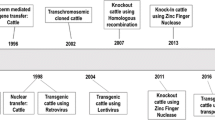
Abstract
Great strides in technological advancements have been made in the past decade in cattle genome engineering. First, the success of cloning cattle by somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) or chromatin transfer (CT) is a significant advancement that has made obsolete the need for using embryonic stem (ES) cells to conduct cell-mediated genome engineering, whereby site-specific genetic modifications can be conducted in bovine somatic cells via DNA homologous recombination (HR) and whereby genetically engineered cattle can subsequently be produced by animal cloning from the genetically modified cells. With this approach, a chosen bovine genomic locus can be precisely modified in somatic cells, such as to knock out (KO) or knock in (KI) a gene via HR, a gene-targeting strategy that had almost exclusively been used in mouse ES cells. Furthermore, by the creative application of embryonic cloning to rejuvenate somatic cells, cattle genome can be sequentially modified in the same line of somatic cells and complex genetic modifications have been achieved in cattle. Very recently, the development of designer nucleases—such as zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs) and transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALENs), and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (CRISPR/Cas9)—has enabled highly efficient and more facile genome engineering in cattle. Most notably, by employing such designer nucleases, genomes can be engineered at single-nucleotide precision; this process is now often referred to as genome or gene editing. The above achievements are a drastic departure from the traditional methods of creating genetically modified cattle, where foreign DNAs are randomly integrated into the animal genome, most often along with the integrations of bacterial or viral DNAs. Here, I review the most recent technological developments in cattle genome engineering by highlighting some of the major achievements in creating genetically engineered cattle for agricultural and biomedical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SCNT:
-
Somatic cell nuclear transfer
- CT:
-
Chromatin transfer
- ES:
-
Embryonic stem cells
- HR:
-
Homologous recombination
- KO:
-
Knock out
- KI:
-
Knock in
- PN:
-
Pronuclear
- CGH:
-
Comparative genomic hybridization
- ZFNs:
-
Zinc finger nucleases
- TALENs:
-
Transcription activator-like effector nuclease
- CRISPR/Cas9:
-
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9
- HDR:
-
Homology-directed repair
- NHEJ:
-
Nonhomologous end joining
- PGK:
-
Phosphoglycerate kinase-1
- ST SV40:
-
Promoter and thymidine kinase enhancer
- CAG:
-
Chicken beta-actin promoter with CMV enhancer
- HAC:
-
Human artificial chromosome
- Indel:
-
Insertion or deletion of DNA base pair(s)
- hEPO:
-
Human erythropoietin
- hSA:
-
Human serum albumin
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
References
Bachiller D, Schellander K, Peli J, Ruther U (1991) Liposome-mediated DNA uptake by sperm cells. Mol Reprod Dev 30:194–200
Bandaranayake AD, Almo SC (2014) Recent advances in mammalian protein production. FEBS Lett 588:253–60
Bosze Z, Baranyi M, Whitelaw CB (2008) Producing recombinant human milk proteins in the milk of livestock species. Adv Exp Med Biol 606:357–93
Carlson DF, Tan W, Lillico SG, Stverakova D, Proudfoot C, Christian M, Voytas DF, Long CR, Whitelaw CB, Fahrenkrug SC (2012) Efficient TALEN-mediated gene knockout in livestock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:17382–7
Carlson DF, Tan W, Hackett PB, Fahrenkrug SC (2013) Editing livestock genomes with site-specific nucleases. Reprod Fertil Dev 26:74–82
