Abstract
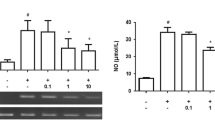
Acute encephalopathy is a generic term for acute brain dysfunction occurring after infection. Acute encephalopathy induced by influenza virus results in high mortality, and most cases of influenza-associated encephalopathy (IAE) result in brain edema. Administration of diclofenac sodium (DCF), a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), is associated with a significant increased mortality rate of IAE. These previous clinical findings proposed further investigation of DCF administration and brain edema to clarify how DCF aggravates IAE. Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) is the predominant water channel protein in the mammalian brain, and is mainly expressed in astrocytes. AQP4 plays an important role in brain water homeostasis. Therefore, we investigated a possible association between DCF and AQP4 production in astrocytes. We stimulated cultured rat astrocytes with three cytokines, interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor α, and interferon γ, and then treated with DCF. DCF enhanced proinflammatory cytokine-induced AQP4 gene and protein expression in astrocytes, whereas DCF alone did not change the AQP4 gene expression. The addition of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) inhibitor abrogated AQP4 gene and protein expression completely in astrocytes treated with cytokines alone and in those also treated with DCF. In conclusion, this study demonstrated that AQP4 is upregulated in astrocyte by proinflammatory cytokines, and that the addition of DCF further augments AQP4 production. This effect is mediated via NF-κB signaling. The enhancement of AQP4 production by DCF may explain the significantly increased mortality rates in IAE patients treated with DCF.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe Y, Ikeshima-Kataoka H, Goda W, Niikura T, Yasui M (2012) An astrocyte-specific enhancer of the aquaporin-4 gene functions through a consensus sequence of POU transcription factors in concert with multiple upstream elements. J Neurochem 120:899–912
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP (2003) The molecular basis of water transport in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:991–1001
Amiry-Moghaddam M, Otsuka T, Hurn PD, Traystman RJ, Haug FM, Froehner SC, Adams ME, Neely JD, Agre P, Ottersen OP, Bhardwaj A (2003) An alpha-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2106–2111
Aoyama M, Kakita H, Kato S, Tomita M, Asai K (2012) Region-specific expression of a water channel protein, aquaporin 4, on brain astrocytes. J Neurosci Res 90:2272–2280
Belay ED, Bresee JS, Holman RC, Khan AS, Shahriari A, Schonberger LB (1999) Reye’s syndrome in the United States from 1981 through 1997. New Engl J Med 340:1377–1382
Binder DK, Steinhauser C (2006) Functional changes in astroglial cells in epilepsy. Glia 54:358–368
Bloch O, Papadopoulos MC, Manley GT, Verkman AS (2005) Aquaporin-4 gene deletion in mice increases focal edema associated with staphylococcal brain abscess. J Neurochem 95:254–262
Gunnarson E, Zelenina M, Aperia A (2004) Regulation of brain aquaporins. Neuroscience 129:947–955
Hinz B, Brune K (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2–10 years later. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 300:367–375
Hinz B, Brune K (2004) Pain and osteoarthritis: new drugs and mechanisms. Curr Opin Rheumatol 16:628–633
Kakita H, Aoyama M, Hussein MH, Kato S, Suzuki S, Ito T, Togari H, Asai K (2009) Diclofenac enhances proinflammatory cytokine-induced nitric oxide production through NF-kappaB signaling in cultured astrocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharm 238:56–63
Kawada J, Kimura H, Kamachi Y, Nishikawa K, Taniguchi M, Nagaoka K, Kurahashi H, Kojima S, Morishima T (2006) Analysis of gene-expression profiles by oligonucleotide microarray in children with influenza. J Gen Virol 87:1677–1683
Kawashima H, Watanabe Y, Morishima T, Togashi T, Yamada N, Kashiwagi Y, Takekuma K, Hoshika A, Mori T (2003) NOx (nitrite/nitrate) in cerebral spinal fluids obtained from patients with influenza-associated encephalopathy. Neuropediatrics 34:137–140
Kawashima H, Amaha M, Ioi H, Yamanaka G, Kashiwagi Y, Sasamoto M, Takekuma K, Hoshika A, Watanabe Y (2005) Nitrite/nitrate (NOx) and zinc concentrations in influenza-associated encephalopathy in children with different sequela. Neurochem Res 30:311–314
Kimelberg HK (2004) Water homeostasis in the brain: basic concepts. Neuroscience 129:851–860
