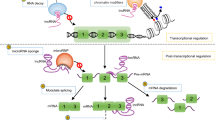
Abstract
Stroke has become the most disabling and the second most fatal disease in the world. It has been a top priority to reveal the pathophysiology of stroke at cellular and molecular levels. A large number of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are identified to be abnormally expressed after stroke. Here, we summarize 35 lncRNAs associated with stroke, and clarify their functions on the prognosis through signal transduction and predictive values as biomarkers. Changes in the expression of these lncRNAs mediate a wide range of pathological processes in stroke, including apoptosis, inflammation, angiogenesis, and autophagy. Based on the exploration of the functions and mechanisms of lncRNAs in stroke, more timely, accurate predictions and more effective, safer treatments for stroke could be developed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen C, Srivastava K, Bayraktutan U (2010) Small GTPase RhoA and its effector rho kinase mediate oxygen glucose deprivation-evoked in vitro cerebral barrier dysfunction. Stroke 41:2056–2063. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.574939
Anrather J, Iadecola C (2016) Inflammation and stroke: an overview. Neurotherapeutics 13:661–670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-016-0483-x
Arbiol-Roca A et al (2018) ANRIL as a genetic marker for cardiovascular events in renal transplant patients—an observational follow-up cohort study. Transpl Int. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13276
Arumugam TV et al (2006) Gamma secretase-mediated Notch signaling worsens brain damage and functional outcome in ischemic stroke. Nat Med 12:621–623. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1403
Askarian-Amiri ME et al (2011) SNORD-host RNA Zfas1 is a regulator of mammary development and a potential marker for breast cancer. RNA 17:878–891. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.2528811
Ayana R, Singh S, Pati S (2017) Decoding crucial LncRNAs implicated in neurogenesis and neurological disorders. Stem Cells Dev 26:541–553. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2016.0290
Bai Y et al (2014) Regulation of CARD8 expression by ANRIL and association of CARD8 single nucleotide polymorphism rs2043211 (p. C10X) with ischemic stroke. Stroke 45:383–388. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.113.003393
Baik SH et al (2015) Pin1 promotes neuronal death in stroke by stabilizing Notch intracellular domain. Ann Neurol 77:504–516. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24347
Bao MH, Szeto V, Yang BB, Zhu SZ, Sun HS, Feng ZP (2018) Long non-coding RNAs in ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis 9:281. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0282-x
Bhalala OG, Srikanth M, Kessler JA (2013) The emerging roles of microRNAs in CNS injuries. Nat Rev Neurol 9:328–339. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2013.67
Bobinger T et al (2019) Siponimod (BAF-312) attenuates perihemorrhagic edema and improves survival in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 50:3246–3254. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.027134
Cai J, Shangguan S, Li G, Cai Y, Deng Y (2019) Knockdown of lncRNA Gm11974 protect against cerebral ischemic reperfusion through miR-766-3p/NR3C2 axis. Artif Cells 47:3847–3853
Calderone A et al (2003) Ischemic insults derepress the gene silencer REST in neurons destined to die. J Neurosci 23:2112–2121
Carneiro MBH et al (2018) NOX2-derived reactive oxygen species control inflammation during Leishmania amazonensis infection by mediating infection-induced neutrophil apoptosis. J Immunol 200:196–208. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1700899
Chen H, Li X (2019) LncRNA ROR is involved in cerebral hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in PC12 cells via regulating miR-135a-5p/ROCK1/2. Am J Transl Res 11:6145–6158
Chen LY, Zuraw BL, Liu FT, Huang S, Pan ZK (2002) IL-1 receptor-associated kinase and low molecular weight GTPase RhoA signal molecules are required for bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine gene transcription. J Immunol 169:3934–3939. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.169.7.3934
Chen DL et al (2016a) Long non-coding RNA XIST regulates gastric cancer progression by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-101 to modulate EZH2 expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35:142. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0420-1
Chen L et al (2016b) MiR-126 inhibits vascular endothelial cell apoptosis through targeting PI3K/Akt signaling. Ann Hematol 95:365–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-015-2567-9
Chen S et al (2017) LncRNA TUG1 sponges microRNA-9 to promote neurons apoptosis by up-regulated Bcl2l11 under ischemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 485:167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.043
