Abstract
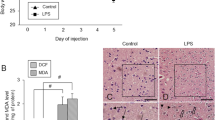
In this study, we observed the effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on neurodegeneration and immune response in the hippocampus. LPS is a gram-negative bacterial cell surface proteoglycan and known as a bacterial endotoxin. For this, we investigated the optimal concentration of LPS influencing the ICR mouse hippocampus to measure the LPS receptor, e.g., toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), expression in mouse hippocampal homogenates. TLR4 expression was significantly and prominently increased in the hippocampal homogenates of the LPS (1 mg/kg)-treated group. Next, we examined pro-inflammatory response in the hippocampus using cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2, a marker for inflammatory response) immunohistochemistry after LPS treatment. COX-2 immunoreactivity was significantly increased in the endothelium of blood vessels in the hippocampus 6 h after LPS treatment, judging from double immunofluorescence study with platelet-derived endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1, a marker for endothelial cells): it decreased 12 h and disappeared 24 h after LPS treatment. In addition, the ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba-1)-immunoreactive (+) microglia were morphologically activated in the mouse hippocampus after LPS treatment. At 24 h after LPS treatment, Iba-1+ microglia of activated forms were abundant in the hippocampus. However, NeuN (a neuron-specific soluble nuclear antigen)+ neurons were not significantly changed in the hippocampus after LPS treatment. Fluoro-jade B (a marker for neuronal degeneration)+ cells were not detected in the hippocampus at any time after LPS treatment. In addition, there were no significant differences in permeability of blood–brain barriers at any time points after LPS treatment. In brief, our results indicate that intraperitoneal administration of 1 mg/kg LPS effectively induces LPS receptor (TLR4) expression in the hippocampus, and the treatment increases corticosterone levels, inflammation in the blood vessels, and microglial activation in the hippocampus without any neuronal damage.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4:499–511
Arai H, Furuya T, Yasuda T, Miura M, Mizuno Y, Mochizuki H (2004) Neurotoxic effects of lipopolysaccharide on nigral dopaminergic neurons are mediated by microglial activation, interleukin-1β, and expression of caspase-11 in mice. J Biol Chem 279:51647–51653
Beutler B (2004) Inferences, questions and possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature 430:257–263
Breder CD, Saper CB (1996) Expression of inducible cyclooxygenase mRNA in the mouse brain after systemic administration of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Brain Res 713:64–69
Buttini M, Limonta S, Boddeke HWGM (1996) Peripheral administration of lipopolysaccharide induces activation of microglial cells in rat brain. Neurochem Int 29:25–35
Candelario-Jalil E, Alvarez D, Merino N, León OS (2003) Delayed treatment with nimesulide reduces measures of oxidative stress following global ischemic brain injury in gerbils. Neurosci Res 47:245–253
Cao C, Matsumura K, Yamagata K, Watanabe Y (1995) Induction by lipopolysaccharide of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in rat brain; its possible role in the febrile response. Brain Res 697:187–196
Cao C, Matsumura K, Yamagata K, Watanabe Y (1996) Endothelial cells of the rat brain vasculature express cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in response to systemic interleukin-1 beta: a possible site of prostaglandin synthesis responsible for fever. Brain Res 733:263–272
Cao C, Matsumura K, Yamagata K, Watanabe Y (1997) Involvement of cyclooxygenase-2 in LPS-induced fever and regulation of its mRNA by LPS in the rat brain. Am J Physiol 272:R1712–R1725
Chakravarty S, Herkenham M (2005) Toll-like receptor 4 on non hematopoietic cells sustains CNS inflammation during endotoxemia, independent of systemic cytokines. J Neurosci 25:1788–1796
Dangerfield J, Larbi KY, Huang MT, Dewar A, Nourshargh S (2002) PECAM-1 (CD31) homophilic interaction up-regulates α6β1 on transmigrated neutrophils in vivo and plays a functional role in the ability of α6 integrins to mediate leukocyte migration through the perivascular basement membrane. J Exp Med 196:1201–1211
