-src-transformed metastatic fibroblasts transfected with plasmids for expressing ΔN(1–55)RhoGDIβ. Although the expression of ΔN(1–55)RhoGDIβ had no effect on the rate of growth in vitro, it suppressed experimental metastasis and decreased the rate of growth in vivo. In addition, ΔN(1–55)RhoGDIβ-expressing cells had enhanced adhesion to fibronectin, laminin, and collagens but reduced retention in the lung after intravenous injection. Also, the expression of ΔN(1–55)RhoGDIβ promoted anoikis without affecting the levels of activated Rac1 or Cdc42. Furthermore, ΔN(1–55)RhoGDIβ did not affect the expression or phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase, p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinases, or Akt1 before or after induction of anoikis. Thus, ΔN(1–55)RhoGDIβ appears to promote anoikis by undefined mechanisms, thereby suppressing metastasis in v-src-transformed fibroblasts.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- EMEM:
-
Eagle’s minimum essential medium
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- FAK:
-
Focal adhesion kinase
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- HBSS:
-
Hanks’ balanced salt solution
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PAK1:
-
p21/Cdc42/Rac1-activated kinase 1
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- RhoGDI:
-
Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor
- RhoGEF:
-
Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
References
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A (2002) Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 420(6916):629–635
Ueda T, Kikuchi A, Ohga N, Yamamoto J, Takai Y (1990) Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of a novel regulatory protein inhibiting the dissociation of GDP from and the subsequent binding of GTP to rhoB p20, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem 265(16):9373–9380
Takahashi K, Sasaki T, Mammoto A, Takaishi K, Kameyama T, Tsukita S, Takai Y (1997) Direct interaction of the Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor with ezrin/radixin/moesin initiates the activation of the Rho small G protein. J Biol Chem 272(37):23371–23375
Del Pozo MA, Kiosses WB, Alderson NB, Meller N, Hahn KM, Schwartz MA, Takebe H (2002) Integrins regulate GTP-Rac localized effector interactions through dissociation of Rho-GDI. Nat Cell Biol 4(3):232–239
Lelias JM, Adra CN, Wulf GM, Guillemot JC, Khagad M, Caput D, Lim B (1993) cDNA cloning of a human mRNA preferentially expressed in hematopoietic cells and with homology to a GDP-dissociation inhibitor for the rho GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(4):1479–1483
Leffers H, Nielsen MS, Andersen AH, Honore B, Madsen P, Vandekerckhove J, Celis JE (1993) Identification of two human Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor proteins whose overexpression leads to disruption of the actin cytoskeleton. Exp Cell Res 209(2):165–174
Ota T, Maeda M, Suto S, Tatsuka M (2004) LyGDI functions in cancer metastasis by anchoring Rho proteins to the cell membrane. Mol Carcinog 39(4):206–220
Danley DE, Chuang TH, Bokoch GM (1996) Defective Rho GTPase regulation by IL-1 beta-converting enzyme-mediated cleavage of D4 GDP dissociation inhibitor. J Immunol 157(2):500–503
Zhou X, Suto S, Ota T, Tatsuka M (2004) Nuclear translocation of cleaved LyGDI dissociated from Rho and Rac during Trp53-dependent ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis of thymus cells in vitro. Radiat Res 162(3):287–295
Na S, Chuang TH, Cunningham A, Turi TG, Hanke JH, Bokoch GM, Danley DE (1996) D4-GDI, a substrate of CPP32, is proteolyzed during Fas-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 271(19):11209–11213
Rickers A, Brockstedt E, Mapara MY, Otto A, Dorken B, Bommert K (1998) Inhibition of CPP32 blocks surface IgM-mediated apoptosis and D4-GDI cleavage in human BL60 Burkitt lymphoma cells [published erratum appears in Eur J Immunol 1998 Mar; 28(3):1122]. Eur J Immunol 28(1):296–304