Chen F, Zhang L, Wang E, Zhang C, Li X (2018) LncRNA GAS5 regulates ischemic stroke as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-137 to regulate the Notch1 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 496:184–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.022
Chen Z, Chen X, Guo R, Meng J (2019) Protective effects of lncRNA H19 silence against hypoxia-induced injury in PC-12 cells by regulating miR-28 Int. J Biol Macromol 121:546–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.033
Chen Z, He M, Chen J, Li C, Zhang Q (2020) Long non-coding RNA SNHG7 inhibits NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis by targeting the miR-34a/SIRT1 axis in liver cancer. Oncol Lett 20:893–901. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.11635
Clemens JA, Stephenson DT, Yin TG, Smalstig EB, Panetta JA, Little SP (1998) Drug-induced neuroprotection from global ischemia is associated with prevention of persistent but not transient activation of nuclear factor-kappa B in rats. Stroke 29:677–682. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.Str.29.3.677
Dahariya S, Paddibhatla I, Kumar S, Raghuwanshi S, Pallepati A, Gutti RK (2019) Long non-coding RNA: classification, biogenesis and functions in blood cells. Mol Immunol 112:82–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2019.04.011
Darsalia V, Heldmann U, Lindvall O, Kokaia Z (2005) Stroke-induced neurogenesis in aged brain. Stroke 36:1790–1795. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000173151.36031.be
Deng Y et al (2019) Silencing of long noncoding RNA Nespas aggravates microglial cell death and neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke. Stroke 50:1850–1858. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023376
Dharap A, Nakka VP, Vemuganti R (2012) Effect of focal ischemia on long noncoding RNAs. Stroke 43:2800–2802. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.669465
Ding G et al (2008) Angiogenesis detected after embolic stroke in rat brain using magnetic resonance T2*WI. Stroke 39:1563–1568. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.502146
Dong FX, Yao RQ, Yu HL, Liu YP (2017) Neuroprotection of Ro25-6981 against ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain injury via inhibition of autophagy. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:743–752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0409-5
Dong B et al (2018) LncRNA-FENDRR mediates VEGFA to promote the apoptosis of brain microvascular endothelial cells via regulating miR-126 in mice with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Microcirculation 25:e12499. https://doi.org/10.1111/micc.12499
Engreitz JM et al (2013) The Xist lncRNA exploits three-dimensional genome architecture to spread across the X chromosome. Science 341:1237973. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1237973
Fan B et al (2020) Long noncoding RNA mediates stroke-induced neurogenesis. Stem Cells. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.3189
Foehr ED, Lin X, O'Mahony A, Geleziunas R, Bradshaw RA, Greene WC (2000) NF-kappa B signaling promotes both cell survival and neurite process formation in nerve growth factor-stimulated PC12 cells. J Neurosci 20:7556–7563
Gabory A, Jammes H, Dandolo L (2010) The H19 locus: role of an imprinted non-coding RNA in growth and development. BioEssays 32:473–480. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.200900170
Gai HY, Wu C, Zhang Y, Wang D (2019) Long non-coding RNA CHRF modulates the progression of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via miR-126/SOX6 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 514:550–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.04.161
Gao M, Fu J, Wang Y (2020) The lncRNA FAL1 protects against hypoxia-reoxygenation- induced brain endothelial damages through regulating PAK1. J Bioenerg Biomembr 52:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-019-09819-2
Ginet V et al (2014) Involvement of autophagy in hypoxic-excitotoxic neuronal death. Autophagy 10:846–860. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.28264
Graff-Radford J, Jones DT, Strand EA, Rabinstein AA, Duffy JR, Josephs KA (2014) The neuroanatomy of pure apraxia of speech in stroke. Brain Lang 129:43–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2014.01.004
Green DR, Levine B (2014) To be or not to be? How selective autophagy and cell death govern cell fate. Cell 157:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.049
Gruber AJ, Zavolan M (2019) Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation in health and disease. Nat Rev Genet 20:599–614. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0145-z
Guo D, Ma J, Yan L, Li T, Li Z, Han X, Shui S (2017) Down-regulation of Lncrna MALAT1 attenuates neuronal cell death through suppressing beclin1-dependent autophagy by regulating Mir-30a in cerebral ischemic stroke. Cell Physiol Biochem 43:182–194. https://doi.org/10.1159/000480337
Guo X et al (2018) Identification of novel LncRNA biomarkers and construction of LncRNA-related networks in Han Chinese patients with ischemic stroke. Cell Physiol Biochem 50:2157–2175. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495058
