Abstract
Substance abuse is one of the significant problems in social and public health worldwide. Vast numbers of evidence illustrate that motivational and reinforcing impacts of addictive drugs are primarily attributed to their ability to change dopamine signaling in the reward circuit. However, the roles of classic neurotransmitters, especially dopamine and neuromodulators, monoamines, and neuropeptides, in reinforcing characteristics of abused drugs have been extensively investigated. It has recently been revealed that central immune signaling includes cascades of chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines released by neurons and glia via downstream intracellular signaling pathways that play a crucial role in mediating rewarding behavioral effects of drugs. More interestingly, inflammatory responses in the central nervous system modulate the mesolimbic dopamine signaling and glutamate-dependent currents induced by addictive drugs. This review summarized researches in the alterations of inflammatory responses accompanied by rewarding and reinforcing properties of addictive drugs, including cocaine, methamphetamine, and opioids that were evaluated by conditioned place preference and self-administration procedures as highly common behavioral tests to investigate the motivational and reinforcing impacts of addictive drugs.
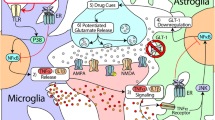
Graphical Abstract

The neuroinflammatory responses affect the rewarding properties of psychostimulants and opioids.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- BLA:
-
Basolateral amygdala
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CPP:
-
Conditioned place preference
- CCR:
-
CC chemokines
- CCL2/MCP-1:
-
Chemokine monocyte chemotactic protein-1
- CXCR:
-
CXC chemokines
- CX3CR1:
-
CX3C-receptor 1
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
- GDNF:
-
Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- KO:
-
Knockout
- MyD88:
-
Myeloid differentiation factor 88
- NSAID:
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κβ
- NAc:
-
Nucleus accumbens
- PRRs:
-
Pattern recognition receptors
- PDE:
-
Phosphodiesterase
- PFC:
-
Prefrontal cortex
- SA:
-
Self-administration
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- TLRs:
-
Toll-like receptors
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- VTA:
-
Ventral tegmental area
- WT:
-
Wild-type
References
Alizamini MM, Kavianpour M, Karimi-Haghighi S, Fatahi Z, Haghparast A (2018) Intra-hippocampal administration of orexin receptor antagonists dose-dependently attenuates reinstatement of morphine seeking behavior in extinguished rats. Peptides 110:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2018.10.011
Arezoomandan R, Haghparast A (2016) Administration of the glial cell modulator, minocycline, in the nucleus accumbens attenuated the maintenance and reinstatement of morphine-seeking behavior. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 94(3):257–264. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2015-0209
Attarzadeh-Yazdi G, Karimi S, Azizi P, Yazdi-Ravandi S, Hesam S, Haghparast A (2013) Inhibitory effects of forced swim stress and corticosterone on the acquisition but not expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference: involvement of glucocorticoid receptor in the basolateral amygdala. Behav Brain Res 252:339–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.06.018
Attarzadeh-Yazdi G, Arezoomandan R, Haghparast A (2014) Minocycline, an antibiotic with inhibitory effect on microglial activation, attenuates the maintenance and reinstatement of methamphetamine-seeking behavior in rat. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 53:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.04.008
Azam S, Jakaria M, Kim IS, Kim J, Haque ME, Choi DK (2019) Regulation of toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway by polyphenols in the treatment of age-linked neurodegenerative diseases: focus on TLR4 signaling. Front Immunol 10:1000. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01000
Backstrom P, Hyytia P (2007) Involvement of AMPA/kainate, NMDA, and mGlu5 receptors in the nucleus accumbens core in cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 192(4):571–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0753-8
Baik JH (2020) Stress and the dopaminergic reward system. Exp Mol Med 52(12):1879–1890. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-00532-4
Ballestín R, Alegre-Zurano L, Ferrer-Pérez C, Cantacorps L, Miñarro J, Valverde O, Rodríguez-Arias M (2020) Neuroinflammatory and behavioral susceptibility profile of mice exposed to social stress towards cocaine effects. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 105:110123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.110123
Banisadr G, Fontanges P, Haour F, Kitabgi P, Rostène W, Mélik Parsadaniantz S (2002) Neuroanatomical distribution of CXCR4 in adult rat brain and its localization in cholinergic and dopaminergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 16(9):1661–1671. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02237.x
Banjara M, Ghosh C (2017) Sterile neuroinflammation and strategies for therapeutic intervention. Int J Inflamm. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8385961
Bardo MT (1998) Neuropharmacological mechanisms of drug reward: beyond dopamine in the nucleus accumbens. Crit Rev Neurobiol 12(1–2):37–67. https://doi.org/10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v12.i1-2.30
Bauer ME, Teixeira AL (2019) Inflammation in psychiatric disorders: what comes first? Ann N Y Acad Sci 1437(1):57–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13712
Beardsley PM, Shelton KL, Hendrick E, Johnson KW (2010) The glial cell modulator and phosphodiesterase inhibitor, AV411 (ibudilast), attenuates prime- and stress-induced methamphetamine relapse. Eur J Pharmacol 637(1–3):102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.04.010
Becher B, Spath S, Goverman J (2017) Cytokine networks in neuroinflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 17(1):49–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.123
