Abstract
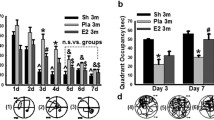
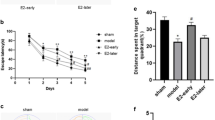
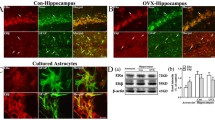
Although a substantial number of pre-clinical and experimental studies have investigated effects of 17β-estradiol, its precise molecular mechanism of action in the early state of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion remains controversial. The present study attempted to verify whether post-ischemic estradiol treatment (33.3 μg/kg for seven consecutive days) affects previously reported number of hippocampal apoptotic cells and amount of DNA fragmentation characteristic for apoptosis as well as the expression of key elements within synaptosomal Akt and Erk signal transduction pathways (NF-κB, Bax, Bcl-2, cytochrome C, caspase 3, and PARP). Additionally, alterations of aforementioned molecules linked to protection in various neurodegenerative disorders were monitored in the cytosolic, mitochondrial, and nuclear fractions associating investigated kinases and NF-κB with gene expression of their downstream effectors—Bcl-2, Bax, and caspase 3. The results revealed that an initial increase in the number of apoptotic cells and amount of DNA fragmentation induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion was significantly reduced by 17β-estradiol. In synaptic regions, an altered profile with respect to the protein expression of Bcl-2 and phosphorylated Akt was detected, although the level of other examined proteins was not modified. In other investigated sub-cellular fractions, 17β-estradiol elicited phosphorylation and translocation of Akt and Erk along with modulation of the expression of their subsequent effectors. Our findings support the concept that repeated post-ischemic 17β-estradiol treatment attenuates neurodegeneration induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in hippocampus through the activation of investigated kinases and regulation of their downstream molecules in sub-cellular manner indicating a time window and regime of its administration as a valid therapeutic intervention.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arevalo MA, Iñigo Azcoitia I, Garcia-Segura LM (2015) The neuroprotective actions of oestradiol and oestrogen receptors. Nat Rev Neurosci 16:17–29
Bingham D, Macrae IM, Carswell HV (2005) Detrimental effects of 17beta-oestradiol after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:414–420
Bondeau N, Widmann C, Lazdunski M, Heurteaux C (2001) Activation of the nuclear factor-κB is a key event in brain tolerance. J Neurosci 21:4668–4677
Brann D, Raz L, Wang R, Vadlamudi R, Zhang Q (2012) Oestrogen signalling and neuroprotection in cerebral ischaemia. J Neuroendocrinol 24:34–47
Cargnello M, Roux PP (2011) Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 75:50–83
Choi YC, Lee JH, Hong KW, Lee KS (2004) 17 Beta-estradiol prevents focal cerebral ischemic damages via activation of Akt and CREB in association with reduced PTEN phosphorylation in rats. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 18(5):547–557
Costain WJ, Rasquinha I, Sandhu JK, Rippstein P, Zurakowski B, Slinn J, MacManus JP, Stanimirovic DB (2008) Cerebral ischemia causes dysregulation of synaptic adhesion in mouse synaptosomes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28(1):99–110
Desagher S, Martinou JC (2000) Mitochondria as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 10(9):369–377
Drakulić D, Veličković N, Stanojlović M, Grković I, Mitrović N, Lavrnja I, Horvat A (2013) Low-dose dexamethasone treatment promotes the pro-survival signalling pathway in the adult rat prefrontal cortex. J Neuroendocrinol 25:605–616
Dubal DB, Wise PM (2001) Neuroprotective effects of estradiol in middle-aged female rats. Endocrinology 142(1):43–48
Dubal DB, Kashon ML, Pettigrew LC, Ren JM, Finklestein SP, Rau SW, Wise PM (1998) Estradiol protects against ischemic injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 18(11):1253–1258
