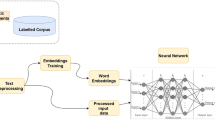
Abstract
With the increasing popularity of user-generated content on social media, the number of toxic texts is also on the rise. Such texts cause adverse effects on users and society at large, therefore, the identification of toxic comments is a growing need of the day. While toxic comment classification has been studied for resource-rich languages like English, no work has been done for Roman Urdu despite being a widely used language on social media in South Asia. This paper addresses the challenge of Roman Urdu toxic comment detection by developing a first-ever large labeled corpus of toxic and non-toxic comments. The developed corpus, called RUT (Roman Urdu Toxic), contains over 72 thousand comments collected from popular social media platforms and has been labeled manually with a strong inter-annotator agreement. With this dataset, we train several classification models to detect Roman Urdu toxic comments, including classical machine learning models with the bag-of-words representation and some recent deep models based on word embeddings. Despite the success of the latter in classifying toxic comments in English, the absence of pre-trained word embeddings for Roman Urdu prompted to generate different word embeddings using Glove, Word2Vec and FastText techniques, and compare them with task-specific word embeddings learned inside the classification task. Finally, we propose an ensemble approach, reaching our best F1-score of 86.35%, setting the first-ever benchmark for toxic comment classification in Roman Urdu.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Agrawal, S., & Awekar, A. (2018). Deep learning for detecting cyberbullying across multiple social media platforms. In Advances in Information Retrieval - 40th European Conference on IR Research, ECIR 2018, Grenoble, France, March 26-29, 2018, Proceedings, pp. 141–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-76941-7_11
van Aken, B., Risch, J., Krestel, R., & Löser, A. (2018). Challenges for toxic comment classification: An in-depth error analysis. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Abusive Language Online, ALW@EMNLP 2018. Brussels, Belgium, October 31, 2018, pp. 33–42 (2018). https://aclanthology.info/papers/W18-5105/w18-5105
Al-garadi, M. A., Varathan, K. D., & Ravana, S. D. (2016). Cybercrime detection in online communications: The experimental case of cyberbullying detection in the twitter network. Computers in Human Behavior, 63, 433–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.051.
Albadi, N., Kurdi, M., & Mishra, S. (2018). Are they our brothers? analysis and detection of religious hate speech in the arabic twittersphere. In U. Brandes, C. Reddy, A. Tagarelli (Eds.), IEEE/ACM 2018 International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining, ASONAM 2018. Barcelona, Spain, August 28-31, 2018, pp. 69–76. IEEE Computer Society (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ASONAM.2018.8508247.
Ameer, I., Siddiqui, M. H.F ., Sidorov, G., & Gelbukh, A. F. (2019). CIC at semeval-2019 task 5: Simple yet very efficient approach to hate speech detection, aggressive behavior detection, and target classification in twitter. In J. May, E. Shutova, A. Herbelot, X. Zhu, M. Apidianaki, S. M. Mohammad (Eds.) Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, SemEval@NAACL-HLT 2019. Minneapolis, MN, USA, June 6–7, 2019, pp. 382–386. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019). https://aclweb.org/anthology/papers/S/S19/S19-2067/
Aulia, N., & Budi, I. (2019). Hate speech detection on indonesian long text documents using machine learning approach. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on Computing and Artificial Intelligence, ICCAI 2019. Bali, Indonesia, April 19-22, 2019., pp. 164–169. ACM (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3330482.3330491.