Bell RL, Lopez MF, Cui C, Egli M, Johnson KW, Franklin KM, Becker HC (2015) Ibudilast reduces alcohol drinking in multiple animal models of alcohol dependence. Addict Biol 20(1):38–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12106
Benjamins JA (2013) Direct effects of secretory products of immune cells on neurons and glia. J Neurol Sci 333(1):30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2013.06.001
Ben-Shaanan TL, Azulay-Debby H, Dubovik T, Starosvetsky E, Korin B, Schiller M et al (2016) Activation of the reward system boosts innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Med 22(8):940–944. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4133
Blednov YA, Da Costa AJ, Tarbox T, Ponomareva O, Messing RO, Harris RA (2018) Apremilast alters behavioral responses to ethanol in mice: I. reduced consumption and preference. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 42(5):926–938. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.13616
Bowman GL, Dayon L, Kirkland R, Wojcik J, Peyratout G, Severin IC et al (2018) Blood-brain barrier breakdown, neuroinflammation, and cognitive decline in older adults. Alzheimers Dement 14(12):1640–1650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2018.06.2857
Brady LJ, Hofford RS, Tat J, Calipari ES, Kiraly DD (2019) Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor alters the pharmacodynamic properties of cocaine in female mice. ACS Chem Neurosci 10(10):4213–4220. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00309
Broadbear JH, Winger G, Woods JH (2004) Self-administration of fentanyl, cocaine and ketamine: effects on the pituitary-adrenal axis in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 176(3–4):398–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1891-x
Burkovetskaya ME, Liu Q, Vadukoot AK, Gautam N, Alnouti Y, Kumar S et al (2020) KVA-D-88, a novel preferable phosphodiesterase 4B inhibitor, decreases cocaine-mediated reward properties in vivo. ACS Chem Neurosci 11(15):2231–2242. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00170
Calipari ES, Godino A, Peck EG, Salery M, Mervosh NL, Landry JA et al (2018) Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor controls neural and behavioral plasticity in response to cocaine. Nat Commun 9(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01881-x
Cannella LA, Andrews AM, Tran F, Razmpour R, McGary H, Collie C et al (2020) Experimental traumatic brain injury during adolescence enhances cocaine rewarding efficacy and dysregulates dopamine and neuroimmune systems in brain reward substrates. J Neurotrauma 37(1):27–42. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2019.6472
Carboni E, Spielewoy C, Vacca C, Nosten-Bertrand M, Giros B, Di Chiara G (2001) Cocaine and amphetamine increase extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens of mice lacking the dopamine transporter gene. J Neurosci 21(9):RC141–RC144. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-09-j0001.2001
Carroll ME, Campbell UC, Heideman P (2001) Ketoconazole suppresses food restriction-induced increases in heroin self-administration in rats: sex differences. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 9(3):307–316. https://doi.org/10.1037//1064-1297.9.3.307
Chavoshinezhad S, Mohseni Kouchesfahani H, Salehi MS, Pandamooz S, Ahmadiani A, Dargahi L (2019) Intranasal interferon beta improves memory and modulates inflammatory responses in a mutant APP-overexpressing rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res Bull 150:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.06.015
Chen JX, Huang KM, Liu M, Jiang JX, Liu JP, Zhang YX et al (2017) Activation of TLR4/STAT3 signaling in VTA contributes to the acquisition and maintenance of morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Behav Brain Res 335:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.08.022
Choi DY, Lee MK, Hong JT (2013) Lack of CCR5 modifies glial phenotypes and population of the nigral dopaminergic neurons, but not MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 49:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2012.08.001
Contarino A, Kitchener P, Vallée M, Papaleo F, Piazza PV (2017) CRF(1) receptor-deficiency increases cocaine reward. Neuropharmacology 117:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.01.024
Cooper S, Robison AJ, Mazei-Robison MS (2017) Reward circuitry in addiction. Neurotherapeutics 14(3):687–697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-017-0525-z
Covington HE 3rd, Miczek KA (2005) Intense cocaine self-administration after episodic social defeat stress, but not after aggressive behavior: dissociation from corticosterone activation. Psychopharmacology 183(3):331–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0190-5
Cui C, Shurtleff D, Harris RA (2014) Neuroimmune mechanisms of alcohol and drug addiction. Int Rev Neurobiol 118:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-801284-0.00001-4
Der-Avakian A, Will MJ, Bland ST, Deak T, Nguyen KT, Schmid MJ et al (2005) Surgical and pharmacological suppression of glucocorticoids prevents the enhancement of morphine conditioned place preference by uncontrollable stress in rats. Psychopharmacology 179(2):409–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2041-1
Der-Avakian A, Bland ST, Schmid MJ, Watkins LR, Spencer RL, Maier SF (2006) The role of glucocorticoids in the uncontrollable stress-induced potentiation of nucleus accumbens shell dopamine and conditioned place preference responses to morphine. Psychoneuroendocrinology 31(5):653–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2006.02.004
Dhaiban S, Al-Ani M, Elemam NM, Al-Aawad MH, Al-Rawi Z, Maghazachi AA (2021) Role of peripheral immune cells in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Sci 3(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.02.015
Di Vito A, Donato G, Tomassoni D (2017) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of neuroinflammation. Biomed Res Int 2017:8417183. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8417183
Dietz D, Wang H, Kabbaj M (2007) Corticosterone fails to produce conditioned place preference or conditioned place aversion in rats. Behav Brain Res 181(2):287–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2007.04.005