Kozuka N, Itofusa R, Kudo Y, Morita M (2005) Lipopolysaccharide and proinflammatory cytokines require different astrocyte states to induce nitric oxide production. J Neurosci Res 82:717–728
Kozuka N, Kudo Y, Morita M (2007) Multiple inhibitory pathways for lipopolysaccharide- and pro-inflammatory cytokine-induced nitric oxide production in cultured astrocytes. Neuroscience 144:911–919
Lee M, Lee SJ, Choi HJ, Jung YW, Frøkiaer J, Nielsen S, Kwon TH (2008) Regulation of AQP4 protein expression in rat brain astrocytes: role of P2X7 receptor activation. Brain Res 1195:1–11
Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS (2000) Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med 6:159–163
Maricich SM, Neul JL, Lotze TE, Cazacu AC, Uyeki TM, Demmler GJ, Clark GD (2004) Neurologic complications associated with influenza A in children during the 2003–2004 influenza season in Houston, Texas. Pediatrics 114:626–633
Minghetti L (2004) Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in inflammatory and degenerative brain diseases. J Neuropath Exp Neur 63:901–910
Miyachi T, Asai K, Tsuiki H, Mizuno H, Yamamoto N, Yokoi T, Aoyama M, Togari H, Wada Y, Miura Y, Kato T (2001) Interleukin-1beta induces the expression of lipocortin 1 mRNA in cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Neurosci Res 40:53–60
Mizuguchi M, Yamanouchi H, Ichiyama T, Shiomi M (2007) Acute encephalopathy associated with influenza and other viral infections. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 186:45–56
Nagao T, Morishima T, Kimura H, Yokota S, Yamashita N, Ichiyama T, Kurihara M, Miyazaki C, Okabe N (2008) Prognostic factors in influenza-associated encephalopathy. Pediatr Infect Dis J 27:384–389
Nielsen S, Nagelhus EA, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Bourque C, Agre P, Ottersen OP (1997) Specialized membrane domains for water transport in glial cells: high-resolution immunogold cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J Neurosci 17:171–180
Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS (2005) Aquaporin-4 gene disruption in mice reduces brain swelling and mortality in pneumococcal meningitis. J Biol Chem 280:13906–13912
Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS (2007) Aquaporin-4 and brain edema. Pediatr Nephrol 22:778–784
Papadopoulos MC, Saadoun S, Binder DK, Manley GT, Krishna S, Verkman AS (2004) Molecular mechanisms of brain tumor edema. Neuroscience 129:1011–1020
Powell-Jackson PR, Tredger JM, Williams R (1984) Hepatotoxicity to sodium valproate. Gut 25:673–681
Saez-Llorens X, McCracken GH (2003) Bacterial meningitis in children. Lancet 361:2139–2148
Schrör K (2007) Aspirin and Reye syndrome: a review of the evidence. Paediatr Drugs 9:195–204
Seifert G, Schilling K, Steinhauser C (2006) Astrocyte dysfunction in neurological disorders: a molecular perspective. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:194–206
Unterberg AW, Stover J, Kress B, Kiening KL (2004) Edema and brain trauma. Neuroscience 129:1021–1029
Vajda Z, Pedersen M, Fuchtbauer EM, Wertz K, Stodkilde-Jorgensen H, Sulyok E, Doczi T, Neely JD, Agre P, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S (2002) Delayed onset of brain edema and mislocalization of aquaporin-4 in dystrophin-null transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13131–13136
Yamanaka G, Kawashima H, Suganami Y, Watanabe C, Watanabe Y, Miyajima T, Takekuma K, Oguchi S, Hoshika A (2006) Diagnostic and predictive value of CSF d-ROM level in influenza virus-associated encephalopathy. J Neurol Sci 243:71–75
Yukutake Y, Yasui M (2010) Regulation of water permeability through aquaporin-4. Neuroscience 168:885–891
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Christopher McPherson at NIEHS for helpful comments regarding this manuscript. This study was supported in part by a Health and Labor Sciences Research Grant on “Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases” from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, by a Grant-in Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas “Elucidation of glia-neuron network mediated information processing systems” and by a Grant-in Aid for Scientific Research (C) and a Grant-in Aid for Young Scientists (B) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asai, H., Kakita, H., Aoyama, M. et al. Diclofenac Enhances Proinflammatory Cytokine-Induced Aquaporin-4 Expression in Cultured Astrocyte. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 393–400 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9905-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9905-z