Han P, Chang C-P (2015) Long non-coding RNA and chromatin remodeling. RNA Biol 12:1094–1098. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1063770
Han WD et al (2015) miR-26a enhances autophagy to protect against ethanol-induced acute liver injury. J Mol Med 93:1045–1055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1282-2
Han Q et al (2018) Long noncoding RNA CRCMSL suppresses tumor invasive and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma through nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of HMGB2. Oncogene 38:3019–3032. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0614-4
Hankey GJ (2017) Stroke. Lancet 389:641–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)30962-x
He X et al (2016) Role of Wnt/beta-catenin in the tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia induced by electroacupuncture pretreatment. Neurochem Int 97:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2016.03.011
Hu C, Bai X, Liu C, Hu Z (2019) Long noncoding RNA XIST participates hypoxia-induced angiogenesis in human brain microvascular endothelial cells through regulating miR-485/SOX7 axis. Am J Transl Res 11:6487–6497
Hu SK, Zheng JJ, Du ZY, Wu G (2020) Knock down of lncRNA H19 promotes axon sprouting and functional recovery after cerebral ischemic stroke. Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146681
Huang W, Tian Y, Dong S, Cha Y, Li J, Guo X, Yuan X (2017) The long non-coding RNA SNHG3 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to promote malignant development of colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 38:1402–1410. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5837
Jeon H, Ai J, Sabri M, Tariq A, Macdonald RL (2010) Learning deficits after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Neuroscience 169:1805–1814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.06.039
Jeong HG et al (2018) Ceria nanoparticles synthesized with aminocaproic acid for the treatment of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 49:3030–3038. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022631
Jia D, Niu Y, Li D, Liu Z (2018a) lncRNA C2dat1 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting miR-34a-5p in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Res 26:753–764. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504017X15024946480113
Jia J, Zhang M, Li Q, Zhou Q, Jiang Y (2018b) Long noncoding ribonucleic acid NKILA induces the endoplasmic reticulum stress/autophagy pathway and inhibits the nuclear factor-k-gene binding pathway in rats after intracerebral hemorrhage. J Cell Physiol 233:8839–8849. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26798
Jiang H, Zhang H, Hu X, Li W (2018) Knockdown of long non-coding RNA XIST inhibits cell viability and invasion by regulating miR-137/PXN axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Biol Macromol 111:623–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.022
Jin R, Liu L, Zhang S, Nanda A, Li G (2013) Role of inflammation and its mediators in acute ischemic stroke J Cardiovasc. Transl Res 6:834–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-013-9508-6
Jing H, Liu L, Jia Y, Yao H, Ma F (2019) Overexpression of the long non-coding RNA Oprm1 alleviates apoptosis from cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through the Oprm1/miR-155/GATA3 axis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:2431–2439. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1626408
Johnson R (2012) Long non-coding RNAs in Huntington's disease neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 46:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.006
Kabeya Y et al (2000) LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J 19:5720–5728. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.21.5720
Khalil AM et al (2009) Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:11667–11672. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0904715106
Khan MA, Khan MJ (2018) Nano-gold displayed anti-inflammatory property via NF-kB pathways by suppressing COX-2 activity. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:1149–1158. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1446968
Khan MR, Xiang SX, Song ZY, Wu M (2017) The p53-inducible long noncoding RNA TRINGS protects cancer cells from necrosis under glucose starvation. EMBO J 36:3483–3500. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201696239
Kong Q, Hao Y, Li X, Wang X, Ji B, Wu Y (2018) HDAC4 in ischemic stroke: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Clin Epigenet. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-018-0549-1
Kopp F, Mendell JT (2018) Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 172:393–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.011
