Abstract
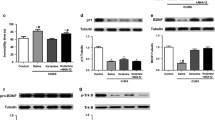
Clinical studies have found that ketamine has a rapid and lasting antidepressant effect, especially in the case of patients with major depressive disorder (MDD). The molecular mechanisms, however, remain unclear. In this study, we observe the effects of S-Ketamine on the expression of Rac1, neuronal morphology, and synaptic transmission function in the hippocampus of stressed rats. Chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) was used to construct stressed rats. The rats were given a different regimen of ketamine (20 mg/kg, i.p.) and Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766 (50 µg, ICV) treatment. The depression-like behavior of rats was evaluated by sucrose preference test and open-field test. The protein expression of Rac1, GluA1, synapsin1, and PSD95 in the hippocampus was detected by Western blot. Pull-down analysis was used to examine the activity of Rac1. Golgi staining and electrophysiological study were used to observe the neuronal morphology and long-term potentiation (LTP). Our results showed that ketamine can up-regulate the expression and activity of Rac1; increase the spine density and the expression of synaptic-related proteins such as GluA1, Synapsin1, and PSD95 in the hippocampus of stressed rats; reduce the CUMS-induced LTP impairments; and consequently improve depression-like behavior. However, Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766 could have effectively reversed ketamine-mediated changes in the hippocampus of rats and counteracted its antidepressant effects. The specific mechanism of S-Ketamine's antidepressant effect may be related to the up-regulation of the expression and activity of Rac1 in the hippocampus of stressed rats, thus enhancing synaptic plasticity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleksandrova LR, Wang YT, Phillips AG (2020) Ketamine and its metabolite, (2R,6R)-HNK, restore hippocampal LTP and long-term spatial memory in the Wistar-Kyoto rat model of depression. Mol Brain 13:92. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-020-00627-z
Angst J, Hengartner MP, Gamma A, von Zerssen D, Angst F (2013) Mortality of 403 patients with mood disorders 48 to 52 years after their psychiatric hospitalisation. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 263:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-012-0380-1
Banasr M, Valentine GW, Li XY, Gourley SL, Taylor JR, Duman RS (2007) Chronic unpredictable stress decreases cell proliferation in the cerebral cortex of the adult rat. Biol Psychiatry 62:496–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.02.006
Bath KG, Jing DQ, Dincheva I, Neeb CC, Pattwell SS, Chao MV, Lee FS, Ninan I (2012) BDNF Val66Met impairs fluoxetine-induced enhancement of adult hippocampus plasticity. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:1297–1304. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2011.318
Benoist M, Palenzuela R, Rozas C, Rojas P, Tortosa E, Morales B, González-Billault C, Ávila J, Esteban JA (2013) MAP1B-dependent Rac1 activation is required for AMPA receptor endocytosis during long-term depression. EMBO J 32:2287–2299. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2013.166
Chapman DP, Perry GS (2008) Depression as a major component of public health for older adults. Prev Chronic Dis 5:A22
Chen LY, Rex CS, Babayan AH, Kramár EA, Lynch G, Gall CM, Lauterborn JC (2010) Physiological activation of synaptic Rac1>PAK (p-21 activated kinase) signaling is defective in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome. J Neurosci 30:10977–10984. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1077-10.2010
Cipriani A, Zhou X, Del GC, Hetrick SE, Qin B, Whittington C, Coghill D, Zhang Y, Hazell P, Leucht S, Cuijpers P, Pu J, Cohen D, Ravindran AV, Liu Y, Michael KD, Yang L, Liu L, Xie P (2016) Comparative efficacy and tolerability of antidepressants for major depressive disorder in children and adolescents: a network meta-analysis. Lancet 388:881–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30385-3
Colledge M, Snyder EM, Crozier RA, Soderling JA, Jin Y, Langeberg LK, Lu H, Bear MF, Scott JD (2003) Ubiquitination regulates PSD-95 degradation and AMPA receptor surface expression. Neuron 40:595–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00687-1
Cornwell BR, Salvadore G, Furey M, Marquardt CA, Brutsche NE, Grillon C, Zarate CA Jr (2012) Synaptic potentiation is critical for rapid antidepressant response to ketamine in treatment-resistant major depression. Biol Psychiatry 72:555–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.03.029
Drevets WC (2000) Functional anatomical abnormalities in limbic and prefrontal cortical structures in major depression. Prog Brain Res 126:413–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(00)26027-5