Kettritz R, Xu YX, Faass B, Klein JB, Muller EC, Otto A, Busjahn A, Luft FC, Haller H (2000) TNF-alpha-mediated neutrophil apoptosis involves Ly-GDI, a Rho GTPase regulator. J Leukoc Biol 68(2):277–283
Krieser RJ, Eastman A (1999) Cleavage and nuclear translocation of the caspase 3 substrate Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor, D4-GDI, during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6(5):412–419
Essmann F, Wieder T, Otto A, Muller EC, Dorken B, Daniel PT (2000) GDP dissociation inhibitor D4-GDI (Rho-GDI 2), but not the homologous rho-GDI 1, is cleaved by caspase-3 during drug-induced apoptosis. Biochem J 346(Pt 3):777–783
Thiede B, Siejak F, Dimmler C, Rudel T (2002) Prediction of translocation and cleavage of heterogeneous ribonuclear proteins and Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor 2 during apoptosis by subcellular proteome analysis. Proteomics 2(8):996–1006
Tatsuka M, Ota T, Maeda M, Wada M, Yamagishi N, Taniguchi S, Seiki M, Odashima S (1997) A BALB/c 3T3-transformed cell line suitable for transfection assay of metastasis-inducing genes. Int J Cancer 71(1):88–93
Jiang WG, Watkins G, Lane J, Cunnick GH, Douglas-Jones A, Mokbel K, Mansel RE (2003) Prognostic value of rho GTPases and rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors in human breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res 9(17):6432–6440
Seraj MJ, Harding MA, Gildea JJ, Welch DR, Theodorescu D (2000) The relationship of BRMS1 and RhoGDI2 gene expression to metastatic potential in lineage related human bladder cancer cell lines. Clin Exp Metastasis 18(6):519–525
Tapper J, Kettunen E, El-Rifai W, Seppala M, Andersson LC, Knuutila S (2001) Changes in gene expression during progression of ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 128(1):1–6
Yanagawa T, Watanabe H, Takeuchi T, Fujimoto S, Kurihara H, Takagishi K (2004) Overexpression of autocrine motility factor in metastatic tumor cells: possible association with augmented expression of KIF3A and GDI-beta. Lab Invest 84(4):513–522
Gildea JJ, Seraj MJ, Oxford G, Harding MA, Hampton GM, Moskaluk CA, Frierson HF, Conaway MR, Theodorescu D (2002) RhoGDI2 is an invasion and metastasis suppressor gene in human cancer. Cancer Res 62(22):6418–6423
Keep NH, Barnes M, Barsukov I, Badii R, Lian LY, Segal AW, Moody PC, Roberts GC (1997) A modulator of rho family G proteins, rhoGDI, binds these G proteins via an immunoglobulin-like domain and a flexible N-terminal arm. Structure 5(5):623–633
Gosser YQ, Nomanbhoy TK, Aghazadeh B, Manor D, Combs C, Cerione RA, Rosen MK (1997) C-terminal binding domain of Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor directs N-terminal inhibitory peptide to GTPases. Nature 387(6635):814–819
Longenecker K, Read P, Derewenda U, Dauter Z, Liu X, Garrard S, Walker L, Somlyo AV, Nakamoto RK, Somlyo AP, Derewenda ZS (1999) How RhoGDI binds Rho. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 55(Pt 9):1503–1515
Hoffman GR, Nassar N, Cerione RA (2000) Structure of the Rho family GTP-binding protein Cdc42 in complex with the multifunctional regulator RhoGDI. Cell 100(3):345–356
Scheffzek K, Stephan I, Jensen ON, Illenberger D, Gierschik P (2000) The Rac–RhoGDI complex and the structural basis for the regulation of Rho proteins by RhoGDI. Nat Struct Biol 7(2):122–126
Lian LY, Barsukov I, Golovanov AP, Hawkins DI, Badii R, Sze KH, Keep NH, Bokoch GM, Roberts GC (2000) Mapping the binding site for the GTP-binding protein Rac-1 on its inhibitor RhoGDI-1. Struct Fold Des 8(1):47–55
Golovanov AP, Chuang TH, DerMardirossian C, Barsukov I, Hawkins D, Badii R, Bokoch GM, Lian LY, Roberts GC (2001) Structure–activity relationships in flexible protein domains: regulation of rho GTPases by RhoGDI and D4 GDI. J Mol Biol 305(1):121–135