Kotake Y, Nakagawa T, Kitagawa K, Suzuki S, Liu N, Kitagawa M, Xiong Y (2010) Long non-coding RNA ANRIL is required for the PRC2 recruitment to and silencing of p15INK4B tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene 30:1956–1962. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.568
Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L, Chipuk JE, Bonzon C, Sullivan BA, Green DR, Newmeyer DD (2005) BH3 domains of BH3-only proteins differentially regulate Bax-mediated mitochondrial membrane permeabilization both directly and indirectly. Mol Cell 17:525–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2005.02.003
Lam GY, Huang J, Brumell JH (2010) The many roles of NOX2 NADPH oxidase-derived ROS in immunity. Semin Immunopathol 32:415–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-010-0221-0
Li Q, Yan J, Mao AP, Li C, Ran Y, Shu HB, Wang YY (2011) Tripartite motif 8 (TRIM8) modulates TNFalpha- and IL-1beta-triggered NF-kappaB activation by targeting TAK1 for K63-linked polyubiquitination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:19341–19346. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1110946108
Li T et al (2015) Amplification of long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 promotes metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 75:3181–3191. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3721
Li B et al (2017a) Morin promotes prostate cancer cells chemosensitivity to paclitaxel through miR-155/GATA3 axis. Oncotarget 8:47849–47860. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18133
Li L, Wang M, Mei Z, Cao W, Yang Y, Wang Y, Wen A (2017b) lncRNAs HIF1A-AS2 facilitates the up-regulation of HIF-1alpha by sponging to miR-153-3p, whereby promoting angiogenesis in HUVECs in hypoxia. Biomed Pharmacother 96:165–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.113
Li CJ et al (2018a) Long noncoding RNA Bmncr regulates mesenchymal stem cell fate during skeletal aging. J Clin Invest 128:5251–5266. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI99044
Li N, Zhan X, Zhan X (2018b) The lncRNA SNHG3 regulates energy metabolism of ovarian cancer by an analysis of mitochondrial proteomes. Gynecol Oncol 150:343–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2018.06.013
Li XJ, Chen MH, Shi QX, Zhang HF, Xu SW (2020) Hydrogen sulfide exposure induces apoptosis and necroptosis through lncRNA3037/miR-15a/BCL2-A20 signaling in broiler trachea. Sci Total Environ 699:134296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134296
Liang Z, Chi YJ, Lin GQ, Xiao LF, Su GL, Yang LM (2018) LncRNA MEG3 participates in neuronal cell injury induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage via inhibiting the Pi3k/Akt pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:2824–2831. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201805_14983
Liepelt A et al (2014) Translation control of TAK1 mRNA by hnRNP K modulates LPS-induced macrophage activation. RNA 20:899–911. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.042788.113
Liu B et al (2015) A cytoplasmic NF-kappaB interacting long noncoding RNA blocks IkappaB phosphorylation and suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell 27:370–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.02.004
Liu J et al (2017) Downregulation of the long non-coding RNA Meg3 promotes angiogenesis after ischemic brain injury by activating Notch signaling. Mol Neurobiol 54:8179–8190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0270-z
Liu N et al (2018) Hepatitis B Virus-Upregulated LNC-HUR1 promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by blocking p53 activity. Hepatology 68:2130–2144. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30098
Liu B, Cao W, Xue J (2019) LncRNA ANRIL protects against oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced injury in PC-12 cells: potential role in ischaemic stroke. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:1384–1395. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1596944
Liz J et al (2014) Regulation of pri-miRNA processing by a long noncoding RNA transcribed from an ultraconserved region. Mol Cell 55:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.05.005
Ma L, Bajic VB, Zhang Z (2013) On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol 10:925–933. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.24604
Mao Q, Liang XL, Zhang CL, Pang YH, Lu YX (2019) LncRNA KLF3-AS1 in human mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorates pyroptosis of cardiomyocytes and myocardial infarction through miR-138–5p/Sirt1 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther 10: Article 393. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1522-4
Marani M, Tenev T, Hancock D, Downward J, Lemoine NR (2002) Identification of novel isoforms of the BH3 domain protein Bim which directly activate Bax to trigger apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 22:3577–3589. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.22.11.3577-3589.2002
Matouk IJ et al (2010) The oncofetal H19 RNA connection: hypoxia, p53 and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803:443–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.01.010