Dubal DB, Shughrue PJ, Wilson ME, Merchenthaler I, Wise PM (1999) Estradiol modulates bcl-2 in cerebral ischemia: a potential role for estrogen receptors. J Neurosci 19(15):6385–6393
Friguls B, Petegnief V, Justicia C, Pallàs M, Planas AM (2002) Activation of Erk and Akt signaling in focal cerebral ischemia: modulation by TGF-alpha and involvement of NMDA receptor. Neurobiol Dis 11:443–456
Garcia-Segura LM, Azcoitia I, DonCarlos LL (2001) Neuroprotection by estradiol. Prog Neurobiol 63:29–60
Gibson CL (2013) Cerebral ischemic stroke: is gender important? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33:1355–1361
Gordon KB, Macrae IM, Carswell HV (2005) Effects of 17beta-oestradiol on cerebral ischaemic damage and lipid peroxidation. Brain Res 1036:155–162
Grodstein F, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Rexrode K (2008) Postmenopausal hormone therapy and stroke: role of time since menopause and age at initiation of hormone therapy. Arch Intern Med 168(8):861–866
Harukuni I, Hurn PD, Crain BJ (2001) Deleterious effect of beta-estradiol in a rat model of transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res 900:137–142
Hofmeijer J, van Putten MJ (2012) Ischemic cerebral damage: an appraisal of synaptic failure. Stroke 43:607–615
Jia J, Guan D, Zhu W, Alkayed NJ, Wang MM, Hua Z, Xu Y (2009) Estrogen inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis in experimental stroke. Exp Neurol 215(1):48–52
Jover T, Tanaka H, Calderone A, Oguro K, Bennett MVL, Etgen AM, Zukin RS (2002) Estrogen protects against global ischemia-induced neuronal death and prevents activation of apoptotic signaling cascades in the hippocampal CA1. J Neurosci 22:2115–2124
Jover-Menguala T, Miyawakia T, Latuszeka A, Alborchb E, ZukinaRS Suzanne, Etgen AM (2010) Acute estradiol protects CA1 neurons from ischemia-induced apoptotic cell death via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Brain Res 1321C:1–12
Koellhoffer EC, McCullough LD (2013) The effects of estrogen in ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res 4:390–401
Lebesgue D, Chevaleyre V, Zukin RS, Etgen AM (2009) Estradiol rescues neurons from global ischemia induced cell death: multiple cellular pathways of neuroprotection. Steroids 74:555–561
Li J, Siegel M, Yuan M, Zeng Z, Finnucan L, Persky R, Hurn PD, McCullough LD (2011) Estrogen enhances neurogenesis and behavioral recovery after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31(2):413–425
Li V, Kong J, Szelemej P, Bi X (2012) Delayed neuronal death in ischemic stroke: molecular pathways. INTECH Open Access Publisher, Rijeka
Liu M, Dziennis S, Hurn PD, Alkayed NJ (2009) Mechanisms of gender-linked ischemic brain injury. Restor Neurol Neurosci 27(3):163–179
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2009) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 (-Delta DeltaC(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Lobo RA (2013) Where are we 10 years after the Women’s Health Initiative? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98(5):1771–1780
Ma YL, Qin P, Li Y, Shen L, Wang SQ, Dong HL, Hou WG, Xiong LZ (2013) The effects of different doses of estradiol (E2) on cerebral ischemia in an in vitro model of oxygen and glucose deprivation and reperfusion and in a rat model of middle carotid artery occlusion. BMC Neurosci 14:118
Manthey D, Behl C (2006) From structural biochemistry to expression profiling: neuroprotective activities of estrogen. Neuroscience 138(3):845–850
Markwell MA, Haas SM, Bieber LL, Tolbert NE (1978) A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem 87:206–210
Mattson MP, Duan W (1999) “Apoptotic” biochemical cascades in synaptic compartments: roles in adaptive plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurosci Res 58:152–166
