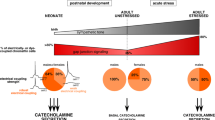
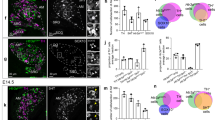
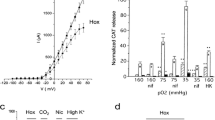
Abstract
The adrenal medullary tissue contributes to maintain body homeostasis in reaction to stressful environmental changes via the release of catecholamines into the blood circulation in response to splanchnic nerve activation. Accordingly, chromaffin cell stimulus-secretion coupling undergoes temporally restricted periods of anatomo-functional remodeling in response to prevailing hormonal requirements of the organism. The postnatal development of the adrenal medulla and response to stress are remarkable physiological situations in which the stimulus-secretion coupling is critically affected. Catecholamine secretion from rat chromaffin cells is under a dual control involving an incoming initial command arising from the sympathetic nervous system that releases acetylcholine at the splanchnic nerve terminal-chromaffin cell synapses and a local gap junction-mediated intercellular communication. Interestingly, these two communication pathways are functionally interconnected within the gland and exhibit coordinated plasticity mechanisms. This article reviews the physiological and molecular evidence that the adrenal medullary tissue displays anatomical and functional adaptative remodeling of cell–cell communications upon physiological (postnatal development) and/or physiopathological (stress) situations associated with specific needs in circulating catecholamine levels.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbara JG, Takeda K (1996) Quantal release at a neuronal nicotinic synapse from rat adrenal gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9905–9909
Barbara JG, Lemos VS, Takeda K (1998) Pre- and post-synaptic muscarinic receptors in thin slices of rat adrenal gland. Eur J Neurosci 10:3535–3545
Brumwell CL, Johnson JL, Jacob MH (2002) Extrasynaptic alpha 7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expression in developing neurons is regulated by inputs, targets, and activity. J Neurosci 22:8101–8109
Buttigieg J, Brown S, Zhang M, Lowe M, Holloway AC, Nurse CA (2008) Chronic nicotine in utero selectively suppresses hypoxic sensitivity in neonatal rat adrenal chromaffin cells. FASEB J 22:1317–1326
Buttigieg J, Brown S, Holloway AC, Nurse CA (2009) Chronic nicotine blunts hypoxic sensitivity in perinatal rat adrenal chromaffin cells via upregulation of KATP channels: role of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha. J Neurosci 29:7137–7147
Carabelli V, Marcantoni A, Comunanza V, de Luca A, Díaz J, Borges R, Carbone E (2007) Chronic hypoxia up-regulates alpha1H T-type channels and low-threshold catecholamine secretion in rat chromaffin cells. J Physiol 584:149–165
Chang Q, Balice-Gordon RJ (2000) Gap junctional communication among developing and injured motor neurons. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 32:242–249
Colomer C, Olivos-Oré LA, Coutry N, Mathieu M-N, Arthaud S, Fontanaud P, Iankova I, Macari F, Thouënnon E, Yon L, Anouar Y, Guérineau NC (2008a) Functional remodeling of gap junction-mediated electrical communication between adrenal chromaffin cells in stressed rats. J Neurosci 28:6616–6626
Colomer C, Lafont C, Guérineau NC (2008b) Stress-induced intercellular communication remodeling in the rat adrenal medulla. Ann NY Acad Sci 1148:106–111
Colomer C, Desarménien MG, Guérineau NC (2009) Revisiting the stimulus-secretion coupling in the adrenal medulla: role of gap junction-mediated intercellular communication. Mol Neurobiol 40:87–100
Colomer C, Olivos-Oré LA, Vincent A, McIntosh JM, Artalejo AR, Guérineau NC (2010) Functional characterization of alpha9-containing cholinergic nicotinic receptors in the rat adrenal medulla: implication in stress-induced functional plasticity. J Neurosci 30:6732–6742
Daikoku S, Kinutani M, Sako M (1977) Development of the adrenal medullary cells in rats with reference to synaptogenesis. Cell Tissue Res 179:77–86