Duman RS, Aghajanian GK (2012) Synaptic dysfunction in depression: potential therapeutic targets. Science 338:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222939
Duman JG, Blanco FA, Cronkite CA, Ru Q, Erikson KC, Mulherkar S, Saifullah AB, Firozi K, Tolias KF (2021) Rac-maninoff and Rho-vel: The symphony of Rho-GTPase signaling at excitatory synapses. Small GTPases 5:1–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/21541248.2021.1885264
Duman JG, Mulherkar S, Tu YK, Cheng JX, Tolias KF (2015) Mechanisms for spatiotemporal regulation of Rho-GTPase signaling at synapses. Neurosci Lett 601:4–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.05.034
Elias BC, Bhattacharya S, Ray RM, Johnson LR (2010) Polyamine-dependent activation of Rac1 is stimulated by focal adhesion-mediated Tiam1 activation. Cell Adhes Migr 4:419–430. https://doi.org/10.4161/cam.4.3.12043
Elzinga BM, Nyhan MJ, Crowley LC, O’Donovan TR, Cahill MR, McKenna SL (2013) Induction of autophagy by Imatinib sequesters Bcr-Abl in autophagosomes and down-regulates Bcr-Abl protein. Am J Hematol 88:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.23428
Golden SA, Christoffel DJ, Heshmati M, Hodes GE, Magida J, Davis K, Cahill ME, Dias C, Ribeiro E, Ables JL, Kennedy PJ, Robison AJ, Gonzalez-Maeso J, Neve RL, Turecki G, Ghose S, Tamminga CA, Russo SJ (2013) Epigenetic regulation of RAC1 induces synaptic remodeling in stress disorders and depression. Nat Med 19:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3090
Govek EE, Newey SE, Aelst LV (2005) The role of the Rho GTPases in neuronal development. Genes Dev 19:1–49. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1256405
Groh C, Kelber C, Grübel K, Rössler W (2014) Density of mushroom body synaptic complexes limits intraspecies brain miniaturization in highly polymorphic leaf-cutting ant workers. Proc Biol Sci 281:20140432. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2014.0432
Gu L, Xie J, Long J, Chen Q, Chen Q, Pan R, Yan Y, Wu G, Liang B, Tan J, Xie X, Wei B, Su L (2013) Epidemiology of major depressive disorder in mainland china: a systematic review. PLoS ONE 8:e65356. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065356
Gu J, Tian X, Wang W, Yang Q, Lin P, Ma Y, Xiong Y, Xu D, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Lu S, Lin Z, Luo J, Xiao F, Wang X (2018) Inhibition of Cgkii suppresses seizure activity and hippocampal excitation by regulating the postsynaptic delivery of Glua1. Cell Physiol Biochem 46:160–177. https://doi.org/10.1159/000488419
Hallam KT, Horgan JE, McGrath C, Norman TR (2004) An investigation of the effect of tacrine and physostigmine on spatial working memory deficits in the olfactory bulbectomised rat. Behav Brain Res 153:481–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2004.01.005
Hao X, Zhu X, Li P, Lv F, Min S (2016) NMDA receptor antagonist enhances antidepressant efficacy and alleviates learning-memory function impairment induced by electroconvulsive shock with regulating glutamate receptors expression in hippocampus. J Affect Disord 190:819–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.11.021
Hashimoto K (2019) Rapid-acting antidepressant ketamine, its metabolites and other candidates: a historical overview and future perspective. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 73:613–627. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12902
Hashimoto K (2020) Molecular mechanisms of the rapid-acting and long-lasting antidepressant actions of (R)-ketamine. Biochem Pharmacol 177:113935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113935
Hillhouse TM, Porter JH, Negus SS (2014) Comparison of antidepressant-like and abuse-related effects of phencyclidine in rats. Drug Dev Res 75:479–488. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.21228
Hou H, Chávez AE, Wang CC, Yang H, Gu H, Siddoway BA, Hall BJ, Castillo PE, Xia H (2014) The Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766 suppresses CREB signaling by targeting NMDA receptor function. J Neurosci 34:14006–14012. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1659-14.2014
Huang J, Shen C, Ye R, Shi Y, Li W (2021) The effect of early maternal separation combined with adolescent chronic unpredictable mild stress on behavior and synaptic plasticity in adult female rats. Front Psychiatry 12:539299. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.539299
Hunt MJ, Raynaud B, Garcia R (2006) Ketamine dose-dependently induces high-frequency oscillations in the nucleus accumbens in freely moving rats. Biol Psychiatry 60:1206–1214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.01.020