Badjatiya, P., Gupta, S., Gupta, M., & Varma, V. (2017). Deep learning for hate speech detection in tweets. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web Companion, Perth, Australia, April 3-7, 2017, pp. 759–760. International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee. https://doi.org/10.1145/3041021.3054223
Basile, V., Bosco, C., Fersini, E., Nozza, D., Patti, V., Pardo, F.M.R., Rosso, P., & Sanguinetti, M. (2019). Semeval-2019 task 5: Multilingual detection of hate speech against immigrants and women in twitter. In: J. May, E. Shutova, A. Herbelot, X. Zhu, M. Apidianaki, S.M. Mohammad (eds.) Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, SemEval@NAACL-HLT 2019, Minneapolis, MN, USA, June 6-7, 2019, pp. 54–63. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019). https://aclweb.org/anthology/papers/S/S19/S19-2007/
Bilal, A., Rextin, A., Kakakhel, A., & Nasim, M. (2017). Roman-txt: forms and functions of roman urdu texting. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services, MobileHCI 2017, Vienna, Austria, pp. 15:1–15:9. ACM (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3098279.3098552
Bögel, T. (2012). Urdu - roman transliteration via finite state transducers. In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Finite State Methods and Natural Language Processing, FSMNLP 2012, Donostia-San Sebastiían, Spain, July 23-25, 2012, pp. 25–29 (2012). http://aclweb.org/anthology/W/W12/W12-6204.pdf
Bojanowski, P., Grave, E., Joulin, A., & Mikolov, T. (2017). Enriching word vectors with subword information. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics , 5, 135–146.
Chung, Y., Kuzmenko, E., Tekiroglu, S. S., & Guerini, M. (2019). CONAN - counter narratives through nichesourcing: a multilingual dataset of responses to fight online hate speech. In A. Korhonen, D.R. Traum, L. Màrquez (Eds.), Proceedings of the 57th Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL 2019, Florence, Italy, July 28- August 2, 2019, Volume 1: Long Papers, pp. 2819–2829. Association for Computational Linguistics (2019). https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/P19-1271/
Eberhard, D.M., Simons, G.F., Fennig, C.D.: Urdu. Ethnologue: Languages of the World Twenty-second edition. Dallas, Texas: SIL International (2019). https://www.ethnologue.com/language/urd. “Last accessed: 25-07-2019”
ElSherief, M., Nilizadeh, S., Nguyen, D., Vigna, G., & Belding, E. M. (2018). Peer to peer hate: Hate speech instigators and their targets. In: Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Web and Social Media, ICWSM 2018, Stanford, California, USA, June 25–28, 2018., pp. 52–61. AAAI Press. https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/ICWSM/ICWSM18/paper/view/17905
Fersini, E., Rosso, P., & Anzovino, M. (2018). Overview of the task on automatic misogyny identification at ibereval 2018. In: P. Rosso, J. Gonzalo, R. Martínez, S. Montalvo, J.C. de Albornoz (eds.) Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Evaluation of Human Language Technologies for Iberian Languages (IberEval 2018) co-located with 34th Conference of the Spanish Society for Natural Language Processing (SEPLN 2018), Sevilla, Spain, September 18th, 2018., CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 2150, pp. 214–228. CEUR-WS.org (2018). http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2150/overview-AMI.pdf
Fortuna, P., Bonavita, I., Nunes, S. (2018). Merging datasets for hate speech classification in italian. In: T. Caselli, N. Novielli, V. Patti, P. Rosso (eds.) Proceedings of the Sixth Evaluation Campaign of Natural Language Processing and Speech Tools for Italian. Final Workshop (EVALITA 2018) co-located with the Fifth Italian Conference on Computational Linguistics (CLiC-it 2018), Turin, Italy, December 12-13, 2018., CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 2263. CEUR-WS.org (2018). http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2263/paper037.pdf
Gambäck, B., Sikdar, U.K.: Using convolutional neural networks to classify hate-speech. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Abusive Language Online, ALW@ACL 2017, Vancouver, BC, Canada, August 4, 2017, pp. 85–90 (2017). https://aclanthology.info/papers/W17-3013/w17-3013
Georgakopoulos, S. V., Tasoulis, S. K., Vrahatis, A. G., & Plagianakos, V. P. (2018). Convolutional neural networks for toxic comment classification. In Proceedings of the 10th Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, SETN 2018. Patras, Greece, July 09-12, 2018, pp. 35:1–35:6. ACM (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3200947.3208069
Ghulam, H., Zeng, F., Li, W., & Xiao, Y. (2018). Deep learning-based sentiment analysis for roman urdu text. In: 2018 International Conference on Identification, Information and Knowledge in the Internet of Things, IIKI 2018, Beijing, China, October 19–21, 2018, Procedia Computer Science, vol. 147, pp. 131–135. Elsevier (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.01.202
Guggilla, C., Miller, T., Gurevych, I. (2016). CNN- and lstm-based claim classification in online user comments. In: COLING 2016, 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Proceedings of the Conference: Technical Papers, December 11–16, 2016, Osaka, Japan, pp. 2740–2751 (2016). http://aclweb.org/anthology/C/C16/C16-1258.pdf
Haidar, B., Chamoun, M., & Serhrouchni, A. (2017). Multilingual cyberbullying detection system: Detecting cyberbullying in arabic content. In 1st Cyber Security in Networking Conference, CSNet 2017. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, October 18-20, 2017, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CSNET.2017.8242005.