de Diego AM, Gandía L, García AG (2008) A physiological view of the central and peripheral mechanisms that regulate the release of catecholamines at the adrenal medulla. Acta Physiol 192:287–301
del Toro R, Levitsky KL, López-Barneo J, Chiara MD (2003) Induction of T-type calcium channel gene expression by chronic hypoxia. J Biol Chem 278:22316–22324
Douglas WW (1968) Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol 34:451–474
Ducsay CA, Hyatt K, Mlynarczyk M, Root BK, Kaushal KM, Myers DA (2007) Long-term hypoxia modulates expression of key genes regulating adrenomedullary function in the late gestation ovine fetus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R1997–R2005
García-Fernández M, Mejías R, López-Barneo J (2007) Developmental changes of chromaffin cell secretory response to hypoxia studied in thin adrenal slices. Pflügers Arch 454:93–100
Goldstein DS, Kopin IJ (2007) Evolution of concepts of stress. Stress 10:109–120
Hamelink C, Tjurmina O, Damadzic R, Young WS, Weihe E, Lee HW, Eiden LE (2002) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide is a sympathoadrenal neurotransmitter involved in catecholamine regulation and glucohomeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:461–466
Inoue M, Harada K, Matsuoka H, Sata T, Warashina A (2008) Inhibition of TASK1-like channels by muscarinic receptor stimulation in rat adrenal medullary cells. J Neurochem 106:1804–1814
Kandler K, Katz LC (1995) Neuronal coupling and uncoupling in the developing nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5:98–105
Kuri BA, Chan SA, Smith CB (2009) PACAP regulates immediate catecholamine release from adrenal chromaffin cells in an activity-dependent manner through a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. J Neurochem 110:1214–1225
Kvetnansky R, Sun CL, Lake CR, Thoa N, Torda T, Kopin IJ (1978) Effect of handling and forced immobilization on rat plasma levels of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. Endocrinology 103:1868–1874
Kvetnansky R, Sabban EL, Palkovits M (2009) Catecholaminergic systems in stress: structural and molecular genetic approaches. Physiol Rev 89:535–606
Lau AF, Kurata WE, Kanemitsu MY, Loo LW, Warn-Cramer BJ, Eckhart W, Lampe PD (1996) Regulation of connexin43 function by activated tyrosine protein kinases. J Bioenerg Biomembr 28:359–668
Lee K, Ito A, Koshimura K, Ohue T, Takagi Y, Miwa S (1995) Differential effects of hypoxia on ligand binding properties of nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors on cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem 64:874–882
Levitsky KL, López-Barneo J (2009) Developmental change of T-type Ca2+ channel expression and its role in rat chromaffin cell responsiveness to acute hypoxia. J Physiol 587:1917–1929
Martin AO, Mathieu M-N, Chevillard C, Guérineau NC (2001) Gap junctions mediate electrical signaling and ensuing cytosolic Ca2+ increases between chromaffin cells in adrenal slices: a role in catecholamine release. J Neurosci 21:5397–5405
Martin AO, Mathieu M-N, Guérineau NC (2003) Evidence for long-lasting cholinergic control of gap junctional communication between adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurosci 23:3669–3678
Martin AO, Alonso G, Guérineau NC (2005) Agrin mediates a rapid switch from electrical coupling to chemical neurotransmission during synaptogenesis. J Cell Biol 169:503–514
Mentis GZ, Diaz E, Moran LB, Navarrete R (2002) Increased incidence of gap junctional coupling between spinal motoneurones following transient blockade of NMDA receptors in neonatal rats. J Physiol 544:757–764
Mochizuki-Oda N, Takeuchi Y, Matsumura K, Oosawa Y, Watanabe Y (1997) Hypoxia-induced catecholamine release and intracellular Ca2+ increase via suppression of K+ channels in cultured rat adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem 69:377–387
Muñoz-Cabello AM, Toledo-Aral JJ, López-Barneo J, Echevarría M (2005) Rat adrenal chromaffin cells are neonatal CO2 sensors. J Neurosci 25:6631–6640
Nurse CA, Buttigieg J, Thompson R, Zhang M, Cutz E (2006) Oxygen sensing in neuroepithelial and adrenal chromaffin cells. Novartis Found Symp 272:106–114