Kang HJ, Voleti B, Hajszan T, Rajkowska G, Stockmeier CA, Licznerski P, Lepack A, Majik MS, Jeong LS, Banasr M, Son H, Duman RS (2012) Decreased expression of synapse-related genes and loss of synapses in major depressive disorder. Nat Med 18:1413–1417. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2886
Kessler RC, Berlund P, Demler O, Jin R, Koretz D, Merikangas KR, Rush AJ, Walters EE, Wang PS (2003) The epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results for the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R). JAMA 289:3095–3105. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.23.3095
Kishimoto T, Chawia JM, Hagi K, Zarate CA, Kane JM, Bauer M, Correll CU (2016) Single-dose infusion ketamine and non-ketamine N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists for unipolar and bipolar depression: a meta-analysis of efficacy, safety and time trajectories. Psychol Med 46:1459–1472. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291716000064
Lenze EJ, Farber NB, Kharasch E, Schweiger J, Yingling M, Olney J, Newcomer JW (2016) Ninety-six hour ketamine infusion with co-administered clonidine for treatment-resistant depression: a pilot randomised controlled trial. World J Biol Psychiatry 26:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3109/15622975.2016.1142607
Li Z, Van Aelst L, Cline HT (2000) Rho GTPases regulate distinct aspects of dendritic arbor growth in Xenopus central neurons in vivo. Nat Neurosci 3:217–225. https://doi.org/10.1038/72920
Li N, Lee B, Liu RJ, Banasr M, Dwyer JM, Iwata M, Li XY, Aghajanian G, Duman RS (2010) mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 329:959–964. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1190287
Li N, Liu RJ, Dwyer JM, Banasr M, Lee B, Son H, Li XY, Aghajanian G, Duman RS (2011) Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists rapidly reverse behavioral and synaptic deficits caused by chronic stress exposure. Biol Psychiatry 69:754–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.12.015
Li J, Chai A, Wang L, Ma Y, Wu Z, Yu H, Mei L, Lu L, Zhang C, Yue W, Xu L, Rao Y, Zhang D (2015) Synaptic P-Rex1 signaling regulates hippocampal long-term depression and autism-like social behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:E6964-6972. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1512913112
Li JM, Liu LL, Su WJ, Wang B, Zhang T, Zhang Y, Jiang CL (2019) Ketamine may exert antidepressant effects via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome to upregulate AMPA receptors. Neuropharmacology 146:149–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.11.022
Liu L, Wu B, Cai H, Li D, Ma Y, Zhu X, Lv Z, Fan Y, Zhang X (2018) Tiam1 promotes thyroid carcinoma metastasis by modulating EMT via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Exp Cell Res 362:532–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.12.019
Lorenzetti V, Costafreda SG, Rimmer RM, Rasenick MM, Marangell LB, Fu CHY (2020) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor association with amygdala response in major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 267:103–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2020.01.159
Luo L (2002) Actin cytoskeleton regulation in neuronal morphogenesis and structural plasticity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 18:601–635. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.18.031802.150501
Luo KR, Hong CJ, Liou YJ, Hou SJ, Huang YH, Tsai SJ (2010) Differential regulation of neurotrophin S100B and BDNF in two rat models of depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:1433–1439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.07.033
Lynch MA (2004) Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol Rev 84:87–136. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00014.2003
Mao X, Fan C, Yu X, Chen B, Jin F (2017) DDEFL1 correlated with Rho GTPases activity in breast cancer. Oncotarget 8:112487–112497. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22095
Marland JRK, Pan DX, Buttery PC (2011) Rac GTPase-activating protein (Rac GAP) α1-Chimaerin undergoes proteasomal degradation and is stabilized by diacylglycerol signaling in neurons. J Biol Chem 286:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.166728
Martinez LA, Tejada-Simon MV (2011) Pharmacological inactivation of the small GTPase Rac1 impairs long-term plasticity in the mouse hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 61:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.04.017
Muellerleile J, Blistein A, Rohlmann A, Scheiwe F, Missler M, Schwarzacher SW, Jedlicka P (2020) Enhanced LTP of population spikes in the dentate gyrus of mice haploinsufficient for neurobeachin. Sci Rep 10:16058. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72925-4
Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2010) Animal models of neuropsychiatric disorders. Nat Neurosci 13:1161–1169. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2647
Newport DJ, Carpenter LL, McDonald WM, Potash JB, Tohen M, Nemeroff CB (2015) Ketamine and other NMDA antagonists: Early clinical trials and possible mechanisms in depression. Am J Psychiatry 172:950–966. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15040465
Oh D, Han S, Seo J, Lee JR, Choi J, Groffen J, Kim K, Cho YS, Choi HS, Shin H, Woo J, Won H, Park SK, Kim SY, Jo J, Whitcomb DJ, Cho K, Kim H, Bae YC, Heisterkamp N, Choi SY, Kim E (2010) Regulation of synaptic Rac1 activity, long-term potentiation maintenance, and learning and memory by BCR and ABR Rac1 GTPase-activating proteins. J Neurosci 30:14134–14144. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1711-10.2010
Pandya CD, Hoda N, Crider A, Peter D, Kutiyanawalla A, Kumar S, Ahmed AO, Turecki G, Hernandez CM, Terry AV, Pillai A (2017) Transglutaminase 2 overexpression induces depressive-like behavior and impaired TrkB signaling in mice. Mol Psychiatry 22:745–753. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.199
Pennucci R, Talpo F, Astro V, Montinaro V, Morè L, Cursi M, Castoldi V, Chiaretti S, Bianchi V, Marenna S, Cambiaghi M, Tonoli D, Leocani L, Biella G, D’Adamo P, de Curtis I (2016) Loss of either Rac1 or Rac3 GTPase differentially affects the behavior of mutant mice and the development of functional GABAergic networks. Cereb Cortex 26:873–890. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhv274
Qi RZ, Ching YP, Kung HF, Wang JH (2004) Alpha-chimaerin exists in a functional complex with the Cdk5 kinase in brain. FEBS Lett 561:177–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(04)00174-7
Qiu A, Zhang H, Wang C, Chong YS, Shek LP, Gluckman PD, Meaney MJ, Fortier MV, Wu Y (2021) Canonical TGF-beta signaling regulates the relationship between prenatal maternal depression and amygdala development in early life. Transl Psychiatry 11:170. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01292-z
Rajkowska G, Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, Wei J, Dilley G, Pittman SD, Meltzer HY, Overholser JC, Roth BL, Stockmeier CA (1999) Morphometric evidence for neuronal and glial prefrontal cell pathology in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 45:1085–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-3223(99)00041-4
Ren L, Zhang F, Min S, Hao X, Qin P, Zhu X (2016) Propofol ameliorates electroconvulsive shock-induced learning and memory impairment by regulation of synaptic metaplasticity via autophosphorylation of CaMKIIa at Thr 305 in stressed rats. Psychiatry Res 240:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2016.03.053
Rezaei M, Shariat Bagheri MM, Ahmadi M (2021) Clinical and demographic predictors of response to anodal tDCS treatment in major depression disorder (MDD). J Psychiatr Res 138:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.03.047
Salahudeen MS, Wright CM, Peterson GM (2020) Esketamine: new hope for the treatment of treatment-resistant depression? A narrative review. Ther Adv Drug Saf 11:2042098620937899. https://doi.org/10.1177/2042098620937899
Simma N, Bose T, Kahlfuss S, Mankiewicz J, Lowinus T, Lühder F, Schüler T, Schraven B, Heine M, Bommhardt U (2014) NMDA-receptor antagonists block B-cell function but foster IL-10 production in BCR/CD40-activated B cells. Cell Commun Signal 12:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-014-0075-5
Sindermann L, Redlich R, Opel N, Böhnlein J, Dannlowski U, Leehr EJ (2021) Systematic transdiagnostic review of magnetic-resonance imaging results: depression, anxiety disorders and their co-occurrence. J Psychiatr Res 142:226–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.07.022
Sinyor M, Schaffer A, Levitt A (2010) The sequenced treatment alternatives to relieve depression (STAR*D) trial: a review. Can J Psychiatry 55:126–135. https://doi.org/10.1177/070674371005500303
Smith KR, Rajgor D, Hanley JG (2017) Differential regulation of the Rac1 GTPase-activating protein (GAP) BCR during oxygen/glucose deprivation in hippocampal and cortical neurons. J Biol Chem 292:20173–20183. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.796292
Stein IS, Park DK, Claiborne N, Zito K (2021) Non-ionotropic NMDA receptor signaling gates bidirectional structural plasticity of dendritic spines. Cell Rep 34:108664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108664
Tolias KF, Bikoff JB, Burette A, Paradis S, Harrar D, Tavazoie S, Weinberg RJ, Greenberg ME (2005) The Rac1-GEF Tiam1 couples the NMDA receptor to the activity-dependent development of dendritic arbors and spines. Neuron 45:525–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2005.01.024
