Abstract
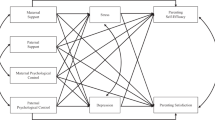
The current study, operating from a stress-process framework, examined the interactive effects of supportive parenting practices (i.e., mothers’ use of positive communication, positive parenting, and parental involvement) and maternal psychological control on mother- and child-reported child depressive symptoms in a community-recruited sample of 9–12 year-olds. Discrepancies between reports of depressive symptoms were also examined. Maternal psychological control was uniquely associated with child-, not mother-, reported depressive symptoms. Parental involvement was uniquely associated with mother-, not child-, reported depressive symptoms. Positive parent–child communication was associated with both reports of child depressive symptoms at the bivariate level, but not when unique associations were examined. Positive parenting was unrelated to either report of depressive symptoms. No interaction effects were detected. The current findings highlight the differential importance of parenting practices on child depressive symptoms, and also indicate the necessity of gathering both parent and child reports of symptomatology and family functioning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garber J, Gallerani CM, Frankel SA (2009) Depression in children. In Handbook of depression, 2nd ed.. Guilford Press, New York, pp 405–443
Lima NN, do Nascimento VB, de Carvalho SM, de Abreu LC, Neto ML et al (2013) Childhood depression: a systematic review. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 9:1417–1425
Lewinsohn PM, Hops H, Roberts RE, Seeley JR, Andrews JA (1993) Adolescent psychopathology: I. Prevalence and incidence of depression and other DSM-III—R disorders in high school students. J Abnorm Psychol 102:133–144
Costello EJ, Pine DS, Hammen C, March JS, Plotsky PM et al (2002) Development and natural history of mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 52:529–542
Harrington R, Rutter M, Fombonne E (1996) Developmental pathways in depression: multiple meanings, antecedents, and endponts. Dev Psychopathol 8:601–616
Dallaire DH, Pineda AQ, Cole DA, Ciesla JA, Jacquez F et al (2006) Relation of positive and negative parenting to children’s depressive symptoms. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 35:313–322
Wimsatt AR, Fite PJ, Grassetti SN, Rathert JL (2013) Positive communication moderates the relationship between corporal punishment and child depressive symptoms. Child Adolesc Ment Health 18:225–230
Lyneham HJ, Rapee RM (2006) Evaluation of therapist-supported parent-implemented CBT for anxiety disorders in rural children. Behav Res Ther 44:1287–1300
Cicchetti D, Toth SL (1998) The development of depression in children and adolescents. Am Psychol 53:221–241
Brennan PA, Le Brocque R, Hammen C (2003) Maternal depression, parent–child relationships, and resilient outcomes in adolescence. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42:1469–1477
DeLay D, Hafen CA, Cunha JM, Weber LND, Laursen B (2013) Perceptions of parental support buffer against depression for Brazilian youth with interpersonal difficulties. Int J Behav Dev 37:29–34
Muris P, Meesters C, Schouten E, Hoge E (2004) Effects of perceived control on the relationship between perceived parental rearing behaviors and symptoms of anxiety and depression in nonclinical preadolescents. J Youth Adolesc 33:51–58
Plunkett SW, Henry CS, Robinson LC, Behnke A, Falcon PC III (2007) Adolescent perceptions of parental behaviors, adolescent self-esteem, and adolescent depressed mood. J Child Fam Stud 16:760–772
Vazsonyi AT, Belliston LM (2006) The cultural and developmental significance of parenting processes in adolescent anxiety and depression symptoms. J Youth Adolesc 35:491–505
Yu S, Clemens R, Yang H, Li X, Stanton B et al (2006) Youth and parental perceptions of parental monitoring and parent-adolescent communication, youth depression, and youth risk behaviors. Soc Behav Pers 34:1297–1310
Colder CR, Lochman JE, Wells KC (1997) The moderating effects of children’s fear and activity level on relations between parenting practices and childhood symptomatology. J Abnorm Child Psychol 25:251–263
Bruce AE, Cole DA, Dallaire DH, Jacquez FM, Pineda AQ et al (2006) Relations of parenting and negative life events to cognitive diatheses for depression in children. J Abnorm Child Psychol 34:321–333
Stouthamer-Loeber M, Loeber R, Wei E, Farrington DP, Wikström P-OH (2002) Risk and promotive effects in the explanation of persistent serious delinquency in boys. J Consult Clin Psychol 70:111–123
Bayer J, Sanson A, Hemphill SA (2006) Parent influences on early childhood internalizing difficulties. J Appl Dev Psychol 27:542–559
Pearson J, Muller C, Frisco ML (2006) Parental involvement, family structure, and adolescent sexual decision making. Sociol Perspect 49:67–90
Fan X, Chen M (2001) Parental involvement and students’ academic achievement: a meta-analysis. Educ Psychol Rev 13:1–22
El Nokali NE, Bachman HJ, Votruba-Drzal E (2010) Parent involvement and children’s academic and social development in elementary school. Child Dev 81:988–1005