Dong Z, Han H, Wang M, Xu L, Hao W, Cao J (2006) Morphine conditioned place preference depends on glucocorticoid receptors in both hippocampus and nucleus accumbens. Hippocampus 16(10):809–813. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20216
Erb S, Shaham Y, Stewart J (1998) The role of corticotropin-releasing factor and corticosterone in stress- and cocaine-induced relapse to cocaine seeking in rats. J Neurosci 18(14):5529–5536. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.18-14-05529.1998
Faure J, Stein DJ, Daniels W (2009) Maternal separation fails to render animals more susceptible to methamphetamine-induced conditioned place preference. Metab Brain Dis 24(4):541–559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-009-9158-1
Ferrer-Pérez C, Escrivá-Martinez T, Montagud-Romero S, Ballestín R, Reguilón MD, Miñarro J, Rodríguez-Arias M (2019a) Correction: Indomethacin blocks the increased conditioned rewarding effects of cocaine induced by repeated social defeat. PLoS ONE 14(2):e0212397. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212397
Ferrer-Pérez C, Reguilón MD, Manzanedo C, Miñarro J, Rodríguez-Arias M (2019b) Social housing conditions modulate the long-lasting increase in cocaine reward induced by intermittent social defeat. Front Behav Neurosci 13:148. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00148
Fitzgerald KA, Kagan JC (2020) Toll-like receptors and the control of immunity. Cell 180(6):1044–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.041
Flagel SB, Vázquez DM, Robinson TE (2003) Manipulations during the second, but not the first, week of life increase susceptibility to cocaine self-administration in female rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 28(10):1741–1751. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300228
Fujita Y, Kunitachi S, Iyo M, Hashimoto K (2012) The antibiotic minocycline prevents methamphetamine-induced rewarding effects in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 101(2):303–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2012.01.005
Gallistel CR, Shizgal P, Yeomans JS (1981) A portrait of the substrate for self-stimulation. Psychol Rev 88(3):228–273. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295x.88.3.228
Ganguly P, Honeycutt JA, Rowe JR, Demaestri C, Brenhouse HC (2019) Effects of early life stress on cocaine conditioning and AMPA receptor composition are sex-specific and driven by TNF. Brain Behav Immun 78:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.01.006
Gao YJ, Ji RR (2010) Chemokines, neuronal-glial interactions, and central processing of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Ther 126(1):56–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.01.002
Gao SQ, Zhang H, He JG, Zheng HL, Zhang PW, Xu JF et al (2020) Neuronal HMGB1 in nucleus accumbens regulates cocaine reward memory. Addict Biol 25(2):e12739. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12739
Gardner EL (2011) Addiction and brain reward and antireward pathways. Adv Psychosom Med 30:22–60. https://doi.org/10.1159/000324065
Ghahremani MH, Eghtesad E, Tahsili-Fahadan P, Sharifzadeh M, Amini M, Tootian Z (2006) Inhibition of the cyclooxygenase pathway attenuates morphine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85(2):356–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2006.09.002
Glabinski AR, Ransohoff RM (2003) Roles of chemokines and their receptors in neuroinflammation. In: Wood PL (ed) Neuroinflammation: mechanisms and management. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 99–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59259-297-5_4
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, Marchetto MC, Gage FH (2010) Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 140(6):918–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.016
Goeders NE, Clampitt DM (2002) Potential role for the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in the conditioned reinforcer-induced reinstatement of extinguished cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 161(3):222–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1007-4
Goeders NE, Guerin GF (1996) Effects of surgical and pharmacological adrenalectomy on the initiation and maintenance of intravenous cocaine self-administration in rats. Brain Res 722(1–2):145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(96)00206-5
Goeders NE, Peltier RL, Guerin GF (1998) Ketoconazole reduces low dose cocaine self-administration in rats. Drug Alcohol Depend 53(1):67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0376-8716(98)00108-2
Graf EN, Wheeler RA, Baker DA, Ebben AL, Hill JE, McReynolds JR et al (2013) Corticosterone acts in the nucleus accumbens to enhance dopamine signaling and potentiate reinstatement of cocaine seeking. J Neurosci 33(29):11800–11810. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1969-13.2013
Guyon A, Skrzydelski D, De Giry I, Rovère C, Conductier G, Trocello JM et al (2009) Long term exposure to the chemokine CCL2 activates the nigrostriatal dopamine system: a novel mechanism for the control of dopamine release. Neuroscience 162(4):1072–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.05.048
Harrison JK, Jiang Y, Chen S, Xia Y, Maciejewski D, McNamara RK et al (1998) Role for neuronally derived fractalkine in mediating interactions between neurons and CX3CR1-expressing microglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(18):10896–10901. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.18.10896
He J, Crews FT (2008) Increased MCP-1 and microglia in various regions of the human alcoholic brain. Exp Neurol 210(2):349–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.11.017
Hernández-Flórez D, Valor L (2016) Selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors: a new therapeutic option in inflammation and autoimmunity. Reumatol Clin 12(6):303–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reuma.2016.07.011 (Inhibidores selectivos de fosfodiesterasas, una nueva opción terapéutica en inflamación y autoinmunidad.)