Nurse CA, Buttigieg J, Brown S, Holloway AC (2009) Regulation of oxygen sensitivity in adrenal chromaffin cells. Ann NY Acad Sci 1177:132–139
Olivos L, Artalejo AR (2008) Muscarinic excitation-secretion coupling in chromaffin cells. Acta Physiol 192:213–220
Oomori Y, Habara Y, Kanno T (1998) Muscarinic and nicotinic receptor-mediated Ca2+ dynamics in rat adrenal chromaffin cells during development. Cell Tissue Res 294:109–123
Parker TL, Kesse WK, Tomlinson A, Coupland RE (1988) Ontogenesis of preganglionic sympathetic innervation of rat adrenal chromaffin cells. In: Liss AR (ed) Progress in catecholamine research, part A: basic aspects and peripheral mechanisms. New York: Alan R. Liss Inc, pp 227–232
Sala F, Nistri A, Criado M (2008) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of adrenal chromaffin cells. Acta Physiol 192:203–212
Seidler FJ, Slotkin TA (1985) Adrenomedullary function in the neonatal rat: responses to acute hypoxia. J Physiol 358:1–16
Slotkin TA (1986) Development of the sympathoadrenal axis. In: Gootman PM (ed) Developmental neurobiology of the autonomic nervous system. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 69–96
Souvannakitti D, Kuri B, Yuan G, Pawar A, Kumar GK, Smith C, Fox AP, Prabhakar NR (2010) Neonatal intermittent hypoxia impairs neuronal nicotinic receptor expression and function in adrenal chromaffin cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299:C381–C388
Spray DC, Bennett MV (1985) Physiology and pharmacology of gap junctions. Annu Rev Physiol 47:281–303
Stroth N, Eiden LE (2010) Stress hormone synthesis in mouse hypothalamus and adrenal gland triggered by restraint is dependent on pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide signaling. Neuroscience 165:1025–1030
Tai TC, Claycomb R, Her S, Bloom AK, Wong DL (2002) Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the rat phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene. Mol Pharmacol 61:1385–1392
Thompson RJ, Jackson A, Nurse CA (1997) Developmental loss of hypoxic chemosensitivity in rat adrenomedullary chromaffin cells. J Physiol 498:503–510
Thompson RJ, Buttigieg J, Zhang M, Nurse CA (2007) A rotenone-sensitive site and H2O2 are key components of hypoxia-sensing in neonatal rat adrenomedullary chromaffin cells. Neuroscience 145:130–141
Upham BL, Trosko JE (2009) Oxidative-dependent integration of signal transduction with intercellular gap junctional communication in the control of gene expression. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:297–307
Wakade AR (1981) Studies on secretion of catecholamines evoked by acetylcholine or transmural stimulation of the rat adrenal gland. J Physiol 313:463–480
Wakade AR, Wakade TD (1983) Contribution of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors in the secretion of catecholamines evoked by endogenous and exogenous acetylcholine. Neuroscience 10:973–978
Wallace BG, Qu Z, Huganir RL (1991) Agrin induces phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Neuron 6:869–878
Xiao Y, Meyer EL, Thompson JM, Surin A, Wroblewski J, Kellar KJ (1998) Rat alpha3/beta4 subtype of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor stably expressed in a transfected cell line: pharmacology of ligand binding and function. Mol Pharmacol 54:322–333
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche, Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale, Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer and Région Languedoc-Roussillon.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A commentary to this article can be found at doi:10.1007/s10571-010-9607-8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guérineau, N.C., Desarménien, M.G. Developmental and Stress-Induced Remodeling of Cell–Cell Communication in the Adrenal Medullary Tissue. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30, 1425–1431 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9583-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9583-z