Carroll D (2011) Genome engineering with zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 188:773–82
Carroll D (2014) Genome engineering with targetable nucleases. Annu Rev Biochem 83:409–39
Cermak T, Doyle EL, Christian M, Wang L, Zhang Y, Schmidt C, Baller JA, Somia NV, Bogdanove AJ, Voytas DF (2011) Efficient design and assembly of custom TALEN and other TAL effector-based constructs for DNA targeting. Nucleic Acids Res 39:e82
Chan AW, Kukolj G, Skalka AM, Bremel RD (1999) Timing of DNA integration, transgenic mosaicism, and pronuclear microinjection. Mol Reprod Dev 52:406–13
Cibelli JB, Stice SL, Golueke PJ, Kane JJ, Jerry J, Blackwell C, Ponce De Leon FA, Robl JM (1998) Cloned transgenic calves produced from nonquiescent fetal fibroblasts. Science 280:1256–8
Donovan DM, Kerr DE, Wall RJ (2005) Engineering disease resistant cattle. Transgenic Res 14:563–7
Durai S, Mani M, Kandavelou K, Wu J, Porteus MH, Chandrasegaran S (2005) Zinc finger nucleases: custom-designed molecular scissors for genome engineering of plant and mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res 33:5978–90
Fan Z, Li W, Lee SR, Meng Q, Shi B, Bunch TD, White KL, Kong IK, Wang Z (2014) Efficient gene targeting in golden Syrian hamsters by the CRISPR/Cas9 system. PLoS One 9:e109755
Gaj T, Gersbach CA, Barbas CF 3rd (2013) Zfn, Talen, and CRISPR/Cas-based methods for genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol 31:397–405
Golovan SP, Meidinger RG, Ajakaiye A, Cottrill M, Wiederkehr MZ, Barney DJ, Plante C, Pollard JW, Fan MZ, Hayes MA, Laursen J, Hjorth JP, Hacker RR, Phillips JP, Forsberg CW (2001) Pigs expressing salivary phytase produce low-phosphorus manure. Nat Biotechnol 19:741–5
Gupta RM, Musunuru K (2014) Expanding the genetic editing tool kit: ZFNs, TALENs, and CRISPR-Cas9. J Clin Invest 124:4154–61
Hammer RE, Pursel VG, Rexroad CE Jr, Wall RJ, Bolt DJ, Ebert KM, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL (1985) Production of transgenic rabbits, sheep and pigs by microinjection. Nature 315:680–3
He Y, Ning T, Xie T, Qiu Q, Zhang L, Sun Y, Jiang D, Fu K, Yin F, Zhang W, Shen L, Wang H, Li J, Lin Q, Sun Y, Li H, Zhu Y, Yang D (2011) Large-scale production of functional human serum albumin from transgenic rice seeds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:19078–83
Heo, Y., Quan, X., Xu, Y., Baek, S., Choi, H., Kim, N. & KIM, J. (2014) CRISPR/Cas9 nuclease-mediated gene knock-in in bovine pluripotent stem cells and embryos. Stem Cells Dev. doi:10.1089/scd.2014.0278
Hofmann A, Kessler B, Ewerling S, Weppert M, Vogg B, Ludwig H, Stojkovic M, Boelhauve M, Brem G, Wolf E, Pfeifer A (2003) Efficient transgenesis in farm animals by lentiviral vectors. EMBO Rep 4:1054–60
Hsu PD, Lander ES, Zhang F (2014) Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell 157:1262–78
Kambadur R, Sharma M, Smith TP, Bass JJ (1997) Mutations in myostatin (GDF8) in double-muscled Belgian Blue and Piedmontese cattle. Genome Res 7:910–6
Kandavelou K, Chandrasegaran S (2009) Custom-designed molecular scissors for site-specific manipulation of the plant and mammalian genomes. Methods Mol Biol 544:617–36
Karatzas CN (2003) Designer milk from transgenic clones. Nat Biotechnol 21:138–9
Kim H, Kim JS (2014) A guide to genome engineering with programmable nucleases. Nat Rev Genet 15:321–34
Kim HJ, Lee HJ, Kim H, Cho SW, Kim JS (2009) Targeted genome editing in human cells with zinc finger nucleases constructed via modular assembly. Genome Res 19:1279–88
Koller BH, Smithies O (1992) Altering genes in animals by gene targeting. Annu Rev Immunol 10:705–30