Hofford RS, Prendergast MA, Bardo MT (2015) Pharmacological manipulation of glucocorticoid receptors differentially affects cocaine self-administration in environmentally enriched and isolated rats. Behav Brain Res 283:196–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.01.049
Hofford RS, Prendergast MA, Bardo MT (2018) Modified single prolonged stress reduces cocaine self-administration during acquisition regardless of rearing environment. Behav Brain Res 338:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.10.023
Homberg JR, van den Akker M, Raasø HS, Wardeh G, Binnekade R, Schoffelmeer AN, de Vries TJ (2002) Enhanced motivation to self-administer cocaine is predicted by self-grooming behaviour and relates to dopamine release in the rat medial prefrontal cortex and amygdala. Eur J Neurosci 15(9):1542–1550. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.01976.x
Hong SI, Nguyen TL, Ma SX, Kim HC, Lee SY, Jang CG (2017) TRPV1 modulates morphine-induced conditioned place preference via p38 MAPK in the nucleus accumbens. Behav Brain Res 334:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.07.017
Hu W, Lu T, Chen A, Huang Y, Hansen R, Chandler LJ, Zhang HT (2011) Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 decreases ethanol intake in mice. Psychopharmacology 218(2):331–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2290-8
Hutchinson MR, Watkins LR (2014) Why is neuroimmunopharmacology crucial for the future of addiction research? Neuropharmacology 76:218–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.05.039
Hutchinson MR, Northcutt AL, Chao LW, Kearney JJ, Zhang Y, Berkelhammer DL et al (2008) Minocycline suppresses morphine-induced respiratory depression, suppresses morphine-induced reward, and enhances systemic morphine-induced analgesia. Brain Behav Immun 22(8):1248–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2008.07.008
Hutchinson MR, Northcutt AL, Hiranita T, Wang X, Lewis SS, Thomas J et al (2012) Opioid activation of toll-like receptor 4 contributes to drug reinforcement. J Neurosci 32(33):11187–11200. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0684-12.2012
Kampman KM (2019) The treatment of cocaine use disorder. Sci Adv 5(10):eaax1532. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aax1532
Karimi S, Attarzadeh-Yazdi G, Yazdi-Ravandi S, Hesam S, Azizi P, Razavi Y, Haghparast A (2014) Forced swim stress but not exogenous corticosterone could induce the reinstatement of extinguished morphine conditioned place preference in rats: involvement of glucocorticoid receptors in the basolateral amygdala. Behav Brain Res 264:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.01.045
Karimi-Haghighi S, Dargahi L, Haghparast A (2020) Cannabidiol modulates the expression of neuroinflammatory factors in stress- and drug-induced reinstatement of methamphetamine in extinguished rats. Addict Biol 25(2):e12740. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12740
Kashima DT, Grueter BA (2017) Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency alters nucleus accumbens synaptic physiology and drug reward behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(33):8865–8870. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1705974114
Kawasaki Y, Zhang L, Cheng JK, Ji RR (2008) Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. J Neurosci 28(20):5189–5194. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3338-07.2008
Keller CM, Cornett EM, Guerin GF, Goeders NE (2013) Combinations of oxazepam and metyrapone attenuate cocaine and methamphetamine cue reactivity. Drug Alcohol Depend 133(2):405–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2013.06.025
Kennedy RH, Silver R (2016) Neuroimmune signaling: cytokines and the CNS. In: Pfaff DW, Volkow ND (eds) Neuroscience in the 21st century. Springer New York, New York, pp 1–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6434-1_174-1
Kigerl KA, de Rivero Vaccari JP, Dietrich WD, Popovich PG, Keane RW (2014) Pattern recognition receptors and central nervous system repair. Exp Neurol 258:5–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.01.001
Kim J, Connelly KL, Unterwald EM, Rawls SM (2017) Chemokines and cocaine: CXCR4 receptor antagonist AMD3100 attenuates cocaine place preference and locomotor stimulation in rats. Brain Behav Immun 62:30–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.08.015
Knapp CM, Foye MM, Ciraulo DA, Kornetsky C (1999) The type IV phosphodiesterase inhibitors, Ro 20–1724 and rolipram, block the initiation of cocaine self-administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 62(1):151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0091-3057(98)00154-3
Kölliker-Frers R, Udovin L, Otero-Losada M, Kobiec T, Herrera MI, Palacios J et al (2021) Neuroinflammation: an integrating overview of reactive-neuroimmune cell interactions in health and disease. Mediat Inflamm. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9999146
Kosten TA, Miserendino MJ, Kehoe P (2000) Enhanced acquisition of cocaine self-administration in adult rats with neonatal isolation stress experience. Brain Res 875(1–2):44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02595-6
Kubera M, Filip M, Budziszewska B, Basta-Kaim A, Wydra K, Leskiewicz M et al (2008) Immunosuppression induced by a conditioned stimulus associated with cocaine self-administration. J Pharmacol Sci 107(4):361–369. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.fp0072106
Lacagnina MJ, Kopec AM, Cox SS, Hanamsagar R, Wells C, Slade S et al (2017) Opioid self-administration is attenuated by early-life experience and gene therapy for anti-inflammatory IL-10 in the nucleus accumbens of male rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 42(11):2128–2140. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.82
Lai M, Zhu H, Sun A, Zhuang D, Fu D, Chen W et al (2014) The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor rolipram attenuates heroin-seeking behavior induced by cues or heroin priming in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17(9):1397–1407. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1461145714000595
Le Thuc O, Stobbe K, Cansell C, Nahon JL, Blondeau N, Rovère C (2017) Hypothalamic inflammation and energy balance disruptions: spotlight on chemokines. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 8:197. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00197
