Abstract
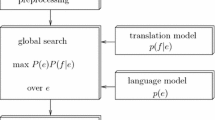
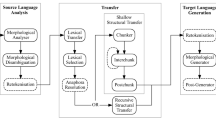
This work aims to improve an N-gram-based statistical machine translation system between the Catalan and Spanish languages, trained with an aligned Spanish–Catalan parallel corpus consisting of 1.7 million sentences taken from El Periódico newspaper. Starting from a linguistic error analysis above this baseline system, orthographic, morphological, lexical, semantic and syntactic problems are approached using a set of techniques. The proposed solutions include the development and application of additional statistical techniques, text pre- and post-processing tasks, and rules based on the use of grammatical categories, as well as lexical categorization. The performance of the improved system is clearly increased, as is shown in both human and automatic evaluations of the system, with a gain of about 1.1 points BLEU observed in the Spanish-to-Catalan direction of translation, and a gain of about 0.5 points in the reverse direction. The final system is freely available online as a linguistic resource.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bangalore, S., & Riccardi, G. (2000). Stochastic finite-state models for spoken language machine translation. In Workshop on Embedded Machine Translation Systems, Seattle, WA.
Brown, P., della Pietra, S., et al. (1993). The mathematics of statistical machine translation. Computational Linguistics, 19(2), 263–311.
Carreras, X., Chao, I., et al. (2004). FreeLing: An open-source suite of language analyzers. In Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Lisbon, Portugal.
Casacuberta, F., & Vidal, E. (2004). Machine translation with inferred stochastic finite-state transducers. Computational Linguistics, 30(2), 205–225.
Crego, J. M., de Gispert, A., et al. (2006). N-gram-based SMT System Enhanced with Reordering. In Human Language Technology Conference (HLT-NAACL’06): Proceedings of the Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation, New York.
Crego, J. M., & Mariño, J. B. (2007). Improving SMT by coupling reordering and decoding. Machine Translation, 20(3), 199–215.
de Gispert, A., & Mariño, J. (2006). Catalan-English statistical machine translation without parallel corpus: Bridging through Spanish. In Proceedings of LREC 5th Workshop on Strategies for developing Machine Translation for Minority Languages (SALTMIL’06). Genova, 65–68.
Mariño, J. B., Banchs, R. E., et al. (2006). N-gram based machine translation. Computational Linguistics, 32(4), 527–549.
Newcombe, R. G. (1998). Two-sided confidence intervals for the single proportion: Comparison of seven methods. Statistics in Medicine, 17(8), 857–872.
Niessen, S., & Ney, H. (2000). Improving SMT quality with morpho-syntactic analysis. In International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Saarbrücken, Germany.
Och, F. J. (2003). Minimum error rate training in statistical machine translation. In 41st Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Sapporo, Japan.
Popović, M., de Gispert, A., et al. (2006). Morpho-syntactic information for automatic error analysis of statistical machine translation output. In HLT/NAACL Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation, New York.
Popović, M., & Ney, H. (2004). Towards the use of word stems and suffixes for statistical machine translation. In International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Lisbon, Portugal.
Popović, M., & Ney, H. (2006). POS-based word reorderings for statistical machine translation. In International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Genoa, Italy.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank TALP Research Center and Barcelona Media Innovation Center for its support and permission to publish this research. We would like to give credit to the anonymous reviewers of this paper for their valuable suggestions. This work has been partially funded by the Spanish Department of Science and Innovation through the Juan de la Cierva fellowship program and the Spanish Government under the BUCEADOR project (TEC2009-14094-C04-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farrús, M., Costa-jussà, M.R., Mariño, J.B. et al. Overcoming statistical machine translation limitations: error analysis and proposed solutions for the Catalan–Spanish language pair. Lang Resources & Evaluation 45, 181–208 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10579-011-9137-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10579-011-9137-0