Matsui T et al (1996) Rho-associated kinase, a novel serine/threonine kinase, as a putative target for small GTP binding protein Rho. EMBO J 15:2208–2216
Mehta SL, Kim T, Vemuganti R (2015) Long noncoding RNA FosDT promotes ischemic brain injury by interacting with REST-associated chromatin-modifying proteins. J Neurosci 35:16443–16449. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2943-15.2015
Michelhaugh SK, Lipovich L, Blythe J, Jia H, Kapatos G, Bannon MJ (2011) Mining Affymetrix microarray data for long non-coding RNAs: altered expression in the nucleus accumbens of heroin abusers. J Neurochem 116:459–466. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07126.x
Miller SA, White JA, Chowdhury R, Gales DN, Tameru B, Tiwari AK, Samuel T (2018) Effects of consumption of whole grape powder on basal NF-kappaB signaling and inflammatory cytokine secretion in a mouse model of inflammation. J Nutr Intermed Metab 11:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnim.2017.11.002
Mineo M et al (2016) The long non-coding RNA HIF1A-AS2 facilitates the maintenance of mesenchymal glioblastoma stem-like cells in hypoxic niches. Cell Rep 15:2500–2509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.018
Mojsa B, Lassot I, Desagher S (2014) Mcl-1 ubiquitination: unique regulation of an essential survival protein. Cells 3:418–437. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells3020418
Nakagawa O, Fujisawa K, Ishizaki T, Saito Y, Nakao K, Narumiya S (1996) ROCK-I and ROCK-II, two isoforms of Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein serine/threonine kinase in mice. FEBS Lett 392:189–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(96)00811-3
Nelson TJ, Chiriac A, Faustino RS, Crespo-Diaz RJ, Behfar A, Terzic A (2009) Lineage specification of Flk-1+ progenitors is associated with divergent Sox7 expression in cardiopoiesis. Differentiation 77:248–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diff.2008.10.012
Nurmi A et al (2004) Nuclear factor-kappa B contributes to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke 35:987–991. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.Str.0000120732.45951.26
Ouyang YB, Lu Y, Yue S, Giffard RG (2012) miR-181 targets multiple Bcl-2 family members and influences apoptosis and mitochondrial function in astrocytes. Mitochondrion 12:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2011.09.001
Park J et al (2018) Long non-coding RNA ChRO1 facilitates ATRX/DAXX-dependent H3.3 deposition for transcription-associated heterochromatin reorganization. Nucleic Acids Res 46:11759–11775. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky923
Park S, Lee M, Chun CH, Jin EJ (2019) The lncRNA, Nespas, is associated with osteoarthritis progression and serves as a potential new prognostic biomarker. Cartilage 10:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947603517725566
Peng WX, Koirala P, Mo YY (2017) LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene 36:5661–5667. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.184
Qi WC, Li ZH, Xia LJ, Dai JS, Zhang Q, Wu CF, Xu S (2019) LncRNA GABPB1-AS1 and GABPB1 regulate oxidative stress during erastin-induced ferroptosis in HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Sci Rep UK 9: Article 16185. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52837-8
Radak D et al (2017) Apoptosis and acute brain ischemia in ischemic stroke. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 15:115–122. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570161115666161104095522
Randolph SA (2016) Ischemic stroke workplace Health Saf 64:444. https://doi.org/10.1177/2165079916665400
Ravanan P, Srikumar IF, Talwar P (2017) Autophagy: the spotlight for cellular stress responses. Life Sci 188:53–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.08.029
Ren X et al (2014) FOXF1 transcription factor is required for formation of embryonic vasculature by regulating VEGF signaling in endothelial cells. Circ Res 115:709–720. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.304382
Ren H et al (2018) Selective NLRP3 (Pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome inhibitor reduces brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 49:184–192. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.018904
Rinn JL et al (2007) Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell 129:1311–1323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.022
Ruan L, Wang B, ZhuGe Q, Jin K (2015) Coupling of neurogenesis and angiogenesis after ischemic stroke. Brain Res 1623:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2015.02.042
Sallam T, Sandhu J, Tontonoz P (2018) Long noncoding RNA discovery in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 122:155–166. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.117.311802
Schmid RM, Perkins ND, Duckett CS, Andrews PC, Nabel GJ (1991) Cloning of an NF-kappa B subunit which stimulates HIV transcription in synergy with p65. Nature 352:733–736