Ledeboer A, Sloane EM, Milligan ED, Frank MG, Mahony JH, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2005) Minocycline attenuates mechanical allodynia and proinflammatory cytokine expression in rat models of pain facilitation. Pain 115(1–2):71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2005.02.009
Lee B, Tiefenbacher S, Platt DM, Spealman RD (2003) Role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in squirrel monkeys. Psychopharmacology 168(1–2):177–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1391-4
Lewitus GM, Konefal SC, Greenhalgh AD, Pribiag H, Augereau K, Stellwagen D (2016) Microglial TNF-α suppresses cocaine-induced plasticity and behavioral sensitization. Neuron 90(3):483–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.03.030
Liddie S, Anderson KL, Paz A, Itzhak Y (2012) The effect of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on the extinction of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. J Psychopharmacol 26(10):1375–1382. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881112447991
Lim G, Kim H, McCabe MF, Chou CW, Wang S, Chen LL et al (2014) A leptin-mediated central mechanism in analgesia-enhanced opioid reward in rats. J Neurosci 34(29):9779–9788. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0386-14.2014
Lin KY, Cherng CG, Yang FR, Lin LC, Lu RB, Yu L (2011) Memantine abolishes the formation of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference possibly via its IL-6-modulating effect in medial prefrontal cortex. Behav Brain Res 220(1):126–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.01.031
Liu X, Hao PD, Yang MF, Sun JY, Mao LL, Fan CD et al (2017) The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor roflumilast decreases ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology 234(16):2409–2419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4631-8
Liu H, Wei J, Liu M, Wu S, Ma C, Liu C et al (2018) Epigenetic upregulation of CXCL12 expression contributes to the acquisition and maintenance of morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Exp Neurol 306:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.04.013
Liu JF, Tian J, Li JX (2019) Modulating reconsolidation and extinction to regulate drug reward memory. Eur J Neurosci 50(3):2503–2512. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.14072
Liu GX, Wei JY, Liu M, Shi WJ, Song LH, Li S et al (2020) Epigenetic upregulation of hippocampal CXCL12 contributes to context spatial memory-associated morphine conditioning. Brain Behav Immun 84:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.11.009
Long-Smith CM, Collins L, Toulouse A, Sullivan AM, Nolan YM (2010) Interleukin-1beta contributes to dopaminergic neuronal death induced by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat glia in vitro. J Neuroimmunol 226(1–2):20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.05.030
Mantsch JR, Goeders NE (1999) Ketoconazole blocks the stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats: relationship to the discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine. Psychopharmacology 142(4):399–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050905
Mantsch JR, Schlussman SD, Ho A, Kreek MJ (2000) Effects of cocaine self-administration on plasma corticosterone and prolactin in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294(1):239–247
Marshall JF, O’Dell SJ (2012) Methamphetamine influences on brain and behavior: unsafe at any speed? Trends Neurosci 35(9):536–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2012.05.006
Matzeu A, Zamora-Martinez ER, Martin-Fardon R (2014) The paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus is recruited by both natural rewards and drugs of abuse: recent evidence of a pivotal role for orexin/hypocretin signaling in this thalamic nucleus in drug-seeking behavior. Front Behav Neurosci 8:117. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00117
McReynolds JR, Taylor A, Vranjkovic O, Ambrosius T, Derricks O, Nino B et al (2017) Corticosterone potentiation of cocaine-induced reinstatement of conditioned place preference in mice is mediated by blockade of the organic cation transporter 3. Neuropsychopharmacology 42(3):757–765. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2016.187
Mediouni S, Jablonski J, Paris JJ, Clementz MA, Thenin-Houssier S, McLaughlin JP, Valente ST (2015) Didehydro-cortistatin A inhibits HIV-1 Tat mediated neuroinflammation and prevents potentiation of cocaine reward in Tat transgenic mice. Curr HIV Res 13(1):64–79. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570162x13666150121111548
Meng S, Quan W, Qi X, Su Z, Yang S (2014) Effect of baclofen on morphine-induced conditioned place preference, extinction, and stress-induced reinstatement in chronically stressed mice. Psychopharmacology 231(1):27–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3204-8
Merkel SF, Razmpour R, Lutton EM, Tallarida CS, Heldt NA, Cannella LA et al (2017) Adolescent traumatic brain injury induces chronic mesolimbic neuroinflammation with concurrent enhancement in the rewarding effects of cocaine in mice during adulthood. J Neurotrauma 34(1):165–181. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2015.4275
Mizuno T, Kawanokuchi J, Numata K, Suzumura A (2003) Production and neuroprotective functions of fractalkine in the central nervous system. Brain Res 979(1–2):65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(03)02867-1
Moffett MC, Goeders NE (2005) Neither non-contingent electric footshock nor administered corticosterone facilitate the acquisition of methamphetamine self-administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 80(2):333–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2004.12.003
MohanKumar SM, MohanKumar PS, Quadri SK (1998) Specificity of interleukin-1beta-induced changes in monoamine concentrations in hypothalamic nuclei: blockade by interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Brain Res Bull 47(1):29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0361-9230(98)00037-9
Montagud-Romero S, Montesinos J, Pavón FJ, Blanco-Gandia MC, Ballestín R, Rodríguez de Fonseca F et al (2020a) Social defeat-induced increase in the conditioned rewarding effects of cocaine: role of CX3CL1. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 96:109753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109753
