Abstract
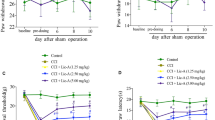
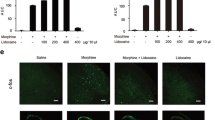
Lidocaine is one of the typical local anesthetics that are frequently used in the peripheral nerve blocks and pain management. Emerging evidence have shown that lidocaine may exert anti-inflammatory effect involving neuropathic pain. However, the effect and underlying mechanism of lidocaine in suppressing neuroinflammation in neuropathic pain are incompletely revealed. In this study, effects of lidocaine on the suppressors of cytokine-signaling protein 3 (SOCS3) in microglia are investigated in chronic constriction injury (CCI) rat model and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated BV-2 cells. It was shown that intrathecal injection of lidocaine substantially alleviated CCI-induced neuropathic pain, as reflected by the decreased thermal latency and mechanical threshold. Lidocaine reduced the CCI-evoked spinal injury and cell apoptosis. CCI induced an significant increase of IBA1+ microglia accompanied by the increase of inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-1β, which were suppressed after lidocaine administration. SOCS3 expression in IBA1+ microglia was notably upregulated in response to lidocaine injection, which presented in a similar pattern in LPS-activated BV-2 cells. Furthermore, lidocaine upregulated SOCS3 expression dependent of pCREB, and CREB silencing greatly discounted this effect. The intrathecal injection of lentiviral vectors LV-SOCS3 efficiently alleviated CCI-evoked neuropathic pain and reduced spinal IBA1+ microglia. SOCS3 overexpression contributed to the inhibition of neuroinflammation by decreasing the expression and activation of p38 MAPK and NF-κB stimulated by LPS. Collectively, lidocaine promoted the SOCS3 expression in microglia, in turn leading to suppression of IBA1+ microglia accumulation and p38 MAPK and NF-κB, which may expand our understanding on lidocaine in suppressing neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babon JJ, Varghese LN, Nicola NA (2014) Inhibition of IL-6 family cytokines by SOCS3. Semin Immunol 26:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2013.12.004
Becker DE, Reed KL (2012) Local anesthetics: review of pharmacological considerations. Anesth Prog 59:90–101. https://doi.org/10.2344/0003-3006-59.2.90 quiz 102–103
Berta T, Lee JE, Park CK (2017) Unconventional role of caspase-6 in spinal microglia activation and chronic pain. Mediators Inflamm 2017:9383184. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9383184
Boontanrart M, Hall SD, Spanier JA, Hayes CE, Olson JK (2016) Vitamin D3 alters microglia immune activation by an IL-10 dependent SOCS3 mechanism. J Neuroimmunol 292:126–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2016.01.015
Chakrabarti S, Jana M, Roy A, Pahan K (2018) Upregulation of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 in microglia by cinnamic acid. Curr Alzheimer Res 15:894–904. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567205015666180507104755
Cheng KI, Lai CS, Wang FY, Wang HC, Chang LL, Ho ST, Tsai HP, Kwan AL (2011) Intrathecal lidocaine pretreatment attenuates immediate neuropathic pain by modulating Nav1.3 expression and decreasing spinal microglial activation. BMC Neurol 11:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-11-71
Cianciulli A, Salvatore R, Porro C, Trotta T, Panaro MA (2016) Folic acid is able to polarize the inflammatory response in LPS activated microglia by regulating multiple signaling pathways. Mediators Inflamm 2016:5240127. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5240127
Cohen SP, Mao J (2014) Neuropathic pain: mechanisms and their clinical implications. BMJ 348:f7656. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f7656
Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2009) Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135531
Eberhardt M, Stueber T, de la Roche J, Herzog C, Leffler A, Reeh PW, Kistner K (2017) TRPA1 and TRPV1 are required for lidocaine-evoked calcium influx and neuropeptide release but not cytotoxicity in mouse sensory neurons. PLoS ONE 12:e0188008. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188008
Fan YX, Qian C, Liu B, Wang C, Liu H, Pan X, Teng P, Hu L, Zhang G, Han Y, Yang M, Wu XF, Liu WT (2018) Induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 via HSF-1-HSP70-TLR4 axis attenuates neuroinflammation and ameliorates postoperative pain. Brain Behav Immun 68:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.10.006
Finnerup NB, Attal N, Haroutounian S, McNicol E, Baron R, Dworkin RH, Gilron I, Haanpaa M, Hansson P, Jensen TS, Kamerman PR, Lund K, Moore A, Raja SN, Rice AS, Rowbotham M, Sena E, Siddall P, Smith BH, Wallace M (2015) Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 14:162–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70251-0
Gierthmuhlen J, Baron R (2016) Neuropathic pain. Semin Neurol 36:462–468. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1584950
Gray A, Marrero-Berrios I, Weinberg J, Manchikalapati D, SchianodiCola J, Schloss RS, Yarmush J (2016) The effect of local anesthetic on pro-inflammatory macrophage modulation by mesenchymal stromal cells. Int Immunopharmacol 33:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.01.019
Hu XM, Zhang H, Xu H, Zhang HL, Chen LP, Cui WQ, Yang W, Shen W (2017) Chemokine receptor CXCR15 regulates CaMKII/CREB pathway in spinal neurons that underlies cancer-induced bone pain. Sci Rep 7:4005. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04198-3
Iwahara N, Hisahara S, Kawamata J, Matsumura A, Yokokawa K, Saito T, Fujikura M, Manabe T, Suzuki H, Matsushita T, Suzuki S, Shimohama S (2017) Role of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) in altering activated microglia phenotype in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. J Alzheimers Dis 55:1235–1247. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-160887
Jensen TS, Finnerup NB (2014) Allodynia and hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain: clinical manifestations and mechanisms. Lancet Neurol 13:924–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70102-4