Hee, C. V., Lefever, E., Verhoeven, B., Mennes, J., Desmet, B., Pauw, G. D., Daelemans, W., & Hoste, V. (2015). Detection and fine-grained classification of cyberbullying events. In G. Angelova, K. Bontcheva, R. Mitkov (Eds.), Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing, RANLP 2015, 7-9 September, 2015, Hissar, Bulgaria, pp. 672–680. RANLP 2015 Organising Committee / ACL (2015). http://aclweb.org/anthology/R/R15/R15-1086.pdf
Hosseinmardi, H., Rafiq, R.I., Han, R., Lv, Q., & Mishra, S. (2016). Prediction of cyberbullying incidents in a media-based social network. In: 2016 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining, ASONAM 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA, August 18–21, 2016, pp. 186–192 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ASONAM.2016.7752233
Ibrahim, M., Torki, M., & El-Makky, N. (2018). Imbalanced toxic comments classification using data augmentation and deep learning. In 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, ICMLA 2018. Orlando, FL, USA, December 17-20, 2018, pp. 875–878. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMLA.2018.00141
Khan, O., & Karim, A. (2012). A rule-based model for normalization of SMS text. In IEEE 24th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, ICTAI 2012, Athens, Greece, November 7-9, 2012, pp. 634–641 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTAI.2012.91.
Kim, Y. (2014). Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, EMNLP 2014, October 25-29, 2014, Doha, Qatar, A meeting of SIGDAT, a Special Interest Group of the ACL, pp. 1746–1751 (2014). http://aclweb.org/anthology/D/D14/D14-1181.pdf
Lai, S., Xu, L., Liu, K., & Zhao, J. (2015). Recurrent convolutional neural networks for text classification. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, January 25-30, 2015, Austin, Texas, USA., vol. 333, pp. 2267–2273. AAAI Press. http://www.aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI15/paper/view/9745
Lee, H. S., Lee, H. R., Park, J. U., & Han, Y. S. (2018). An abusive text detection system based on enhanced abusive and non-abusive word lists. Decision Support Systems, 113, 22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2018.06.009.
Lee, S., & Kim, H. (2015). Why people post benevolent and malicious comments online. Communications of the ACM, 58(11), 74–79. https://doi.org/10.1145/2739042.
Malmasi, S., & Zampieri, M. (2018). Challenges in discriminating profanity from hate speech. Journal of Experimental & Theoretical Artificial Intelligence, 30(2), 187–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/0952813X.2017.1409284.
Mehmood, K., Essam, D., & Shafi, K. (2018). Sentiment analysis system for roman urdu. In Science and Information Conference, pp. 29–42. Springer (2018)
Mehmood, K., Essam, D., Shafi, K., & Malik, M. K. (2019). Discriminative feature spamming technique for roman urdu sentiment analysis. IEEE Access, 7, 47991–48002. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2908420.