Montagud-Romero S, Reguilón MD, Pascual M, Blanco-Gandía MC, Guerri C, Miñarro J, Rodríguez-Arias M (2020b) Critical role of TLR4 in uncovering the increased rewarding effects of cocaine and ethanol induced by social defeat in male mice. Neuropharmacology 182:108368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108368
Montesinos J, Castilla-Ortega E, Sánchez-Marín L, Montagud-Romero S, Araos P, Pedraz M et al (2020) Cocaine-induced changes in CX(3)CL1 and inflammatory signaling pathways in the hippocampus: Association with IL1β. Neuropharmacology 162:107840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107840
Motahari AA, Sahraei H, Meftahi GH (2016) Role of nitric oxide on dopamine release and morphine-dependency. Basic Clin Neurosci 7(4):283–290. https://doi.org/10.15412/j.Bcn.03070401
Mu Y, Ren Z, Jia J, Gao B, Zheng L, Wang G et al (2014) Inhibition of phosphodiesterase10A attenuates morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Mol Brain 7:70. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-014-0070-1
Müller T, Engels P, Fozard JR (1996) Subtypes of the type 4 cAMP phosphodiesterases: structure, regulation and selective inhibition. Trends Pharmacol Sci 17(8):294–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-6147(96)10035-3
Nayak SU, Cicalese S, Tallarida C, Oliver CF, Rawls SM (2020) Chemokine CCR5 and cocaine interactions in the brain: cocaine enhances mesolimbic CCR5 mRNA levels and produces place preference and locomotor activation that are reduced by a CCR5 antagonist. Brain Behav Immun 83:288–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.09.017
Nestler EJ (2004) Historical review: molecular and cellular mechanisms of opiate and cocaine addiction. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25(4):210–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2004.02.005
Niwa M, Nitta A, Yamada Y, Nakajima A, Saito K, Seishima M et al (2007a) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and its inducer inhibit morphine-induced rewarding effects and sensitization. Biol Psychiatry 62(6):658–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.10.009
Niwa M, Nitta A, Yamada Y, Nakajima A, Saito K, Seishima M et al (2007b) An inducer for glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and tumor necrosis factor-alpha protects against methamphetamine-induced rewarding effects and sensitization. Biol Psychiatry 61(7):890–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.06.016
Noda M, Doi Y, Liang J, Kawanokuchi J, Sonobe Y, Takeuchi H et al (2011) Fractalkine attenuates excito-neurotoxicity via microglial clearance of damaged neurons and antioxidant enzyme heme oxygenase-1 expression. J Biol Chem 286(3):2308–2319. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.169839
Northcutt AL, Hutchinson MR, Wang X, Baratta MV, Hiranita T, Cochran TA et al (2015) DAT isn’t all that: cocaine reward and reinforcement require toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Mol Psychiatry 20(12):1525–1537. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.177
Olds J (1962) Hypothalamic substrates of reward. Physiol Rev 42:554–604. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1962.42.4.554
Olds J, Milner P (1954) Positive reinforcement produced by electrical stimulation of septal area and other regions of rat brain. J Comp Physiol Psychol 47(6):419–427. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0058775
Orso R, Creutzberg KC, Centeno-Silva A, Carapeços MS, Levandowski ML, Wearick-Silva LE et al (2017) NFκB1 and NFκB2 gene expression in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of early life stressed mice exposed to cocaine-induced conditioned place preference during adolescence. Neurosci Lett 658:27–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.08.032
Palamarchouk V, Smagin G, Goeders NE (2009) Self-administered and passive cocaine infusions produce different effects on corticosterone concentrations in the medial prefrontal cortex (MPC) of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94(1):163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2009.08.003
Paolicelli RC, Bisht K, Tremblay M (2014) Fractalkine regulation of microglial physiology and consequences on the brain and behavior. Front Cell Neurosci 8:129. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2014.00129
Piazza PV, Marinelli M, Jodogne C, Deroche V, Rougé-Pont F, Maccari S et al (1994) Inhibition of corticosterone synthesis by Metyrapone decreases cocaine-induced locomotion and relapse of cocaine self-administration. Brain Res 658(1–2):259–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(09)90034-8
Pogun S, Baumann MH, Kuhar MJ (1994) Nitric oxide inhibits [3H]dopamine uptake. Brain Res 641(1):83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(94)91818-x
Rivera PD, Hanamsagar R, Kan MJ, Tran PK, Stewart D, Jo YC et al (2019) Removal of microglial-specific MyD88 signaling alters dentate gyrus doublecortin and enhances opioid addiction-like behaviors. Brain Behav Immun 76:104–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2018.11.010
Robb CT, Goepp M, Rossi AG, Yao C (2020) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins, and COVID-19. Br J Pharmacol 177(21):4899–4920. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15206
Robison LS, Alessi L, Thanos PK (2018) Chronic forced exercise inhibits stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine conditioned place preference. Behav Brain Res 353:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.07.009
Rodríguez-Arias M, Montagud-Romero S, Guardia Carrión AM, Ferrer-Pérez C, Pérez-Villalba A, Marco E et al (2018) Social stress during adolescence activates long-term microglia inflammation insult in reward processing nuclei. PLoS ONE 13(10):e0206421. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0206421
Rodríguez-Gómez JA, Kavanagh E, Engskog-Vlachos P, Engskog MK, Herrera AJ, Espinosa-Oliva AM et al (2020) Microglia: agents of the CNS pro-inflammatory response. Cells 9(7):1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071717
Rossi D, Zlotnik A (2000) The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 18:217–242. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.217