Ji RR, Chamessian A, Zhang YQ (2016) Pain regulation by non-neuronal cells and inflammation. Science 354:572–577. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf8924
Kim JH, Hedrick S, Tsai WW, Wiater E, Le Lay J, Kaestner KH, Leblanc M, Loar A, Montminy M (2017) CREB coactivators CRTC2 and CRTC3 modulate bone marrow hematopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:11739–11744. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1712616114
Kuchalik J, Magnuson A, Tina E, Gupta A (2017) Does local infiltration analgesia reduce peri-operative inflammation following total hip arthroplasty? A randomized, double-blind study. BMC Anesthesiol 17:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-017-0354-y
Kwon M, Han J, Kim UJ, Cha M, Um SW, Bai SJ, Hong SK, Lee BH (2017) Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling in the insular cortex alleviates neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. Front Mol Neurosci 10:79. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00079
Leffler A, Lattrell A, Kronewald S, Niedermirtl F, Nau C (2011) Activation of TRPA1 by membrane permeable local anesthetics. Mol Pain 7:62. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-7-62
Li TF, Fan H, Wang YX (2015) Epidural sustained release ropivacaine prolongs anti-allodynia and anti-hyperalgesia in developing and established neuropathic pain. PLoS ONE 10:e0117321. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117321
Liang Y, Xu WD, Peng H, Pan HF, Ye DQ (2014) SOCS signaling in autoimmune diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Eur J Immunol 44:1265–1275. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201344369
Liu X, Williams PR, He Z (2015) SOCS3: a common target for neuronal protection and axon regeneration after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 263:364–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.10.024
Mahony R, Ahmed S, Diskin C, Stevenson NJ (2016) SOCS3 revisited: a broad regulator of disease, now ready for therapeutic use? Cell Mol Life Sci 73:3323–3336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2234-x
Matsuura T, Mori T, Hasaka M, Kuno M, Kawawaki J, Nishikawa K, Narahashi T, Sawada M, Asada A (2012) Inhibition of voltage-gated proton channels by local anaesthetics in GMI-R1 rat microglia. J Physiol 590:827–844. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2011.218149
Ohno-Urabe S, Aoki H, Nishihara M, Furusho A, Hirakata S, Nishida N, Ito S, Hayashi M, Yasukawa H, Imaizumi T, Akashi H, Tanaka H, Fukumoto Y (2018) Role of macrophage Socs3 in the pathogenesis of aortic dissection. J Am Heart Assoc 7(2):e007389. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.007389
Suzuki N, Hasegawa-Moriyama M, Takahashi Y, Kamikubo Y, Sakurai T, Inada E (2011) Lidocaine attenuates the development of diabetic-induced tactile allodynia by inhibiting microglial activation. Anesth Analg 113:941–946. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0b013e31822827a2
Toda S, Sakai A, Ikeda Y, Sakamoto A, Suzuki H (2011) A local anesthetic, ropivacaine, suppresses activated microglia via a nerve growth factor-dependent mechanism and astrocytes via a nerve growth factor-independent mechanism in neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 7:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-7-2
Villarruel EQ, Borda E, Sterin-Borda L, Orman B (2011) Lidocaine-induced apoptosis of gingival fibroblasts: participation of cAMP and PKC activity. Cell Biol Int 35:783–788. https://doi.org/10.1042/CBI20100200
Wang Z, Huang H, Yang S, Huang S, Guo J, Tang Q, Qi F (2016) Long-term effect of ropivacaine nanoparticles for sciatic nerve block on postoperative pain in rats. Int J Nanomed 11:2081–2090. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S101563
Wei J, Li M, Wang D, Zhu H, Kong X, Wang S, Zhou YL, Ju Z, Xu GY, Jiang GQ (2017) Overexpression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 in dorsal root ganglion attenuates cancer-induced pain in rats. Mol Pain 13:1744806916688901. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744806916688901
Yin Y, Liu W, Dai Y (2015) SOCS3 and its role in associated diseases. Hum Immunol 76:775–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2015.09.037
Yu XW, Oh MM, Disterhoft JF (2017) CREB, cellular excitability, and cognition: implications for aging. Behav Brain Res 322:206–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.07.042
Yuan T, Li Z, Li X, Yu G, Wang N, Yang X (2014) Lidocaine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in microglia. J Surg Res 192:150–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2014.05.023
Zhang Y, Tao GJ, Hu L, Qu J, Han Y, Zhang G, Qian Y, Jiang CY, Liu WT (2017) Lidocaine alleviates morphine tolerance via AMPK-SOCS3-dependent neuroinflammation suppression in the spinal cord. J Neuroinflamm 14:211. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0983-6
Zhuang ZY, Wen YR, Zhang DR, Borsello T, Bonny C, Strichartz GR, Decosterd I, Ji RR (2006) A peptide c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor blocks mechanical allodynia after spinal nerve ligation: respective roles of JNK activation in primary sensory neurons and spinal astrocytes for neuropathic pain development and maintenance. J Neurosci 26:3551–3560. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5290-05.2006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ and SBY conceived and designed the study; YZ drafted the manuscript and conducted the experiments. XHH analyzed and interpreted the data; SBY critically revised the manuscript; All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at Jilin University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Hou, X. & Yang, S. Lidocaine Potentiates SOCS3 to Attenuate Inflammation in Microglia and Suppress Neuropathic Pain. Cell Mol Neurobiol 39, 1081–1092 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00703-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00703-6