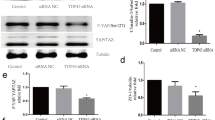
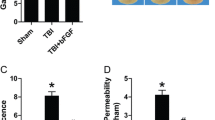
Abstract
Non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIA (NMMHC IIA), a member of Myosin II family, plays a critical role in various cellular physiological processes. Our previous research had suggested that NMMHC IIA could participate in regulating tight junction morphological changes induced by ischemia stroke. Thus, in the current study, we attempted to uncover the regulation pattern of NMMHC IIA on tight junction dysfunction in oxygen glucose-deprived (OGD) mouse brain bEND.3 endothelial cells. The regulation of NMMHC IIA on tight junction in OGD-stimulated bEND.3 cells was evaluated by western blotting assay. Morphologic change of occludin, claudin-5, and ZO-1 tight junction proteins was compared with pretreatment with NMMHC II inhibitor blebbistatin via immunohistochemical staining. Detection of activation of NMMHC IIA on OGD-mediated tight junction transduction pathway was investigated via Koch’s postulate using corresponding protein inhibitor. Our results showed that NMMHC IIA was activated in OGD-stimulated bEND.3 endothelial cells. The inhibition of NMMHC IIA could attenuate the morphologic change of occludin, claudin-5, and ZO-1 tight junction proteins. NMMHC IIA participated in regulating downstream transduction pathway TLR4, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), Akt, JNK1/2, 14-3-3ε, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-кB) and matrix metalloprotein 9 (MMP9). Blocking of these pathways using indicated inhibitors demonstrated that NMMHC IIA destroyed the connection of tight junction via the activation of TLR4/PI3K/Akt/JNK1/2/14-3-3ε/NF-κB/MMP9 pathway. Our study described the key role of NMMHC IIA in OGD-stimulated mouse brain bEND.3 endothelial cells, while also exhibited the molecule effect on tight junction dysfunction via TLR4/PI3K/Akt/JNK1/2/14-3-3ε/NF-κB/MMP9 signal transduction pathway.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butt T, Mufti T, Humayun A, Rosenthal PB, Khan S, Khan S et al (2010) Myosin motors drive long range alignment of actin filaments. J Biol Chem 285:4964–4974
Butt AQ, Ahmed S, Maratha A, Miggin SM (2014) 14-3-3ε and 14-3-3σ inhibit Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated proinflammatory cytokine induction. J Biol Chem 287:38665–38679
Cai M, Yu Z, Wang L, Song X, Zhang J, Zhang Z et al (2016) Tongxinluo reduces brain edema and inhibits post-ischemic inflammation after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 181:136–145
Campos Y, Qiu X, Gomero E, Wakefield R, Horner L, Brutkowski W et al (2016) Alix-mediated assembly of the actomyosin-tight junction polarity complex preserves epithelial polarity and epithelial barrier. Nat Commun 7:11876
Choi C, Kwon J, Lim S, Helfman DM (2016) Integrin β1, myosin light chain kinase and myosin IIA are required for activation of PI3K-AKT signaling following MEK inhibition in metastatic triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 7:63466–63487
Clark K, Middelbeek J, Dorovkov MV, Figdor CG, Ryazanov AG, Lasonder E et al (2008) The alpha-kinases TRPM6 and TRPM7, but not eEF-2 kinase, phosphorylate the assembly domain of myosin IIA, IIB and IIC. FEBS Lett 582:2993–2997
Daquinag AC, Zhang Y, Amaya-Manzanares F, Simmons PJ, Kolonin MG (2011) An isoform of decorin is a resistin receptor on the surface of adipose progenitor cells. Cell Stem Cell 9:2011
Funami K, Matsumoto M, Obuse C, Seya T (2016) 14-3-3-zeta participates in TLR3-mediated TICAM-1 signal-platform formation. Mol Immunol 73:60–68
Garbuzova-Davis S, Mirtyl S, Sallot SA, Hernandez-Ontiveros DG, Haller E, Sanberg PR (2013) Blood-brain barrier impairment in MPS III patients. BMC Neurol 13:174
Greene C, Campbell M (2016) Tight junction modulation of the blood brain barrier: CNS delivery of small molecules. Tissue Barriers 4:e1138017