Duchesne S, Ratelle C (2010) Parental behaviors and adolescents’ achievement goals at the beginning of middle school: emotional problems as potential mediators. J Educ Psychol 102:497–507
Boeldt DL, Rhee SH, DiLalla LF, Mullineaux PY, Schulz-Heik RJ et al (2012) The association between positive parenting and externalizing behaviour. Infant Child Dev 21:85–106
Healey DM, Flory JD, Miller CJ, Halperin JM (2011) Maternal positive parenting style is associated with better functioning in hyperactive/inattentive preschool children. Infant Child Dev 20:148–161
Tolou-Shams M, Paikoff R, McKirnan DJ, Holmbeck GN (2007) Mental health and HIV risk among African American adolescents. Soc Work Ment Health 5:27–58
Compas BE, Champion JE, Forehand R, Cole DA, Reeslund KL et al (2010) Coping and parenting: Mediators of 12-month outcomes of a family group cognitive–behavioral preventive intervention with families of depressed parents. J Consult Clin Psychol 78:623–634
Schwartz OS, Dudgeon P, Sheeber LB, Yap MB, Simmons JG et al (2012) Parental behaviors during family interactions predict changes in depression and anxiety symptoms during adolescence. J Abnorm Child Psychol 40:59–71
Barber BK (1996) Parental psychological control: revisiting a neglected construct. Child Dev 67:3296–3319
Taylor RD, Lopez EI, Budescu M, McGill RK (2011) Parenting practices and adolescent internalizing and externalizing problems: moderating effects of socially demanding kin relations. J Child Fam Stud 21:474–485
Coln KL, Jordan SS, Mercer SH (2013) A unified model exploring parenting practices as mediators of marital conflict and children’s adjustment. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 44:419–429
Mandara J, Pikes CL (2008) Guilt trips and love withdrawal: does mothers’ use of psychological control predict depressive symptoms among african american adolescents? Fam Relat 57:602–612
Soenens B, Luyckx K, Vansteenkiste M, Duriez B, Goossens L (2008) Clarifying the link between parental psychological control and adolescents’ depressive symptoms: reciprocal versus unidirectional models. Merrill Palmer Q 54:411–444
Drake KL, Ginsburg GS (2012) Family factors in the development, treatment, and prevention of childhood anxiety disorders. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 15:144–162
Barber BK, Harmon EL (2002) Violating the self: parental psychological control of children and adolescents. In: Barber BK (ed) Intrusive parenting: how psychological control affects children and adolescents. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC, pp 15–52
Bradford K, Barber BK, Olsen JA, Maughan SL, Erickson LD et al (2004) A multi-national study of interparental conflict, parenting, and adolescent functioning: South Africa, Bangladesh, China, India, Bosnia, Germany, Palestine, Colombia, and the United States. Marriage Fam Rev 35:107–137
Murray KW, Dwyer KM, Rubin KH, Knighton-Wisor S, Booth-LaForce C (2014) Parent–child relationships, parental psychological control, and aggression: maternal and paternal relationships. J Youth Adolesc 43:1361–1373
Barber BK, Xia M, Olsen JA, McNeely CA, Bose K (2012) Feeling disrespected by parents: refining the measurement and understanding of psychological control. J Adolesc 35:273–287
Pearlin LI, Menaghan EG, Lieberman MA, Mullan JT (1981) The stress process. J Health Soc Behav 22:337–356
Darling N, Steinberg L (1993) Parenting style as context: an integrative model. Psychol Bull 113:487–496
Lowe K, Dotterer AM (2013) Parental monitoring, parental warmth, and minority youths’ academic outcomes: exploring the integrative model of parenting. J Youth Adolesc 42:1413–1425
Eisenberg N, Gershoff ET, Fabes RA, Shepard SA, Cumberland AJ et al (2001) Mother’s emotional expressivity and children’s behavior problems and social competence: mediation through children’s regulation. Dev Psychol 37:475–490
Harper FWK, Brown AM, Arias I, Brody G (2006) Corporal punishment and kids: How do parent support and gender influence child adjustment? J Fam Violence 21:197–207
Turner HA, Finkelhor D (1996) Corporal punishment as a stressor among youth. J Marriage Fam 58:155–166
Rohner RP, Bourque SL, Elordi CA (1996) Children’s perceptions of corporal punishment, caretaker acceptance, and psychological adjustment in a poor, biracial southern community. J Marriage Fam 58:842–852
Kaslow NJ, Rehm LP, Pollack SL, Siegel AW (1990) Depression and perception of family functioning in children and their parents. Am J Fam Ther 18:227–235
Kovacs, M (1983) Children’s depression inventory. Book Children’s depression inventory. Unpublished Manuscript, University of Pittsburg, Pennsylvania
De Los Reyes A, Kazdin AE (2005) Informant discrepancies in the assessment of childhood psychopathology: a critical review, theoretical framework, and recommendations for further study. Psychol Bull 131:483–509
Kolko DJ, Kazdin AE (1993) Emotional/behavioral problems in clinic and nonclinic children: Correspondence among child, parent and teacher reports. Child Psychol Psychiatry Allied Discip 34:991–1006
Treutler CM, Epkins CC (2003) Are discrepancies among child, mother, and father reports on children’s behavior related to parents’ psychological symptoms and aspects of parent–child relationships? J Abnorm Child Psychol 31:13–27