Kakunaga T, Crow JD (1980) Cell variants showing differential susceptibility to ultraviolet light-induced transformation. Science 209(4455):505–507
Tatsuka M, Ota T, Yamagishi N, Kashihara Y, Wada M, Matsuda N, Mitsui H, Seiki M, Odashima S (1996) Different metastatic potentials of ras- and src-transformed BALB/c 3T3 A31 variant cells. Mol Carcinog 15(4):300–308
Terada Y, Tatsuka M, Suzuki F, Yasuda Y, Fujita S, Otsu M (1998) AIM-1: a mammalian midbody-associated protein required for cytokinesis. EMBO J 17(3):667–676
Ota T, Maeda M, Tatsuka M, Matsui T, Tanino M, Tanaka T (1999) Decrease of metastatic ability after selection for intravasating ability in Lewis lung carcinoma (3LL) cell line. Cancer Lett 139(1):105–108
Ota T, Suto S, Katayama H, Han ZB, Suzuki F, Maeda M, Tanino M, Terada Y, Tatsuka M (2002) Increased mitotic phosphorylation of histone H3 attributable to AIM-1/Aurora-B overexpression contributes to chromosome number instability. Cancer Res 62(18):5168–5177
Tatsuka M, Maeda M, Ota T (2001) Anticarcinogenic effect and enhancement of metastatic potential of BALB/c 3T3 cells by ginsenoside Rh(2). Jpn J Cancer Res 92(11):1184–1189
Yagi T, Sasayama S, Sasai H, Kakunaga T (1989) Cotransfection of plasmids with ras and myc oncogenes to diploid cells derived from rodent fetuses: alteration of neoplastic transformation frequency depending on the gestation period. Mol Carcinog 1(4):222–228
Kakunaga T (1985) Critical review of the use of established cell lines for in-vitro cell transformation. IARC Sci Publ 67:55–73
Ota T, Matsui T, Kohno H, Maeda M, Tanino M, Odashima S (1995) CD44 participates in tumor cell adhesion to endothelial cells in the experimental metastatic process in B16BL6 melanoma cells. Anticancer Res 15(4):1215–1219
Ota T, Maeda M, Tanino M, Tatsuka M (2001) Functional suppression of integrin beta 4-mediated adhesion caused by in vivo sequential selection for cancer cell intravasation. Anticancer Res 21(1A):205–211
Brunton VG, Avizienyte E, Fincham VJ, Serrels B, Metcalf CA 3rd, Sawyer TK, Frame MC (2005) Identification of Src-specific phosphorylation site on focal adhesion kinase: dissection of the role of Src SH2 and catalytic functions and their consequences for tumor cell behavior. Cancer Res 65(4):1335–1342
Schaller MD, Hildebrand JD, Shannon JD, Fox JW, Vines RR, Parsons JT (1994) Autophosphorylation of the focal adhesion kinase, pp125FAK, directs SH2-dependent binding of pp60src. Mol Cell Biol 14(3):1680–1688
Frisch SM, Ruoslahti E (1997) Integrins and anoikis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9(5):701–706
Frisch SM, Screaton RA (2001) Anoikis mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13(5):555–562
Gilmore AP (2005) Anoikis. Cell Death Differ 12(Suppl. 2):1473–1477
Zugasti O, Rul W, Roux P, Peyssonnaux C, Eychene A, Franke TF, Fort P, Hibner U (2001) Raf-MEK-Erk cascade in anoikis is controlled by Rac1 and Cdc42 via Akt. Mol Cell Biol 21(19):6706–6717
Jaffe AB, Hall A (2002) Rho GTPases in transformation and metastasis. Adv Cancer Res 84:57–80
Sahai E, Marshall CJ (2002) RHO-GTPases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2(2):133–142
Rossman KL, Der CJ, Sondek J (2005) GEF means go: turning on RHO GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(2):167–180
Schmidt A, Hall A (2002) Guanine nucleotide exchange factors for Rho GTPases: turning on the switch. Genes Dev 16(13):1587–1609
Yawata A, Adachi M, Okuda H, Naishiro Y, Takamura T, Hareyama M, Takayama S, Reed JC, Imai K (1998) Prolonged cell survival enhances peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer cells. Oncogene 16(20):2681–2686
Streuli CH, Gilmore AP (1999) Adhesion-mediated signaling in the regulation of mammary epithelial cell survival. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 4(2):183–191
Shanmugathasan M, Jothy S (2000) Apoptosis, anoikis and their relevance to the pathobiology of colon cancer. Pathol Int 50(4):273–279