Ivanov AI, Bachar M, Babbin BA, Adelstein RS, Nusrat A, Parkos CA (2007) A unique role for nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA in regulation of epithelial apical junctions. PLoS ONE 2:e658
Kim T (2015) Determinants of contractile forces generated in disorganized actomyosin bundles. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 14:345–355
Kolega J (2006) The role of myosin II motor activity in distributing myosin asymmetrically and coupling protrusive activity to cell translocation. Mol Biol Cell 17:4435–4445
Kovács M, Tóth J, Hetényi C, Málnási-Csizmadia A, Sellers JR (2004) Mechanism of blebbistatin inhibition of myosin II. J Biol Chem 279:35557–35563
Liu W, Hendren J, Qin X, Shen J, Liu KJ (2009) Normobaric hyperoxia attenuates early blood-brain barrier disruption by inhibiting MMP-9-mediated occludin degradation in focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 108:811–820
Liu WY, Wang ZB, Zhang LC, Wei X, Li L (2012) Tight junction in blood-brain barrier: an overview of structure, regulation, and regulator substances. CNS Neurosci Ther 18(8):609–615
Liu T, Ye Y, Zhang X, Zhu A, Yang Z, Fu Y et al (2016) Downregulation of non-muscle myosin IIA expression inhibits migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells via the c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 13:1639–1644
Lu P, Chen J, Yan L, Yang L, Zhang L, Dai J, Hao Z, Bai T, Xi Y, Li Y, Kang Z, Xv J, Sun G, Yang T (2018) RasGRF2 promotes migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by modulating expression of MMP9 through Src/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Cancer Biol Ther 10:1–9
Luissint AC, Artus C, Glacial F, Ganeshamoorthy K, Couraud PO (2012) Tight junctions at the blood brain barrier: physiological architecture and disease-associated dysregulation. Fluids Barriers CNS 9:23
Lv Y, Fu L (2018) The potential mechanism for Hydroxysafflor yellow A attenuating blood-brain barrier dysfunction via tight junction signaling pathways excavated by an integrated serial affinity chromatography and shotgun proteomics analysis approach. Neurochem Int 112:38–48
Lv Y, Qian Y, Fu L, Chen X, Zhong H, Wei X (2015) Hydroxysafflor yellow A exerts neuroprotective effects in cerebral ischemia reperfusion-injured mice by suppressing the innate immune TLR4-inducing pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 769:324–332
Mashukova A, Wald FA, Salas PJ (2011) Tumor necrosis factor alpha and inflammation disrupt the polarity complex in intestinal epithelial cells by a posttranslational mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 31:756–765
Naydenov NG, Feygin A, Wang D, Kuemmerle JF, Harris G, Conti MA et al (2016) Nonmuscle Myosin IIA Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Barrier in vivo and Plays a Protective Role During Experimental Colitis. Sci Rep 6:24161
Neal CL, Xu J, Li P, Mori S, Yang J, Neal NN et al (2012) Overexpression of 14-3-3ζ in cancer cells activates PI3K via binding the p85 regulatory subunit. Oncogene 31:897–906
Nomura M, Shimizu S, Sugiyama T, Narita M, Ito T, Matsuda H et al (2003) 14-3-3 Interacts directly with and negatively regulates pro-apoptotic Bax. J Biol Chem 278:2058–2065
Pozuelo-Rubio M (2012) 14-3-3 Proteins are Regulators of Autophagy. Cells 1:754–773
Schuster TB, Costina V, Findeisen P, Neumaier M, Ahmad-Nejad P (2011) Identification and functional characterization of 14-3-3 in TLR2 signaling. J Proteome Res 10:4661–4670
Stamatovic SM, Johnson AM, Keep RF, Andjelkovic AV (2016) Junctional proteins of the blood-brain barrier: new insights into function and dysfunction. Tissue Barriers 4:e1154641
Turner JR (2006) Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation: from basic mechanisms to clinical application. Am J Pathol 169:1901–1909