Bidaut-Russel M, Reich M, Cottler LB, Robins LN, Compton WM et al (1995) The diagnostic interview schedule for children (pc-disc v. 3.0): parents and adolescents suggest reasons for expecting discrepant answers. J Abnorm Child Psychol 23:641–659
Albrecht AK, Galambos NL, Jansson SM (2007) Adolescents’ internalizing and aggressive behaviors and perceptions of parents’ psychological control: a panel study examining direction of effects. J Youth Adolesc 36:673–684
Aunola K, Tolvanen A, Viljaranta J, Nurmi JE (2013) Psychological control in daily parent–child interactions increases children’s negative emotions. J Fam Psychol 27:453–462
Bean RA, Barber BK, Crane DR (2006) Parental support, behavioral control, and psychological control among african american youth: The relationships to academic grades, delinquency, and depression. J Fam 27:1335–1355
Loeber R, Farrington DP, Stouthamer-Loeber M, Van Kammen WB (1998) Antisocial behavior and mental health problems: Explanatory factors in childhood and adolescence. Book Antisocial behavior and mental health problems: explanatory factors in childhood and adolescence. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers, Mahwah
Abela JRZ, Gagnon H, Auerbach RP (2007) Hopelessness depression in children: an examination of the symptom component of the hopelessness theory. Cognit Ther Res 31:401–417
Loeber R, Drinkwater M, Yin Y, Anderson SJ, Schmidt LC et al (2000) Stability of family interaction from ages 6 to 18. J Abnorm Child Psychol 28:353–369
Pardini DA, Fite PJ, Burke JD (2008) Bidirectional associations between parenting practices and conduct problems in boys from childhood to adolescence: the moderating effect of age and african–american ethnicity. J Abnorm Child Psychol 36:647–662
Myers K, Winters NC (2002) Ten-year review of rating scales. II. Scales for internalizing disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 41:634–659
Nurcombe B, Seifer R, Scioli A, Tramontana MG, Grapentine WL et al (1989) Is major depressive disorder in adolescence a distinct diagnostic entity? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 28:333–342
Kovacs M (2003) Children’s depression inventory. Book children’s depression inventory. Multi-Health Systems, Toronto
Carey MP, Faulstich ME, Gresham FM, Ruggiero L, Enyart P et al (1987) Children’s depression inventory: construct and discriminant validity across clinical and nonreferred (control) populations”: correction to carey. J Consult Clin Psychol 55:845
Fauber R, Forehand R, Long N, Burke M, Faust J (1987) The relationship of young adolescent children’s depression inventory (CDI) scores to their social and cognitive functioning. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 9:161–172
Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA (2001) Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles. Book Manual for the aseba school-age forms & profiles. University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families, Burlington
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Book Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Erlbaum, Hillsdale
Parent J, Forehand R, Dunbar JP, Watson KH, Reising MM et al (2014) Parent and adolescent reports of parenting when a parent has a history of depression: associations with observations of parenting. J Abnorm Child Psychol 42:173–183
Reynolds AJ (1992) Comparing measures of parental involvement and their effects on academic achievement. Early Child Res Q 7:441–462
McElhaney KB, Porter MR, Thompson LW, Allen JP (2008) Apples and oranges: divergent meanings of parents’ and adolescents’ perceptions of parental influence. J Early Adolesc
Yeh M, Weisz JR (2001) Why are we here at the clinic? Parent–child (DIS) agreement on referral problems at outpatient treatment entry. J Consult Clin Psychol 69:1018
Zolotor AJ, Theodore AD, Runyan DK, Chang JJ, Laskey AL (2011) Corporal punishment and physical abuse: population-based trends for three-to-11-year-old children in the united states. Child Abuse Rev 20:57–66
Aiken LS, West SG (1991) Multiple regression: testing and interpreting interactions. Book multiple regression: testing and interpreting interactions. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks
McNeely CA, Barber BK (2010) How do parents make adolescents feel loved? Perspectives on supportive parenting from adolescents in 12 cultures. J Adolesc Res 25:601–631
Morsbach SK, Prinz RJ (2006) Understanding and improving the validity of self-report of parenting. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 9:1–21
McLeod BD, Weisz JR, Wood JJ (2007) Examining the association between parenting and childhood depression: a meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev 27:986–1003
Loukas A (2009) Examining temporal associations between perceived maternal psychological control and early adolescent internalizing problems. J Abnorm Child Psychol 37:1113–1122
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frazer, A.L., Fite, P.J. Maternal Psychological Control, Use of Supportive Parenting, and Childhood Depressive Symptoms. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 47, 384–396 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-015-0573-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-015-0573-8