McCullough LD, Zeng Z, Blizzard KK, Debchoudhury I, Hurn PD (2005) Ischemic nitric oxide and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 in cerebral ischemia: male toxicity, female protection. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:502–512
McLaughlin B (2004) The kinder side of killer proteases: caspase activation contributes to neuroprotection and CNS remodeling. Apoptosis 9:111–121
Petrone AB, Simpkins JW, Barr TL (2014) 17β-estradiol and inflammation: implications for ischemic stroke. Aging Dis 5(5):340–345
Rutledge RG, Cote C (2003) Mathematics of quantitative kinetic PCR and the application of standard curves. Nucleic Acids Res 31:e93
Sherwin BB (2009) Estrogen therapy: is time of initiation critical for neuroprotection? Nat Rev Endocrinol 5:620–627
Simpkins JW, Rajakumar G, Zhang YQ, Simpkins CE, Greenwald D, Yu CJ, Bodor N, Day AL (1997) Estrogens may reduce mortality and ischemic damage caused by middle cerebral artery occlusion in the female rat. J Neurosurg 87(5):724–730
Singer CA, Rogers KL, Dorsa DM (1998) Modulation of Bcl-2 expression: a potential component of estrogen protection in NT2 neurons. NeuroReport 9(11):2565–2568
Singh M (2001) Ovarian hormones elicit phosphorylation of Akt and extracellular-signal regulated kinase in explants of the cerebral cortex. Endocrine 14:407–415
Stanojlović M, Guševac I, Grković I, Mitrović N, Horvat A, Drakulić D (2014a) Time-related sex differences in cerebral-hypoperfusion induced brain injury. Arch Biol Sci Belgrade 66(4):1673–1680
Stanojlović M, Horvat A, Guševac I, Grković I, Mitrović N, Buzadžić I, Drakulić D (2014b) Time course of cerebral hypoperfusion-induced neurodegenerative changes in the cortex of male and female rats. Folia Biol 60:123–132
Stanojlović M, Zlatković J, Guševac I, Grković I, Mitrović N, Zarić M, Horvat A, Drakulić D (2015) Repeated low-dose 17β-estradiol treatment prevents activation of apoptotic signaling both in the synaptosomal and cellular fraction in rat prefrontal cortex following cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Int. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2015.03.002
Stoltzner SE, Berchtold NC, Cotman CW, Pike CJ (2001) Estrogen regulates bcl-x expression in rat hippocampus. NeuroReport 12(13):2797–2800
Tang H, Zhang Q, Yang L, Dong Y, Khan M, Yang F, Brann DW, Wang R (2014) GPR30 mediates estrogen rapid signaling and neuroprotection. Mol Cell Endocrinol 387(1–2):52–58
Terada K, Kaziro Y, Satoh T (2000) Analysis of Ras-dependent signals that prevent caspase-3 activation and apoptosis induced by cytokine deprivationin hematopoietic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 267:449–455
Wang C, Youle RJ (2009) The role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet 43:95–118
Wang R, Zhang Q-G, Han D, Xu J, Lü Q, Zhang G-Y (2006) Inhibition of MLK3-MKK4/7-JNK1/2 pathway by Akt1 in exogenous estrogen-induced neuroprotection against transient global cerebral ischemia by a non-genomic mechanism in male rats. J Neurochem 99(6):1543–1554
Yang SH, Shi J, Day AL, Simpkins JW (2000) Estradiol exerts neuroprotective effects when administered after ischemic insult. Stroke 31(3):745–749
Yang L, Zhang QG, Zhou C, Yang F, Zhang Y, Wang R, Brann DW (2010) Extranuclear estrogen receptors mediate the neuroprotective effects of estrogen in the rat hippocampus. PLoS One 5(5):e9851
Zhou H, Li XM, Meinkoth J, Pittman RN (2000) Akt regulates cell survival and apoptosis at a postmitochondrial level. J Cell Biol 151:483–494
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of Republic of Serbia, Project Nos. 173044 and 41014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanojlović, M., Guševac, I., Grković, I. et al. Repeated Estradiol Treatment Attenuates Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion-Induced Neurodegeneration in Rat Hippocampus. Cell Mol Neurobiol 36, 989–999 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0289-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0289-0