Abstract
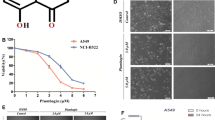
Salvianolic acid B (SalB), the main water-soluble bioactive compounds isolated from the traditional Chinese medical herb Danshen, has been shown to exert anti-cancer effect in several cancer cell lines. The aim of our study was to investigate the potential anti-cancer effect of SalB in human glioma U87 cells. We found that treatment with SalB significantly decreased cell viability of U87 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. SalB also enhanced the intracellular ROS generation and induced apoptotic cell death in U87 cells. Western blot analysis suggested that SalB increased the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and p53 in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, blocking p38 activation by specific inhibitor SB203580 or p38 specific siRNA partly reversed the anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects, and ROS production induced by SalB treatment. The anti-tumor activity of SalB in vivo was also demonstrated in U87 xenograft glioma model. All of these findings extended the anti-cancer effect of SalB in human glioma cell lines, and suggested that these inhibitory effects of SalB on U87 glioma cell growth might be associated with p38 activation mediated ROS generation. Thus, SalB might be concerned as an effective and safe natural anticancer agent for glioma prevention and treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benhar M, Engelberg D, Levitzki A (2002) ROS, stress-activated kinases and stress signaling in cancer. EMBO Rep 3(5):420–425. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvf094
Bradham C, McClay DR (2006) p38 MAPK in development and cancer. Cell Cycle 5(8):824–828
Bulavin DV, Saito S, Hollander MC, Sakaguchi K, Anderson CW, Appella E, Fornace AJ Jr (1999) Phosphorylation of human p53 by p38 kinase coordinates N-terminal phosphorylation and apoptosis in response to UV radiation. EMBO J 18(23):6845–6854. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.23.6845
Cao W, Guo XW, Zheng HZ, Li DP, Jia GB, Wang J (2012) Current progress of research on pharmacologic actions of salvianolic acid B. Chinese journal of integrative medicine 18(4):316–320. doi:10.1007/s11655-011-012-1052-8
Chen YR, Tan TH (2000) The c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and apoptotic signaling (review). Int J Oncol 16(4):651–662
Chen T, Liu W, Chao X, Zhang L, Qu Y, Huo J, Fei Z (2011) Salvianolic acid B attenuates brain damage and inflammation after traumatic brain injury in mice. Brain Res Bull 84(2):163–168. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2010.11.015
Chen T, Fei F, Jiang XF, Zhang L, Qu Y, Huo K, Fei Z (2012) Down-regulation of Homer1b/c attenuates glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity through endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria pathways in rat cortical neurons. Free Radical Biol Med 52(1):208–217. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.10.451
Chiu CC, Chen JY, Lin KL, Huang CJ, Lee JC, Chen BH, Chen WY, Lo YH, Chen YL, Tseng CH, Lin SR (2010) p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways are involved in naphtho[1,2-b] furan-4,5-dione induced anti-proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatoma cells. Cancer Lett 295(1):92–99. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2010.02.017
Cuadrado A, Lafarga V, Cheung PC, Dolado I, Llanos S, Cohen P, Nebreda AR (2007) A new p38 MAP kinase-regulated transcriptional coactivator that stimulates p53-dependent apoptosis. EMBO J 26(8):2115–2126. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601657
Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Chandraratna RA, Ellenbogen RG, Geyer JR, Overland RP, Strand AD, Tapscott SJ, Olson JM (2003) BMP-2 mediates retinoid-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma cells through a paracrine effect. Nat Med 9(8):1033–1038. doi:10.1038/nm904
Hao Y, Xie T, Korotcov A, Zhou Y, Pang X, Shan L, Ji H, Sridhar R, Wang P, Califano J, Gu X (2009) Salvianolic acid B inhibits growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo via cyclooxygenase-2 and apoptotic pathways. Int J Cancer 124(9):2200–2209. doi:10.1002/ijc.24160
Hernandez Losa J, Parada Cobo C, Guinea Viniegra J, Sanchez-Arevalo Lobo VJ, Ramon y Cajal S, Sanchez-Prieto R (2003) Role of the p38 MAPK pathway in cisplatin-based therapy. Oncogene 22(26):3998–4006. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206608
Hur JM, Hyun MS, Lim SY, Lee WY, Kim D (2009) The combination of berberine and irradiation enhances anti-cancer effects via activation of p38 MAPK pathway and ROS generation in human hepatoma cells. J Cell Biochem 107(5):955–964. doi:10.1002/jcb.22198
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA 61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107
Mondal S, Bandyopadhyay S, Ghosh MK, Mukhopadhyay S, Roy S, Mandal C (2012) Natural products: promising resources for cancer drug discovery. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 12(1):49–75
Olson JM, Hallahan AR (2004) p38 MAP kinase: a convergence point in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med 10(3):125–129. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2004.01.007
Park JW, Lee SH, Yang MK, Lee JJ, Song MJ, Ryu SY, Chung HJ, Won HS, Lee CS, Kwon SH, Yun YP, Choi WS, Shin HS (2008) 15,16-dihydrotanshinone I, a major component from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Dansham), inhibits rabbit platelet aggregation by suppressing intracellular calcium mobilization. Arch Pharmacal Res 31(1):47–53
Pelicano H, Carney D, Huang P (2004) ROS stress in cancer cells and therapeutic implications. Drug Resis Updat 7(2):97–110. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2004.01.004
Ralph SJ, Rodriguez-Enriquez S, Neuzil J, Moreno-Sanchez R (2010) Bioenergetic pathways in tumor mitochondria as targets for cancer therapy and the importance of the ROS-induced apoptotic trigger. Mol Aspects Med 31(1):29–59. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2009.12.006
Rock K, McArdle O, Forde P, Dunne M, Fitzpatrick D, O’Neill B, Faul C (2012) A clinical review of treatment outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme—the validation in a non-trial population of the results of a randomised Phase III clinical trial: has a more radical approach improved survival? Br J Radiol 85(1017):e729–e733. doi:10.1259/bjr/83796755
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. New Engl J Med 352(10):987–996. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K, Hau P, Brandes AA, Gijtenbeek J, Marosi C, Vecht CJ, Mokhtari K, Wesseling P, Villa S, Eisenhauer E, Gorlia T, Weller M, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Mirimanoff RO (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10(5):459–466. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7
Takahashi S, Fusaki N, Ohta S, Iwahori Y, Iizuka Y, Inagawa K, Kawakami Y, Yoshida K, Toda M (2012) Downregulation of KIF23 suppresses glioma proliferation. J Neurooncol 106(3):519–529. doi:10.1007/s11060-011-0706-2
Wagner EF, Nebreda AR (2009) Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 9(8):537–549. doi:10.1038/nrc2694
Zhao Y, Hao Y, Ji H, Fang Y, Guo Y, Sha W, Zhou Y, Pang X, Southerland WM, Califano JA, Gu X (2010) Combination effects of salvianolic acid B with low-dose celecoxib on inhibition of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 3(6):787–796. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0243
Zhao Y, Guo Y, Gu X (2011) Salvianolic acid B, a potential chemopreventive agent, for head and neck squamous cell cancer. J Oncol 2011:534548. doi:10.1155/2011/534548
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zi-shu Wang, Peng Luo and Shu-hui Dai contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Zs., Luo, P., Dai, Sh. et al. Salvianolic Acid B Induces Apoptosis in Human Glioma U87 Cells Through p38-Mediated ROS Generation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 921–928 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9958-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9958-z