Krimpenfort P, Rademakers A, Eyestone W, Van Der Schans A, Van Den Broek S, Kooiman P, Kootwijk E, Platenburg G, Pieper F, Strijker R et al (1991) Generation of transgenic dairy cattle using ‘in vitro’ embryo production. Biotechnology (N Y) 9:844–7
Kubisch HM, Larson MA, Eichen PA, Wilson JM, Roberts RM (1997) Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer by perivitelline microinjection of mouse, rat, and cow embryos. Biol Reprod 56:119–24
Kubota C, Tian XC, Yang X (2004) Serial bull cloning by somatic cell nuclear transfer. Nat Biotechnol 22:693–4
Kuroiwa Y, Kasinathan P, Matsushita H, Sathiyaselan J, Sullivan EJ, Kakitani M, Tomizuka K, Ishida I, ROBL JM (2004) Sequential targeting of the genes encoding immunoglobulin-mu and prion protein in cattle. Nat Genet 36:775–80
Kuroiwa Y, Kasinathan P, Sathiyaseelan T, Jiao JA, Matsushita H, Sathiyaseelan J, Wu H, Mellquist J, Hammitt M, Koster J, Kamoda S, Tachibana K, Ishida I, Robl JM (2009) Antigen-specific human polyclonal antibodies from hyperimmunized cattle. Nat Biotechnol 27:173–81
Lee S, Park H, Kong I, Wang Z (2013) 30 a transcription activator-like effector nuclease (Talen)-mediated universal gene knock-in strategy for mammary glands-specific expression of recombinant proteins in dairy cattle. Reprod Fertil Dev 26:129–129
Li T, Yang B (2013) TAL effector nuclease (TALEN) engineering. Methods Mol Biol 978:63–72
Liu GE, Hou Y, Robl JM, Kuroiwa Y, Wang Z (2011) Assessment of genome integrity with array CGH in cattle transgenic cell lines produced by homologous recombination and somatic cell cloning. Genome Integr 2:6
Liu X, Wang Y, Guo W, Chang B, Liu J, Guo Z, Quan F, Zhang Y (2013) Zinc-finger nickase-mediated insertion of the lysostaphin gene into the beta-casein locus in cloned cows. Nat Commun 4:2565
Liu X, Wang Y, Tian Y, Yu Y, Gao M, Hu G, Su F, Pan S, Luo Y, Guo Z, Quan F, Zhang Y (2014) Generation of mastitis resistance in cows by targeting human lysozyme gene to beta-casein locus using zinc-finger nucleases. Proc Biol Sci 281:20133368
Luo J, Song Z, Yu S, Cui D, Wang B, Ding F, Li S, Dai Y, Li N (2014) Efficient generation of myostatin (MSTN) biallelic mutations in cattle using zinc finger nucleases. PLoS One 9:e95225
Matsushita H, Sano A, Wu H, Jiao JA, Kasinathan P, Sullivan EJ, Wang Z, Kuroiwa Y (2014) Triple immunoglobulin gene knockout transchromosomic cattle: bovine lambda cluster deletion and its effect on fully human polyclonal antibody production. PLoS One 9:e90383
Mcpherron AC, Lee SJ (1997) Double muscling in cattle due to mutations in the myostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:12457–61
Moghaddassi S, Eyestone W, Bishop CE (2014) TALEN-mediated modification of the bovine genome for large-scale production of human serum albumin. PLoS One 9:e89631
Mussolino C, Morbitzer R, Lutge F, Dannemann N, Lahaye T, Cathomen T (2011) A novel TALE nuclease scaffold enables high genome editing activity in combination with low toxicity. Nucleic Acids Res 39:9283–93
Pasman Y, Saini SS, Smith E, Kaushik AK (2010) Organization and genomic complexity of bovine lambda-light chain gene locus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 135:306–13
Proudfoot, C., Carlson, D. F., Huddart, R., Long, C. R., Pryor, J. H., King, T. J., Lillico, S. G., Mileham, A. J., Mclaren, D. G., Whitelaw, C. B. & Fahrenkrug, S. C. 2014. Genome edited sheep and cattle. Transgenic Res. doi:10.1007/s11248-014-9832-x
Ramirez CL, Certo MT, Mussolino C, Goodwin MJ, Cradick TJ, Mccaffrey AP, Cathomen T, Scharenberg AM, Joung JK (2012) Engineered zinc finger nickases induce homology-directed repair with reduced mutagenic effects. Nucleic Acids Res 40:5560–8