Sekerdag E, Solaroglu I, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y (2018) Cell death mechanisms in stroke and novel molecular and cellular treatment options. Curr Neuropharmacol 16:1396–1415. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X16666180302115544
Shi J, Wei L (2007) Rho kinase in the regulation of cell death and survival. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 55:61–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-007-0009-7
Shi S et al (2019) X-box binding protein l splicing attenuates brain microvascular endothelial cell damage induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation through the activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B, extracellular signal-regulated kinases, and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha/vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol 234:9316–9327. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27614
Shibata M, Hattori H, Sasaki T, Gotoh J, Hamada J, Fukuuchi Y (2002) Temporal profiles of the subcellular localization of Bim, a BH3-only protein, during middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:810–820. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004647-200207000-00006
Simion V, Haemmig S, Feinberg MW (2019) LncRNAs in vascular biology and disease. Vasc Pharmacol 114:145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2018.01.003
Su J, Zhang T, Wang K, Zhu T, Li X (2014) Autophagy activation contributes to the neuroprotection of remote ischemic perconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurochem Res 39:2068–2077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1396-x
Su Y, Wu H, Pavlosky A, Zou LL, Deng X, Zhang ZX, Jevnikar AM (2016) Regulatory non-coding RNA: new instruments in the orchestration of cell death. Cell Death Dis 7:e2333. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.210
Sun XL, Wang ZL, Wu Q, Jin SQ, Yao J, Cheng H (2019) LncRNA RMST activates TAK1-mediated NF-kappaB signaling and promotes activation of microglial cells via competitively binding with hnRNPK. IUBMB Life 71:1785–1793. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2125
Tobimatsu T, Fujisawa H (1989) Tissue-specific expression of four types of rat calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II mRNAs. J Biol Chem 264:17907–17912
Vausort M, Wagner DR, Devaux Y (2014) Long noncoding RNAs in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circ Res 115:668–677. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.303836
Venna VR, Li J, Hammond MD, Mancini NS, McCullough LD (2014) Chronic metformin treatment improves post-stroke angiogenesis and recovery after experimental stroke. Eur J Neurosci 39:2129–2138. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12556
Wang L, Zhu H (2018) Long noncoding nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 acts as prognosis biomarker and increases cell growth and invasion in cervical cancer by sequestering microRNA101. Mol Med Rep 17:2771–2777. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.8186
Wang S et al (2008) The endothelial-specific microRNA miR-126 governs vascular integrity and angiogenesis. Dev Cell 15:261–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2008.07.002
Wang P, Guan YF, Du H, Zhai QW, Su DF, Miao CY (2012) Induction of autophagy contributes to the neuroprotection of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase in cerebral ischemic stroke. Autophagy 8:77–87. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.8.1.18274
Wang P et al (2014a) Down-regulation of miRNA-30a alleviates cerebral ischemic injury through enhancing beclin 1-mediated autophagy. Neurochem Res 39:1279–1291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1310-6
Wang P et al (2014b) The STAT3-binding long noncoding RNA lnc-DC controls human dendritic cell differentiation. Science 344:310–313. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1251456
Wang J, Cao B, Han D, Sun M, Feng J (2017) Long non-coding RNA H19 induces cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury via activation of autophagy. Aging Dis 8:71–84. https://doi.org/10.14336/Ad.2016.0530
Wang M, Jiang Y-M, Xia L-Y, Wang Y, Li W-Y, Jin T (2018a) LncRNA NKILA upregulation mediates oxygen glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation-induced neuronal cell death by inhibiting NF-κB signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:2524–2530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.010
Wang Y, Li G, Zhao L, Lv J (2018b) Long noncoding RNA HOTTIP alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neuronal injury via modulating miR-143/hexokinase 2 pathway. J Cell Biochem 119:10107–10117. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27348
Wang F-W et al (2019a) APC-activated long noncoding RNA inhibits colorectal carcinoma pathogenesis through reduction of exosome production. J Clin Invest 129:727–743. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci122478