Saika F, Kiguchi N, Wakida N, Kobayashi D, Fukazawa Y, Matsuzaki S, Kishioka S (2018a) Upregulation of CCL7 and CCL2 in reward system mediated through dopamine D1 receptor signaling underlies methamphetamine-induced place preference in mice. Neurosci Lett 665:33–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.11.042
Saika F, Matsuzaki S, Kobayashi D, Kiguchi N, Kishioka S (2018b) Chemokine CXCL1 is responsible for cocaine-induced reward in mice. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep 38(3):145–148. https://doi.org/10.1002/npr2.12018
Schmidt HD, Mietlicki-Baase EG, Ige KY, Maurer JJ, Reiner DJ, Zimmer DJ et al (2016) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation in the ventral tegmental area decreases the reinforcing efficacy of cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 41(7):1917–1928. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.362
Schmoutz CD, Guerin GF, Runyon SP, Dhungana S, Goeders NE (2015) A therapeutic combination of metyrapone and oxazepam increases brain levels of GABA-active neurosteroids and decreases cocaine self-administration in male rats. Behav Brain Res 291:108–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.05.019
Schwarz JM, Hutchinson MR, Bilbo SD (2011) Early-life experience decreases drug-induced reinstatement of morphine CPP in adulthood via microglial-specific epigenetic programming of anti-inflammatory IL-10 expression. J Neurosci 31(49):17835–17847. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3297-11.2011
Seematter G, Binnert C, Martin JL, Tappy L (2004) Relationship between stress, inflammation and metabolism. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 7(2):169–173. https://doi.org/10.1097/00075197-200403000-00011
Shalev U, Marinelli M, Baumann MH, Piazza PV, Shaham Y (2003) The role of corticosterone in food deprivation-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in the rat. Psychopharmacology 168(1–2):170–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1200-5
Shalev U, Finnie PS, Quinn T, Tobin S, Wahi P (2006) A role for corticotropin-releasing factor, but not corticosterone, in acute food-deprivation-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 187(3):376–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0427-y
Shintani F, Kanba S, Nakaki T, Nibuya M, Kinoshita N, Suzuki E et al (1993) Interleukin-1 beta augments release of norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin in the rat anterior hypothalamus. J Neurosci 13(8):3574–3581. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.13-08-03574.1993
Skrzydelski D, Guyon A, Daugé V, Rovère C, Apartis E, Kitabgi P et al (2007) The chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCL12 activates the nigrostriatal dopamine system. J Neurochem 102(4):1175–1183. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04639.x
Snider SE, Hendrick ES, Beardsley PM (2013) Glial cell modulators attenuate methamphetamine self-administration in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 701(1–3):124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.01.016
Stellwagen D, Beattie EC, Seo JY, Malenka RC (2005) Differential regulation of AMPA receptor and GABA receptor trafficking by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Neurosci 25(12):3219–3228. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4486-04.2005
Stringfield SJ, Higginbotham JA, Wang R, Berger AL, McLaughlin RJ, Fuchs RA (2017) Role of glucocorticoid receptor-mediated mechanisms in cocaine memory enhancement. Neuropharmacology 123:349–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.05.022
Szepesi Z, Manouchehrian O, Bachiller S, Deierborg T (2018) Bidirectional microglia–neuron communication in health and disease. Front Cell Neurosci 12:323. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00323
Theberge FR, Li X, Kambhampati S, Pickens CL, St Laurent R, Bossert JM et al (2013) Effect of chronic delivery of the Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist (+)-naltrexone on incubation of heroin craving. Biol Psychiatry 73(8):729–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.12.019
Thompson BE, Sachs BD, Kantak KM, Cherry JA (2004) The type IV phosphodiesterase inhibitor rolipram interferes with drug-induced conditioned place preference but not immediate early gene induction in mice. Eur J Neurosci 19(9):2561–2568. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0953-816X.2004.03357.x
Tikka T, Fiebich BL, Goldsteins G, Keinanen R, Koistinaho J (2001) Minocycline, a tetracycline derivative, is neuroprotective against excitotoxicity by inhibiting activation and proliferation of microglia. J Neurosci 21(8):2580–2588. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.21-08-02580.2001
Tohidpour A, Morgun AV, Boitsova EB, Malinovskaya NA, Martynova GP, Khilazheva ED et al (2017) Neuroinflammation and infection: molecular mechanisms associated with dysfunction of neurovascular unit. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:276. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00276
Vaseghi S, Zarrabian S, Haghparast A (2022) Reviewing the role of the orexinergic system and stressors in modulating mood and reward-related behaviors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 133:104516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.104516
Vatankhah M, Karimi-Haghighi S, Sarihi A, Haghparast A (2018) Intra-accumbal administration of AMN082, a metabotropic glutamate receptor type 7 allosteric agonist, inhibits the acquisition but not the expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in rats. Neurosci Lett 681:56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2018.05.031
Viviani B, Bartesaghi S, Gardoni F, Vezzani A, Behrens MM, Bartfai T et al (2003) Interleukin-1beta enhances NMDA receptor-mediated intracellular calcium increase through activation of the Src family of kinases. J Neurosci 23(25):8692–8700. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.23-25-08692.2003
Volkow ND, Morales M (2015) The brain on drugs: from reward to addiction. Cell 162(4):712–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.046
Vonder Haar C, Ferland JN, Kaur S, Riparip LK, Rosi S, Winstanley CA (2019) Cocaine self-administration is increased after frontal traumatic brain injury and associated with neuroinflammation. Eur J Neurosci 50(3):2134–2145. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.14123
