Abstract
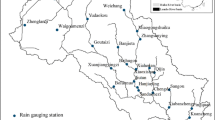
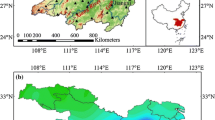
Historical annual dry–wet index for 1470–2003 combined with instrumental precipitation since 1951 were used to identify extremely dry years and events near the northern fringe of the East Asian summer monsoon in China—the Great Bend of the Yellow River (GBYR) region. In total, 49 drought years, of which 26 were severe, were identified. Composites of the dry–wet index under the drought years show an opposite wet pattern over the Southeast China. The longest drought event lasted for 6 years (1528–1533), the second longest one 4 years (1637–1640). The most severe 2-year-long drought occurred in 1928–1929, and the two driest single years were 1900 and 1965. These persistent and extreme drought events caused severe famines and huge losses of human lives. Wavelet transform applied to the dry–wet index indicates that the severe drought years are nested in several significant dry–wet variations across multiple timescales, i.e., the 65–85 year timescale during 1600– 1800, 40–55 year timescale before 1640 and 20–35 year timescale mainly from 1550 to 1640. These timescales of dry–wet variations are discussed in relation to those forcing such as cycles of solar radiation, oscillation in the thermohaline circulation and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO). Comparing 850 hPa winds in Asia in extremely dry and wet years, it was concluded that dry–wet variability in the GBYR region strongly depends upon whether the southerly monsoon flow can reach northern China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonsson K, Chen D, Seppä H (2008) Anticyclonic atmospheric circulation as an analogue for the warm and dry mid-Holocene summer climate in central Scandinavia. Climate of the Past 4:215–224
Central Meteorological Bureau (1981) Atlas of flood and drought in China in the last 500 years. Cartological Press, Beijing, p 332
Currie RG, O’Brien DP (1992) Deterministic signals in USA precipitation records: II. Int J Climatol 12:281–304
Deng YT (1937) History of famine relief in China. Commercial Press, China, p 376
Ding YH (2004) Seasonal march of the East–Asian summer monsoon. In: Chang CP (ed) East Asian monsoon. World Scientific, Beijing, pp 3–53
Feng S, Hu Q, Qian WH (2004) Quality control of daily meteorological data in China, 1951–2000: a new dataset. Int J Climatol 24:853–870
Fu CB (2003) Potential impacts of human-induced land cover change on East Asia monsoon. Glob Planet Change 37:219–229
Gao YX (1962) Several issues about East Asia monsoon. Science Press, China, pp 2–11
Greatbatch RJ, Zhang S (1995) An interdecadal oscillation in an idealized ocean-basin forced by constant heat-flux. J Climate 8:81–91
Guo QY, Cai JN, Shao XM et al (2003) Interdcadal variability of East Aian summer monsoon and its impact on the climate of China. Acta Geogr Sin 4:569–576
Hu Q, Feng S (2001) A southward migration of centennial scale variations of drought/flood in eastern China and the western United States. J Climate 15:1323–1328
Hu HR, Qian WH (2007) Identification of the northernmost boundary of East Asia summer monsoon. Prog Nat Sci 17:812–820
Huang G, Yan ZW (1999) Circulation abnormal index of East Asia summer monsoon and its interannual variation. Chin Sci Bull 44:421–424
Kistler R, Kalnay E, Collins W et al (2001) The NCEP-NCAR 50-year reanalysis: monthly 274 means CD-ROM and documentation. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 82:247–267
Lau KM, Yang S (1997) Climatology and interannual variability of the southeast Asian summer monsoon. Adv Atmos Sci 14:141–162
Linderholm HW (2001) Climatic influence on Scots pine growth on dry and wet soils in the central Scandinavian Mountains, interpreted from tree-ring widths. Silva Fenn 35:415–424
Mitra K, Mukherji S, Dutta SN (1991) Some indications of 18.6 year luni-solar and 10–11 year solar cycles in rainfall in northwest India, the plains of Uttar Pradesh and north-central India. Int J Climatol 11:645–652
Qian Y, Leung LR (2007) A long-term regional simulation and observations of the hydroclimate in China. J Geophy Res D 112. doi:10.1029/2006JD008134
Qian WH, Lu B (2010) Periodic oscillations in millennial global-mean temperature and their causes. Chin Sci Bull 55. doi:10.1007/s11434-010-0000-2
Qian WH, Qin AM (2008) Precipitation division and climate shift in China from 1960 to 2000. Theor Appl Climatol 93. doi:10.1007/s00704-007-0330-4
Qian WH, Zhu YF (2001) Climate change in China from 1880–1998 and its impact on the environmental condition. Clim Change 50: 419–444
Qian WH, Lin X, Zhu YF, Xu Y, Fu JL (2007) Climatic regime shift and decadal anomalous events in China. Clim Change 84:167–189. doi:10.1007/s10584-006-9234-z
Schlesinger ME, Ramankutty N (1994) An oscillation in the global climate system of period 65–70 years. Nature 367:723–726
Shen CM, Wang WC, Gong W, Hao Z (2006) A Pacific Decadal Oscillation record since 1470 AD reconstructed from proxy data of summer rainfall over eastern China. Geophys Res Lett 33:L03702. doi:10.1029/2005GL024804
Shen CM, Wang WC, Hao ZX et al (2007) Exceptional drought events over eastern China during the last five centuries. Clim Change 85:453–471
Song J (2000) Changes in dryness/wetness in China during the last 529 years. Int J Climatol 20:1003–1015
Torrence C, Compo GP (1998) A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 79:61–78
Tu CW, Huang SS (1944) The advance and withdraw of East Asia summer monsoon. Acta Meteorol Sin 18:1–20
Wang B, Lin H (2002) Rainy season of the Asian-Pacific summer monsoon. J Climate 15:386–398
Zhang QY, Tao SY, Chen LT (2003) The inter-annual variability of East Asian summer monsoon indices and its association with the pattern of general circulation over East Asia. Acta Meteorol Sin 61:559–568
Zhao P, Zhu Y, Zhang R (2007) An Asian-Pacific teleconnection in summer tropospheric temperature and associated Asian climate variability. Clim Dyn 29:293–303
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, W., Shan, X., Chen, D. et al. Droughts near the northern fringe of the East Asian summer monsoon in China during 1470–2003. Climatic Change 110, 373–383 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-011-0096-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-011-0096-7