Wang J et al (2019b) Predictive value of long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 in patients with ischemic stroke. Clin Exp Hypertens 41:615–621. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641963.2018.1529774
Wang M et al (2019c) Long noncoding RNA LINC00336 inhibits ferroptosis in lung cancer by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell Death Differ 26:2329–2343. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0304-y
Wang Y et al (2019d) Silencing the lncRNA Maclpil in pro-inflammatory macrophages attenuates acute experimental ischemic stroke via LCP1 in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X19836118
Wat JJ, Wat MJ (2014) Sox7 in vascular development: review, insights and potential mechanisms. Int J Dev Biol 58:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1387/ijdb.130323mw
Wen YD et al (2008) Neuronal injury in rat model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia is associated with activation of autophagic and lysosomal pathways. Autophagy 4:762–769. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.6412
Wen Y, Yu Y, Fu X (2017) LncRNA Gm4419 contributes to OGD/R injury of cerebral microglial cells via IκB phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 487:923
Wu W et al (2017a) Hypoxia induces H19 expression through direct and indirect Hif-1alpha activity, promoting oncogenic effects in glioblastoma. Sci Rep 7:45029. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45029
Wu Z et al (2017b) LncRNA-N1LR enhances neuroprotection against ischemic stroke probably by inhibiting p53 phosphorylation. Mol Neurobiol 54:7670–7685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0246-z
Xie C et al (2016) Neuroprotection by selective neuronal deletion of Atg7 in neonatal brain injury. Autophagy 12:410–423. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1132134
Xu F, Li J, Ni W, Shen YW, Zhang XP (2013) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist 15d-prostaglandin J2 mediates neuronal autophagy after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS ONE 8:e55080. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055080
Xu H, Jin L, Chen Y, Li J (2016a) Downregulation of microRNA-429 protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced apoptosis by increasing Notch1 expression. Int J Mol Med 37:1677–1685. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2558
Xu Q et al (2016b) Long non-coding RNA C2dat1 regulates CaMKIIdelta expression to promote neuronal survival through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway following cerebral ischemia. Cell Death Dis 7:e2173. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.57
Yan B et al (2015) lncRNA-MIAT regulates microvascular dysfunction by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Circ Res 116:1143–1156. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.305510
Yan H, Rao J, Yuan J, Gao L, Huang W, Zhao L, Ren J (2017) Long non-coding RNA MEG3 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate ischemic neuronal death by targeting miR-21/PDCD4 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis 8:3211. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0047-y
Yang L, Lu Z-N (2016) Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes ischemic infarct induced by hypoxia through up-regulating the expression of NOX2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 479:186–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.09.023
Yao X, Yao R, Huang F, Yi J (2019) LncRNA SNHG12 as a potent autophagy inducer exerts neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 514:490–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.04.158
You D, You H (2019) Repression of long non-coding RNA MEG3 restores nerve growth and alleviates neurological impairment after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model. Biomed Pharmacother 111:1447–1457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.067
You J, Fang N, Gu J, Zhang Y, Li X, Zu L, Zhou Q (2014) Noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 1 promote cell proliferation in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Indian J Cancer 51(Suppl 3):e99–e102. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-509X.154092
Yu SJ, Yu MJ, He X, Wen LL, Bu ZQ, Feng J (2019) KCNQ1OT1 promotes autophagy by regulating miR-200a/FOXO3/ATG7 pathway in cerebral ischemic stroke. Aging Cell 18:e12940. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12940
Yu Y, Nangia-Makker P, Farhana L, Majumdar APN (2017) A novel mechanism of lncRNA and miRNA interaction: CCAT2 regulates miR-145 expression by suppressing its maturation process in colon cancer cells. Mol Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0725-5
Zang Y, Zhou X, Wang Q, Li X, Huang H (2018) LncRNA FIRRE/NF-kB feedback loop contributes to OGD/R injury of cerebral microglial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 501:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.194