Wakida N, Kiguchi N, Saika F, Nishiue H, Kobayashi Y, Kishioka S (2014) CC-chemokine ligand 2 facilitates conditioned place preference to methamphetamine through the activation of dopamine systems. J Pharmacol Sci 125(1):68–73. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.14032fp
Wang XY, Zhao M, Ghitza UE, Li YQ, Lu L (2008) Stress impairs reconsolidation of drug memory via glucocorticoid receptors in the basolateral amygdala. J Neurosci 28(21):5602–5610. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0750-08.2008
Wang K, Ye L, Lu H, Chen H, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Zheng JC (2017) TNF-α promotes extracellular vesicle release in mouse astrocytes through glutaminase. J Neuroinflamm 14(1):87. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0853-2
Wang X, Northcutt AL, Cochran TA, Zhang X, Fabisiak TJ, Haas ME et al (2019) Methamphetamine activates toll-like receptor 4 to induce central immune signaling within the ventral tegmental area and contributes to extracellular dopamine increase in the nucleus accumbens shell. ACS Chem Neurosci 10(8):3622–3634. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00225
Wang YC, Chiu WC, Cheng CN, Lee C, Chih Wei Huang A (2021) Examination of neuroinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 beta expression in the medial prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus for the paradoxical effects of reward and aversion induced by morphine. Neurosci Lett 760:136076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136076
Warden AS, Azzam M, DaCosta A, Mason S, Blednov YA, Messing RO et al (2019) Toll-like receptor 3 activation increases voluntary alcohol intake in C57BL/6J male mice. Brain Behav Immun 77:55–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2018.12.004
Weber RJ, Gomez-Flores R, Smith JE, Martin TJ (2009) Neuronal adaptations, neuroendocrine and immune correlates of heroin self-administration. Brain Behav Immun 23(7):993–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2009.05.057
Wen RT, Zhang M, Qin WJ, Liu Q, Wang WP, Lawrence AJ et al (2012) The phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor rolipram decreases ethanol seeking and consumption in alcohol-preferring Fawn-Hooded rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 36(12):2157–2167. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01845.x
Wohleb ES, Godbout JP (2013) Basic aspects of the immunology of neuroinflammation. Inflamm Psychiatry 28:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1159/000343964
Wu Y, Na X, Zang Y, Cui Y, Xin W, Pang R et al (2014) Upregulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in nucleus accumbens attenuates morphine-induced rewarding in a neuropathic pain model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 449(4):502–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.025
Yan Y, Nitta A, Koseki T, Yamada K, Nabeshima T (2012) Dissociable role of tumor necrosis factor alpha gene deletion in methamphetamine self-administration and cue-induced relapsing behavior in mice. Psychopharmacology 221(3):427–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2589-5
Yang J, Yu J, Jia X, Zhu W, Zhao L, Li S, Xu C, Yang C, Wu P, Lu L (2011) Inhibition of nuclear factor-κB impairs reconsolidation of morphine reward memory in rats. Behav Brain Res 216(2):592–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2010.08.047
Yang C, Hawkins KE, Doré S, Candelario-Jalil E (2019) Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 316(2):C135–C153. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00136.2018
Yang Q, Wang G, Zhang F (2020) Role of peripheral immune cells-mediated inflammation on the process of neurodegenerative diseases. Front Immunol 11:2511. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.582825
Yin J, Valin KL, Dixon ML, Leavenworth JW (2017) The role of microglia and macrophages in CNS homeostasis, autoimmunity, and cancer. J Immunol Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5150678
Yue K, Tanda G, Katz JL, Zanettini C (2020) A further assessment of a role for toll-like receptor 4 in the reinforcing and reinstating effects of opioids. Behav Pharmacol 31(2&3):186–195. https://doi.org/10.1097/fbp.0000000000000474
Zhang X, Cui Y, Jing J, Cui Y, Xin W, Liu X (2011) Involvement of p38/NF-κB signaling pathway in the nucleus accumbens in the rewarding effects of morphine in rats. Behav Brain Res 218(1):184–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2010.11.049
Zhang XQ, Cui Y, Cui Y, Chen Y, Na XD, Chen FY et al (2012) Activation of p38 signaling in the microglia in the nucleus accumbens contributes to the acquisition and maintenance of morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Brain Behav Immun 26(2):318–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2011.09.017
Zhong P, Wang W, Yu F, Nazari M, Liu X, Liu QS (2012) Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition impairs cocaine-induced inhibitory synaptic plasticity and conditioned place preference. Neuropsychopharmacology 37(11):2377–2387. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.93
Zhu R, Bu Q, Fu D, Shao X, Jiang L, Guo W et al (2018) Toll-like receptor 3 modulates the behavioral effects of cocaine in mice. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1130-8
Zou JY, Crews FT (2005) TNF alpha potentiates glutamate neurotoxicity by inhibiting glutamate uptake in organotypic brain slice cultures: neuroprotection by NF kappa B inhibition. Brain Res 1034(1–2):11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2004.11.014
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Neuroscience Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Funding
Financial support was solely provided by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK-H and SC participated in the conception of the study, searched, screened, did the data extraction of the studies, drafted, and reviewed the manuscript. FN, AB-H, AH contributed to the conception of the study, reviewed, and edited the manuscript. AK-H and RM prepared tables. All authors read and confirmed the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karimi-Haghighi, S., Chavoshinezhad, S., Mozafari, R. et al. Neuroinflammatory Response in Reward-Associated Psychostimulants and Opioids: A Review. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 649–682 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01223-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01223-6