Abstract
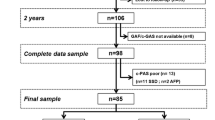
A comparison of clinical features and adult outcome in adolescents with three types of psychotic disorders: schizophrenic (SPh), schizoaffective (SA) and bipolar with psychotic features (BPP). Subjects (n = 41) were finally diagnosed (DSM-IV criteria) with SPh (n = 17), SA (n = 11) or BPP (n = 13). Clinical evaluation took place at onset and at a 3-year follow-up in all 41, and at least after 5 years in 36 patients. Symptoms were rated on the basis of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS), integrating items from the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) and the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School-Age Children-Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL). The Children Global Assessment Scale (C-GAS) and the Global Assessment Scale (GAF) were used to evaluate global functioning. Significant differences in clinical features were found in the three diagnostic groups as regards several parameters, some present on one and not on other rating scales, underscoring the insufficiency of a single scale for accurate analysis of the features of a psychotic disorder. At onset, a comparison using the simple presence/absence of symptoms showed scant differences among groups, while differences emerged if symptom severity was included in the comparison. Functioning at 3- and 5-year follow-ups showed a significantly better outcome in the BPP group and more substantial deterioration, with similar evolution, in the SPh and SA groups. The integration of several rating scales differentiated between diagnostic groups more effectively. The similar adult functioning outcome in the SPh and SA groups showed how difficult it is to clearly separate these two disorders.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. (DSM IV). American Psychiatric Association, Washington DC
Lake CR, Hurwitz N (2007) Schizoaffective disorder merges schizophrenia and bipolar disorders as one disease—there is no schizoaffective disorder. Curr Opin Psychiatry 20:365–379. doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e3281a305ab
Cheniaux E, Landeira-Fernandez J, Lessa Telles L, Lessa JLM, Dias A, Duncan T, Versiani M (2008) Does schizoaffective disorder really exist? A systematic review of the studies that compared schizoaffective disorder with schizophrenia or mood disorders. J Affect Disord 106:209–217. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2007.07.009
Werry JS, Mc Clellan JM, Chard L (1991) Early-onset schizophrenia, bipolar and schizoaffective disorder: a clinical follow-up study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 30:457–465
McClellan J, McCurry C (1999) Early-onset psychotic disorders: diagnostic stability and clinical characteristics. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 8:13–19. doi:10.1007/PL00010686
Hollis C (2000) Adult outcomes of child and adolescent-onset schizophrenia: diagnostic stability and predictive validity. Am J Psychiatry 157:1652–1659. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.157.10.1652
Fraguas D, de Castro MJ, Medina O, Parellada M, Moreno D, Graell M, Merchàn-Naranjo J, Arango C (2008) Does diagnostic classification of early-onset psychosis change over follow-up? Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 39:137–145. doi:10.1007/s10578-007-0076-3
McClellan J, McCurry C, Speltz ML, Jones K (2002) Symptom factors in early-onset psychotic disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 41:791–798. doi:10.1097/00004583-200207000-00010
Ballageer T, Malla A, Manchanda R, Takhar J, Haricharan R (2005) Is adolescent-onset first-episode psychosis different from adult onset? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 44:782–789. doi:10.1097/01.chi.0000164591.55942.ea
Fleischhaker C, Schulz E, Tepper K, Martin M, Hennighausen K, Remschmidt H (2005) Long-term course of adolescent schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 31:769–780. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbi014
Roepcke B, Eggers C (2005) Early-onset schizophrenia: a 15-year follow-up. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 14:341–350. doi:10.1007/s00787-005-0483-6
Cawthron P, James A, Dell J, Seagroatt V (1994) Adolescent onset psychosis a clinical and outcome study. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 35:1321–1332. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.1994.tb01237.x
Schmidt M, Blanz B, Dippe A, Koppe T, Lay B (1995) Course of patients diagnosed as having schizophrenia during first episode occurring under age 18 years. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 245:93–100. doi:10.1007/BF02190735