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G. S., & Dean, J. (2013). Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 26: 27th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2013. Proceedings of a meeting held December 5-8, 2013, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, United States., pp. 3111–3119 (2013). http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5021-distributed-representations-of-words-and-phrases-and-their-compositionality
Nobata, C., Tetreault, J.R., Thomas, A., Mehdad, Y., & Chang, Y. (2016). Abusive language detection in online user content. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on World Wide Web, WWW 2016, Montreal, Canada, April 11–15, 2016, pp. 145–153 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1145/2872427.2883062.
Obadimu, A., Mead, E., Hussain, M. N., & Agarwal, N. (2019). Identifying toxicity within youtube video comment. In R. Thomson, H. Bisgin, C. L. Dancy, & A. Hyder (Eds.), Social, Cultural, and Behavioral Modeling - 12th International Conference, SBP-BRiMS 2019, Washington, DC, USA, July 9–12, 2019, Proceedings, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 11549, pp. 214–223. Springer (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-21741-9_22.
Pennington, J., Socher, R., & Manning, C. (2014). Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, EMNLP 2014, October 25-29, 2014, Doha, Qatar, A meeting of SIGDAT, a Special Interest Group of the ACL, pp. 1532–1543 (2014). http://aclweb.org/anthology/D/D14/D14-1162.pdf
Poletto, F., Stranisci, M., Sanguinetti, M., Patti, V., Bosco, C. (2017). Hate speech annotation: Analysis of an italian twitter corpus. In: R. Basili, M. Nissim, G. Satta (eds.) Proceedings of the Fourth Italian Conference on Computational Linguistics (CLiC-it 2017), Rome, Italy, December 11-13, 2017., CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 2006. CEUR-WS.org (2017). http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2006/paper024.pdf
Ptaszynski, M., Eronen, J. K. K.,& Masui, F. (2017). Learning deep on cyberbullying is always better than brute force. In: IJCAI 2017 3rd Workshop on Linguistic and Cognitive Approaches to Dialogue Agents (LaCATODA 2017), Melbourne, Australia, August, pp. 19–25.
Rafae, A., Qayyum, A., Moeenuddin, M., Karim, A., Sajjad, H., & Kamiran, F. (2015). An unsupervised method for discovering lexical variations in roman urdu informal text. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, EMNLP 2015. Lisbon, Portugal, September 17–21, 2015, pp. 823–828 (2015). http://aclweb.org/anthology/D/D15/D15-1097.pdf.
Reynolds, K., Kontostathis, A., Edwards, L. (2011). Using machine learning to detect cyberbullying. In International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications and Workshops, ICMLA 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, December 18-21, 2011. Volume 2: Special Sessions and Workshop, pp. 241–244 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMLA.2011.152.
Risch, J., & Krestel, R. (2018). Aggression identification using deep learning and data augmentation. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying (TRAC-2018), pp. 150–158.
Ross, B., Rist, M., Carbonell, G., Cabrera, B., Kurowsky, N., & Wojatzki, M. (2017). Measuring the reliability of hate speech annotations: The case of the european refugee crisis. CoRR arXiv:abs/1701.08118.
Rybinski, M., Miller, W., Ser, J. D., Bilbao, M. N., Montes, J. F. A. (2018). On the design and tuning of machine learning models for language toxicity classification in online platforms. In J.D. Ser, E. Osaba, M.N. Bilbao, J.J.S. Medina, M. Vecchio, & X. Yang (Eds.), Intelligent Distributed Computing XII, 12th International Symposium on Intelligent Distributed Computing, IDC 2018, Bilbao, Spain, 15–17 October 2018, Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol. 798, pp. 329–343. Springer (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99626-4_29.
Saeed, H. H., Shahzad, K., & Kamiran, F. (2018). Overlapping toxic sentiment classification using deep neural architectures. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, ICDM Workshops. Singapore, Singapore, November 17–20, 2018, pp. 1361–1366. IEEE (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDMW.2018.00193.