McGill G, Shimamura A, Bates RC, Savage RE, Fisher DE (1997) Loss of matrix adhesion triggers rapid transformation-selective apoptosis in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 138(4):901–911
Petitclerc E, Stromblad S, von Schalscha TL, Mitjans F, Piulats J, Montgomery AM, Cheresh DA, Brooks PC (1999) Integrin alpha(v)beta3 promotes M21 melanoma growth in human skin by regulating tumor cell survival. Cancer Res 59(11):2724–2730
Diaz-Montero CM, McIntyre BW (2003) Acquisition of anoikis resistance in human osteosarcoma cells. Eur J Cancer 39(16):2395–2402
Rennebeck G, Martelli M, Kyprianou N (2005) Anoikis and survival connections in the tumor microenvironment: is there a role in prostate cancer metastasis? Cancer Res 65(24):11230–11235
Valentijn AJ, Zouq N, Gilmore AP (2004) Anoikis. Biochem Soc Trans 32(Pt 3):421–425
Cheng TL, Symons M, Jou TS (2004) Regulation of anoikis by Cdc42 and Rac1. Exp Cell Res 295(2):497–511
Loza-Coll MA, Perera S, Shi W, Filmus J (2005) A transient increase in the activity of Src-family kinases induced by cell detachment delays anoikis of intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 24(10):1727–1737
Wei L, Yang Y, Zhang X, Yu Q (2004) Altered regulation of Src upon cell detachment protects human lung adenocarcinoma cells from anoikis. Oncogene 23(56):9052–9061
Windham TC, Parikh NU, Siwak DR, Summy JM, McConkey DJ, Kraker AJ, Gallick GE (2002) Src activation regulates anoikis in human colon tumor cell lines. Oncogene 21(51):7797–7807
Frame MC (2002) Src in cancer: deregulation and consequences for cell behaviour. Biochim Biophys Acta 1602(2):114–130
Sasaki T, Takai Y (1998) The Rho small G protein family-Rho GDI system as a temporal and spatial determinant for cytoskeletal control. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 245(3):641–645
Zalcman G, Dorseuil O, Garcia-Ranea JA, Gacon G, Camonis J (1999) RhoGAPs and RhoGDIs, (His)stories of two families. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 22:85–113
Olofsson B (1999) Rho guanine dissociation inhibitors: pivotal molecules in cellular signalling. Cell Signal 11(8):545–554
DerMardirossian C, Bokoch GM (2005) GDIs: central regulatory molecules in Rho GTPase activation. Trends Cell Biol 15(7):356–363
Dovas A, Couchman JR (2005) RhoGDI: multiple functions in the regulation of Rho family GTPase activities. Biochem J 390(Pt 1):1–9
Maeda M, Matsui T, Imamura M, Tsukita S (1999) Expression level, subcellular distribution and rho-GDI binding affinity of merlin in comparison with ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins. Oncogene 18(34):4788–4797
Groysman M, Russek CS, Katzav S (2000) Vav, a GDP/GTP nucleotide exchange factor, interacts with GDIs, proteins that inhibit GDP/GTP dissociation. FEBS Lett 467(1):75–80
Yamashita T, Tohyama M (2003) The p75 receptor acts as a displacement factor that releases Rho from Rho-GDI. Nat Neurosci 6(5):461–467
DerMardirossian C, Schnelzer A, Bokoch GM (2004) Phosphorylation of RhoGDI by Pak1 mediates dissociation of Rac GTPase. Mol Cell 15(1):117–127
Dransart E, Olofsson B, Cherfils J (2005) RhoGDIs revisited: novel roles in Rho regulation. Traffic 6(11):957–966
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, by the Nature Science Foundation of China (30570548), Project Research from High Technology Center (H2006-8), Grant for Collaborative Research (C2005-2) of Kanazawa Medical University, the Science Research Promotion Fund of The Promotion and Mutual Aid Corporation for Private Schools of Japan, and by the Two Cell Co. Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ota, T., Maeda, M., Sakita-Suto, S. et al. RhoGDIβ lacking the N-terminal regulatory domain suppresses metastasis by promoting anoikis in v-src-transformed cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 23, 323–334 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-006-9041-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-006-9041-y