Richt JA, Kasinathan P, Hamir AN, Castilla J, Sathiyaseelan T, Vargas F, Sathiyaseelan J, Wu H, Matsushita H, Koster J, Kato S, Ishida I, Soto C, Robl JM, Kuroiwa Y (2007) Production of cattle lacking prion protein. Nat Biotechnol 25:132–8
Robl JM, Wang Z, Kasinathan P, Kuroiwa Y (2007) Transgenic animal production and animal biotechnology. Theriogenology 67:127–33
Sander JD, Reyon D, Maeder ML, Foley JE, Thibodeau- Beganny S, LI X, Regan MR, Dahlborg EJ, Goodwin MJ, Fu F, Voytas DF, Joung JK, Dobbs D (2010) Predicting success of oligomerized pool engineering (OPEN) for zinc finger target site sequences. BMC Bioinform 11:543
Sano A, Matsushita H, Wu H, Jiao JA, Kasinathan P, Sullivan EJ, Wang Z, Kuroiwa Y (2013) Physiological level production of antigen-specific human immunoglobulin in cloned transchromosomic cattle. PLoS One 8:e78119
Sedivy JM, Sharp PA (1989) Positive genetic selection for gene disruption in mammalian cells by homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86:227–31
Selo I, Negroni L, Creminon C, Yvon M, Peltre G, Wal JM (1998) Allergy to bovine beta-lactoglobulin: specificity of human IgE using cyanogen bromide-derived peptides. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 117:20–8
Sendai Y, Sawada T, Urakawa M, Shinkai Y, Kubota K, Hoshi H, Aoyagi Y (2006) alpha1,3-Galactosyltransferase-gene knockout in cattle using a single targeting vector with loxP sequences and cre-expressing adenovirus. Transplantation 81:760–6
Sullivan EJ, Kasinathan S, Kasinathan P, Robl JM, Collas P (2004) Cloned calves from chromatin remodeled in vitro. Biol Reprod 70:146–53
Tan W, Carlson DF, Lancto CA, Garbe JR, Webster DA, Hackett PB, FAHRENKRUG SC (2013) Efficient nonmeiotic allele introgression in livestock using custom endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:16526–31
Wakayama T, Shinkai Y, Tamashiro KL, Niida H, Blanchard DC, Blanchard RJ, Ogura A, Tanemura K, Tachibana M, Perry AC, Colgan DF, Mombaerts P, Yanagimachi R (2000) Cloning of mice to six generations. Nature 407:318–9
Wall RJ, Kerr DE, Bondioli KR (1997) Transgenic dairy cattle: genetic engineering on a large scale. J Dairy Sci 80:2213–24
Wall RJ, Powell AM, Paape MJ, Kerr DE, Bannerman DD, Pursel VG, Wells KD, Talbot N, Hawk HW (2005) Genetically enhanced cows resist intramammary Staphylococcus aureus infection. Nat Biotechnol 23:445–51
Wang S, Zhang K, Ding F, Zhao R, Li S, Li R, Xu L, Song C, Dai Y, Li N (2013) A novel promoterless gene targeting vector to efficiently disrupt PRNP gene in cattle. J Biotechnol 163:377–85
Wright DA, LI T, Yang B, Spalding MH (2014) TALEN-mediated genome editing: prospects and perspectives. Biochem J 462:15–24
Wu J, Kandavelou K, Chandrasegaran S (2007) Custom-designed zinc finger nucleases: what is next? Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2933–44
Xu L, Zhao P, Mariano A, Han R (2013) Targeted myostatin gene editing in multiple mammalian species directed by a single pair of TALE nucleases. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2:e112
Yu S, Luo J, Song Z, Ding F, Dai Y, Li N (2011) Highly efficient modification of beta-lactoglobulin (BLG) gene via zinc-finger nucleases in cattle. Cell Res 21:1638–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editors: Natalay Kouprina and Vladimir Larionov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z. Genome engineering in cattle: recent technological advancements. Chromosome Res 23, 17–29 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-014-9452-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-014-9452-6