Zeng L et al (2011) MicroRNA-210 as a novel blood biomarker in acute cerebral ischemia. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 3:1265–1272
Zhang XN et al (2013) Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced autophagy protects against neuronal injury by mitochondrial clearance. Autophagy 9:1321–1333. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.25132
Zhang J et al (2016) Altered long non-coding RNA transcriptomic profiles in brain microvascular endothelium after cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 277:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.12.014
Zhang B, Wang D, Ji TF, Shi L, Yu JL (2017) Overexpression of lncRNA ANRIL up-regulates VEGF expression and promotes angiogenesis of diabetes mellitus combined with cerebral infarction by activating NF-kappaB signaling pathway in a rat model. Oncotarget 8:17347–17359. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14468
Zhang L et al (2018a) LncRNA SNHG1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies as a competing endogenous RNA through HIF-1alpha/VEGF signaling in ischemic stroke. J Cell Biochem 119:5460–5472. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26705
Zhang SB, Liu TJ, Pu GH, Li BY, Gao XZ, Han XL (2018b) MicroRNA-374 Exerts protective effects by inhibiting SP1 through activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in rat models of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion after sevoflurane preconditioning. Cell Physiol Biochem 46:1455–1470. https://doi.org/10.1159/000489186
Zhang J, Dong B, Hao J, Yi S, Cai W, Luo Z (2019a) LncRNA Snhg3 contributes to dysfunction of cerebral microvascular cells in intracerebral hemorrhage rats by activating the TWEAK/Fn14/STAT3 pathway. Life Sci 237:116929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116929
Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Yin KJ (2019b) Noncoding RNAs and stroke. Neuroscientist 25:22–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858418769556
Zhang X, Liu Z, Shu Q, Yuan S, Xing Z, Song J (2019c) LncRNA SNHG6 functions as a ceRNA to regulate neuronal cell apoptosis by modulating miR-181c-5p/BIM signalling in ischaemic stroke. J Cell Mol Med 23:6120–6130. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14480
Zhang M et al (2020) LncRNA DANCR attenuates brain microvascular endothelial cell damage induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation through regulating of miR-33a-5p/XBP1s. Aging (Albany, NY) 12:1778–1791. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102712
Zhao J et al (2016) MYOSLID is a novel serum response factor-dependent long noncoding RNA that amplifies the vascular smooth muscle differentiation program. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 36:2088–2099. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307879
Zhong Y, Yu C, Qin W (2019) LncRNA SNHG14 promotes inflammatory response induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through regulating miR-136-5p /ROCK1 cancer. Gene Ther 26:234–247. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-018-0067-5
Zhou ZW, Zheng LJ, Ren X, Li AP, Zhou WS (2019) LncRNA NEAT1 facilitates survival and angiogenesis in oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs) via targeting miR-377 and upregulating SIRT1, VEGFA, and BCL-XL. Brain Res 1707:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.10.031
Zhu X et al (2012) miR-126 enhances the sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells to anticancer agents by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor A. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 44:519–526. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gms026
Zhu XH, Yuan YX, Rao SL, Wang P (2016) LncRNA MIAT enhances cardiac hypertrophy partly through sponging miR-150. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:3653–3660
Zhu M, Li N, Luo P, Jing W, Wen X, Liang C, Tu J (2018) Peripheral blood leukocyte expression of lncRNA MIAT and its diagnostic and prognostic value in ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 27:326–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.09.009
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81870909) and China Pharmaceutical University “Double First-Class” Construction Graduate Education and Teaching Project (JGYB201909).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZW: conception of the study, acquisition of data and analysis, drafting the article. XL, Liangliang Huang: conception of the study and revising article critically. GL, YC, BL, XZ: revising article critically. YL, RX: study supervision. WF: review, revision of the manuscript and study supervision. All authors approved the version to be published and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Li, X., Huang, L. et al. Long Non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), A New Target in Stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42, 501–519 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00954-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00954-8