Sanguinetti, M., Poletto, F., Bosco, C., Patti, V., & Stranisci, M. (2018). An italian twitter corpus of hate speech against immigrants. In N. Calzolari, K. Choukri, C. Cieri, T. Declerck, S. Goggi, K. Hasida, H. Isahara, B. Maegaard, J. Mariani, H. Mazo, A. Moreno, J. Odijk, S. Piperidis, T. Tokunaga (Eds.), Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, LREC 2018, Miyazaki, Japan, May 7-12, 2018. European Language Resources Association (ELRA) (2018). http://www.lrec-conf.org/proceedings/lrec2018/summaries/710.html.
Santosh, T., & Aravind, K. (2019). Hate speech detection in hindi-english code-mixed social media text. In: Proceedings of the ACM India Joint International Conference on Data Science and Management of Data, COMAD/CODS 2019, Kolkata, India, January 3-5, 2019, pp. 310–313. ACM (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3297001.3297048.
Shtovba, S., Shtovba, O., & Petrychko, M. (2019). Detection of social network toxic comments with usage of syntactic dependencies in the sentences. In: Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on Computer Modeling and Intelligent Systems (CMIS-2019), Zaporizhzhia, Ukraine, April 15-19, 2019., CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 2353, pp. 313–323. CEUR-WS.org (2019). http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2353/paper25.pdf
Sood, S.O., Antin, J., & Churchill, E. F. (2012). Profanity use in online communities. In: CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI ’12, Austin, TX, USA - May 05 - 10, 2012, pp. 1481–1490 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1145/2207676.2208610.
Sutejo, T. L., & Lestari, D. P. (2018). Indonesia hate speech detection using deep learning. In M. Dong, M. A. Bijaksana, H. Sujaini, A. Romadhony, F. Z. Ruskanda, E. Nurfadhilah, L. R. Aini (Eds.), 2018 International Conference on Asian Language Processing, IALP 2018, Bandung, Indonesia, November 15-17, 2018, pp. 39–43. IEEE (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/IALP.2018.8629154.
Vigna, F. D., Cimino, A., Dell’Orletta, F., Petrocchi, M., & Tesconi, M. (2017). Hate me, hate me not: Hate speech detection on facebook. In A. Armando, R. Baldoni, R. Focardi (Eds.), Proceedings of the First Italian Conference on Cybersecurity (ITASEC17), Venice, Italy, January 17-20, 2017., CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 1816, pp. 86–95. CEUR-WS.org (2017). http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1816/paper-09.pdf.
Waseem, Z., & Hovy, D. (2016). Hateful symbols or hateful people? predictive features for hate speech detection on twitter. In Proceedings of the Student Research Workshop, SRW@HLT-NAACL 2016, The 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, San Diego California, USA, June 12-17, 2016, pp. 88–93. The Association for Computational Linguistics (2016). http://aclweb.org/anthology/N/N16/N16-2013.pdf.
Watanabe, H., Bouazizi, M., & Ohtsuki, T. (2018). Hate speech on twitter: A pragmatic approach to collect hateful and offensive expressions and perform hate speech detection. IEEE Access, 6, 13825–13835. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2806394.
Zhang, Z., Robinson, D., & Tepper, J. (2018). Detecting hate speech on twitter using a convolution-gru based deep neural network. In European Semantic Web Conference—15th International Conference, ESWC 2018, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, June 3-7, 2018, Proceedings, pp. 745–760. Springer (2018).
Zhou, P., Qi, Z., Zheng, S., Xu, J., Bao, H., & Xu, B. (2016). Text classification improved by integrating bidirectional lstm with two-dimensional max pooling. In COLING 2016, 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Proceedings of the Conference: Technical Papers, December 11-16, 2016, Osaka, Japan, pp. 3485–3495 (2016). http://aclweb.org/anthology/C/C16/C16-1329.pdf
Acknowledgements
We thank Louis Bruyns Foundation, Belgium, for their support to complete this research study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saeed, H.H., Ashraf, M.H., Kamiran, F. et al. Roman Urdu toxic comment classification. Lang Resources & Evaluation 55, 971–996 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10579-021-09530-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10579-021-09530-y