Maziade M, Gingras N, Rodrigue C, Bouchard S, Cardinal A, Gauthier B, Tremblay G, Côté S, Fournier C, Boutin P, Hamel M, Roy MA, Martinez M, Mérette C (1996) Long-term stability of diagnosis and symptom dimensions in a systematic sample of patients with onset of schizophrenia in childhood and early adolescence. I: nosology, sex and age of onset. Br J Psychiatry 169:361–370. doi:10.1192/bjp.169.3.361
Lay B, Schmidt MH, Blanz B (1997) Course of adolescent psychotic disorder with schizoaffective episodes. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 6:32–41. doi:10.1007/BF00573638
Lay B, Blanz B, Hartmann M, Schmidt MH (2000) The psychosocial outcome of adolescent-onset schizophrenia: a 12-year follow-up. Schizophr Bull 26:801–816
Jarbin H, Ott Y, Von Knorring AL (2003) Adult outcome of social function in adolescent-onset schizophrenia and affective psychosis. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42:176–183. doi:10.1097/00004583-200302000-00011
McClellan J, McCurry C, Snell J, Dubose A (1999) Early-onset psychotic disorders: course and outcome over a 2-year period. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 38:1380–1388. doi:10.1097/00004583-199911000-00012
Kaufman J, Birmaher B, Brent D, Rao U, Flynn C, Moreci P, Williamson D, Ryan N (1997) Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL): initial reliability and validity data. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36:980–988. doi:10.1097/00004583-199707000-00021
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:261–276
Emsley R, Rabinowitz J, Torreman M (2003) The factor structure for the positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) in recent-onset psychosis. Schizophr Res 61:47–57. doi:10.1016/S0920-9964(02)00302-X
Ventura J, Green MF, Shaner A, Liberman RP (1993) Training and quality assurance with the brief psychiatric rating scale: ‘The Drift Busters’. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 3:221–244
Shaffer D, Gould MS, Brasic J, Ambrosini P, Fisher P, Bird H, Aluwahlia S (1983) A children’s global assessment scale (CGAS). Arch Gen Psychiatry 40:1228–1231
Endicott J, Spitzer RL, Fleiss JL, Cohen J (1976) The global assessment scale: a procedure for measuring overall severity of psychiatric disturbance. Arch Gen Psychiatry 33:766–771
Frazier JA, McClellan J, Findling RL, Vitiello B, Anderson R, Zablotsky B, Williams E, McNamara NK, Jackson JA, Ritz L, Hlastala SA, Pierson L, Varley JA, Puglia M, Maloney AE, Ambler D, Hunt-Harrison T, Hamer RM, Noyes N, Lieberman JA, Sikich L (2007) Treatment of early-onset schizophrenia spectrum disorders (TEOSS): demographic and clinical characteristics. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 46:979–988. doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e31807083fd
Eggers C, Bunk D, Krause D (2000) Schizophrenia with onset before the age of eleven: clinical characteristics of onset and course. J Autism Dev Disord 30:29–38. doi:10.1023/A:1005408010797
Andreasen NC, Arndt S, Alliger R, Miller D, Flaum M (1995) Symptoms of schizophrenia. Methods, meanings and mechanisms. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:341–351
Gupta S, Andreasen NC, Arndt S, Flaum M, Hubbard WC, Ziebell S (1997) The Iowa longitudinal study of recent-onset psychosis: one-year follow-up of first episode patients. Schizophr Res 23:1–13. doi:10.1016/S0920-9964(96)00078-3
Baethge C, Baldessarini RJ, Freudenthal K, Streeruwitz A, Bauer M, Bschor T (2005) Hallucinations in bipolar disorder: characteristics and comparison to unipolar depression and schizophrenia. Bipolar Disord 7:136–145. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5618.2004.00175.x
McClellan J, Breiger D, McCurry C, Hlastala SA (2003) Premorbid functioning in early-onset psychotic disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42:666–672. doi:10.1097/01.CHI.0000046844.56865.6B
Eggers C, Bunk D, Röpcke B (2002) Childhood and adolescent-onset schizophrenia: results from two long-term follow-up studies. Neurol Psychiatry Brain Res 9:183–190
Harrow M, Grossman LS, Herbener ES, Davies EW (2000) Ten-year outcome: patients with schizoaffective disorders, schizophrenia, affective disorders and mood-incongruent psychotic symptoms. Br J Psychiatry 177:421–426. doi:10.1192/bjp.177.5.421
Acknowledgments
Dr. Sebastiano Pellerano, Dr. Marcella Abis and Dr. Maria Celeste Serci participated in data collection; Dr. Simona Corona helped with statistical analyses. Thanks to Dr. Mary Groeneweg for language editing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ledda, M.G., Fratta, A.L., Pintor, M. et al. Early-onset Psychoses: Comparison of Clinical Features and Adult Outcome in 3 Diagnostic Groups. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 40, 421–437 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-009-0134-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-009-0134-0