Utech M, Ivanov AI, Samarin SN, Bruewer M, Turner JR, Mrsny RJ et al (2005) Mechanism of IFN-gamma-induced endocytosis of tight junction proteins: myosin II-dependent vacuolarization of the apical plasma membrane. Mol Biol Cell 16:5040–5052
Wang XT, Pei DS, Xu J, Guan QH, Sun YF, Liu XM et al (2007) Opposing effects of Bad phosphorylation at two distinct sites by Akt1 and JNK1/2 on ischemic brain injury. Cell Signal 19:1844–1856
Wang Y, Liu Q, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Lv Y, Tan Y et al (2016a) Ginsenoside Rg1 Protects against Oxidative Stress-induced Neuronal Apoptosis through Myosin IIA-actin Related Cytoskeletal Reorganization. Int J Biol Sci 12:1341–1356
Wang ZG, Cheng Y, Yu XC, Ye LB, Xia QH, Johnson NR et al (2016b) bFGF Protects Against Blood-Brain Barrier Damage Through Junction Protein Regulation via PI3K-Akt-Rac1 Pathway Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Mol Neurobiol 53:7298–7311
Wen H, Watry DD, Marcondes MC, Fox HS (2004) Selective decrease in paracellular conductance of tight junctions: role of the first extracellular domain of claudin-5. Mol Cell Biol 24:8408–8417
Wickman GR, Julian L, Mardilovich K, Schumacher S, Munro J, Rath N et al (2013) Blebs produced by actin-myosin contraction during apoptosis release damage-associated molecular pattern proteins before secondary necrosis occurs. Cell Death Differ 20:1293–1305
Wu JS, Cheung WM, Tsai YS, Chen YT, Fong WH, Tsai HD et al (2009) Ligand-activated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma protects against ischemic cerebral infarction and neuronal apoptosis by 14-3-3 epsilon upregulation. Circulation 119:1124–1134
Zhai K, Tang Y, Zhang Y, Li F, Wang Y, Cao Z et al (2015) NMMHC IIA inhibition impedes tissue factor expression and venous thrombosis via Akt/GSK3β-NF-κB signalling pathways in the endothelium. Thromb Haemost 114:173
Zhaocheng J, Jinfeng L, Luchang Y, Yequan S, Feng L, Kai W (2016) Ginkgolide A inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human coronary artery endothelial cells via downregulation of TLR4-NF-κB signaling through PI3K/Akt pathway. Pharmazie 71(10):588–591
Zhou C, Wang Y, Peng J, Li C, Liu P, Shen X (2017) SNX10 Plays a Critical Role in MMP9 Secretion via JNK-p38-ERK Signaling Pathway. J Cell Biochem 118:4664–4671
Zhu Y, Bu Q, Liu X, Hu W, Wang Y (2014) Neuroprotective effect of TAT-14-3-3e fusion protein against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. PLoS ONE 9:e93334
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Foundation Project: National Natural Science Foundation of China (81760094, 31602111, 81860020), China; Jiangxi Provincial Education Department Science and Technology Research Youth Project (No. GJJ160238); The Foundation of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology Youth Project (No. 20171BAB215021). The funder has no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the research. YL conceived the experiments. YL, WL, ZR, ZX, LF conducted the experiments and analyzed the results. All authors contributed to the writing and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest, including financial, personal or other relationships, with other individuals or organizations.
Ethical Approval
All animal care and experimental procedures were conducted according to standard ethical guidelines (National Institutes of Health Guide to the use of Laboratory Animals) and approved by Institutional Animal Care and use Committee of Nanchang University. All efforts were made to minimize the number of mice used and their suffering.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Y., Liu, W., Ruan, Z. et al. Myosin IIA Regulated Tight Junction in Oxygen Glucose-Deprived Brain Endothelial Cells Via Activation of TLR4/PI3K/Akt/JNK1/2/14-3-3ε/NF-κB/MMP9 Signal Transduction Pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol 39, 301–319 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00654-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00654-y