Tolias KF, Duman JG, Um K (2011) Control of synapse development and plasticity by Rho GTPase regulatory proteins. Prog Neurobiol 94:133–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.04.011
Tsai NP, Wilkerson JR, Guo W, Maksimova MA, DeMartino GN, Cowan CW, Huber KM, Tsai NP, Wilkerson JR, Guo W, Maksimova MA, DeMartino GN, Cowan CW, Huber KM (2012) Multiple autism-linked genes mediate synapse elimination via proteasomal degradation of a synaptic scaffold PSD-95. Cell 151:1581–1594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.040
Um K, Niu S, Duman JG, Cheng JX, Tu YK, Schwechter B, Liu F, Hiles L, Narayanan AS, Ash RT, Mulherkar S, Alpadi K, Smirnakis SM, Tolias KF (2014) Dynamic control of excitatory synapse development by a Rac1 GEF/GAP regulatory complex. Dev Cell 29:701–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2014.05.011
Van de Ven TJ, VanDongen HMA, VanDongen AMJ (2005) The nonkinase phorbol ester receptor alpha1-chimerin binds the NMDA receptor NR2A subunit and regulates dendritic spine density. J Neurosci 25:9488–9496. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2450-05.2005
Waller JA, Tamm JA, Abdourahman A, Pehrson AL, Li Y, Cajina M, Sánchez C (2017) Chronic vortioxetine treatment in rodents modulates gene expression of neurodevelopmental and plasticity markers. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 27:192–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2016.11.014
Wang X, Chen Y, Zhou X, Liu F, Zhang T, Zhang C (2012) Effects of propofol and ketamine as combined anesthesia for electroconvulsive therapy in patients with depressive disorder. J ECT 28:128–132. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCT.0b013e31824d1d02
Wei Y, Chang L, Hashimoto K (2020) A historical review of antidepressant effects of ketamine and its enantiomers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 190:172870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172870
Yang C, Kobayashi S, Nakao K, Dong C, Han M, Qu Y, Ren Q, Zhang JC, Ma M, Toki H, Yamaguchi JI, Chaki S, Shirayama Y, Nakazawa K, Manabe T, Hashimoto K (2018) AMPA receptor activation-independent antidepressant actions of ketamine metabolite (S)-norketamine. Biol Psychiatry 84:591–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.05.007
Yoshino Y, Roy B, Dwivedi Y (2021) Differential and unique patterns of synaptic miRNA expression in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of depressed subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 46:900–910. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-00861-y
Zhang QG, Wang R, Han D, Dong Y, Brann DW (2009) Role of Rac1 GTPase in JNK signaling and delayed neuronal cell death following global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 1265:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.01.033
Zhu X, Hao X, Luo J, Min S, Xie F, Zhang F (2015) Propofol inhibits inflammatory cytokine-mediated glutamate uptake dysfunction to alleviate learning/memory impairment in depressed rats undergoing electroconvulsive shock. Brain Res 1595:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.07.046
Zhu X, Ye G, Wang Z, Jie L, Hao X (2017) Sub-anesthetic doses of ketamine exert antidepressant-like effects and upregulate the expression of glutamate transporters in the hippocampus of rats. Neurosci Lett 639:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2016.12.070
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Jie Luo and Li Ren PhD. from the Department of Anesthesiology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University for their assistance in the study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81760257), the Science and Technology Department of Hubei Province (No. 2016CFB368) and Natural Science Foundation of Yongchuan District (Ycstc, 2020nb0205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fuxia Yan and Zaiping Wang designed experiments. Fuxia Yan and Zaiping Wang: Designed the study and wrote the protocol. Xianlin Zhu and Fan Zhang established the animal model of depression and performed the behavioral tests, statistical analyses, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Yufeng You, Banglin Wu, and Rongyu Zhu performed the tissue preparation, RT-qPCR and western blotting analysis. Su Yuan and Dawei Liu performed the Golgi staining. Hongbai Wang performed the electrophysiological study. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Zhang, F., You, Y. et al. S-Ketamine Exerts Antidepressant Effects by Regulating Rac1 GTPase Mediated Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus of Stressed Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 299–314 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01180-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01180-6