Davis EJ, Foster TD, Thomas WE (1994) Cellular forms and functions of brain microglia. Brain Res Bull 34:73–78
Dheen ST, Kaur C, Ling EA (2007) Microglial activation and its implications in the brain diseases. Curr Med Chem 14:1189–1197
Gaillard PJ, Voorwinden LH, Nielsen JL, Ivanov A, Atsumi R, Engman H, Ringbom C, de Boer AG, Breimer DD (2001) Establishment and functional characterization of an in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier, comprising a co-culture of brain capillary endothelial cells and astrocytes. Eur J Pharm Sci 12:215–222
Gaillard PJ, de Boer AB, Breimer DD (2003) Pharmacological investigations on lipopolysaccharide-induced permeability changes in the blood-brain barrier in vitro. Microvasc Res 65:24–31
Gao HM, Liu B, Zhang W, Hong JS (2003) Synergistic dopaminergic neurotoxicity of MPTP and inflammogen lipopolysaccharide: relevance to the etiology of Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J 17:1957–1959
Goppelt-Struebe M (1995) Regulation of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase (cyclooxygenase) isozyme expression. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 52:213–222
Guan Z, Fang J (2006) Peripheral immune activation by lipopolysaccharide decreases neurotrophins in the cortex and hippocampus in rats. Brain Behav Immun 20:64–71
Hagberg H, Mallard C (2005) Effect of inflammation on central nervous system development and vulnerability. Curr Opin Neurol 18:117–123
Hald A, Lotharius J (2005) Oxidative stress and inflammation in Parkinson’s disease: is there a causal link? Exp Neurol 193:279–290
Herschman HR (1996) Prostaglandin synthase 2. Biochim Biophys Acta 1299:125–140
Hochweller K, Anderton SM (2005) Kinetics of costimulatory molecule expression by T cells and dendritic cells during the induction of tolerance versus immunity in vivo. Eur J Immunol 35:1086–1096
Kakucska I, Qi Y, Clark BD, Lechan RM (1993) Endotoxin-induced corticotropin-releasing hormone gene expression in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus is mediated centrally by interleukin-1. Endocrinology 133:815–821
Kaur C, Ling EA (1991) Study of the transformation of amoeboid microglial cells into microglia labelled with the isolectin Griffonia simplicifolia in postnatal rats. Acta Anat (Basel) 142:118–125
Kaur C, Ling EA, Wong WC (1985) Transformation of amoeboid microglial cells into microglia in the corpus callosum of the postnatal rat brain. An electron microscopical study. Arch Histol Jpn 48:17–25
Kaya M, Gurses C, Kalayci R, Ekizoglu O, Ahishali B, Orhan N, Oku B, Arican N, Ustek D, Bilgic B, Elmas I, Kucuk M, Kemikler G (2008) Morphological and functional changes of blood–brain barrier in kindled rats with cortical dysplasia. Brain Res 1208:181–191
Kniesel U, Wolburg H (2000) Tight junctions of the blood–brain barrier. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20:57–76
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19:312–318
Laflamme N, Rivest S (2001) Toll-like receptor 4: the missing link of the cerebral innate immune response triggered by circulating gram-negative bacterial cell wall components. FASEB J 15:155–163
Lee SC, Liu W, Roth P, Dickson DW, Berman JW, Brosnan CF (1993) Macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human fetal astrocytes and microglia. Differential regulation by cytokines and lipopolysaccharide, and modulation of class II MHC on microglia. J Immunol 150:594–604
Lee HJ, Ertley RN, Rapoport SI, Bazinet RP, Rao JS (2008) Chronic administration of lamotrigine downregulates COX-2 mRNA and protein in rat frontal cortex. Neurochem Res 33:861–866
Letournel-Boulland ML, Fages C, Rolland B, Tardy M (1994) Lipopolysaccharides (LPS), up-regulate the IL-1-mRNA and down-regulate the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and glutamine synthetase (GS)-mRNAs in astroglial primary cultures. Eur Cytokine Netw 5:51–56
Liberto CM, Albrecht PJ, Herx LM, Yong VW, Levison SW (2004) Pro-regenerative properties of cytokine-activated astrocytes. J Neurochem 89:1092–1100
Linthorst AC, Flachskamm C, Holsboer F, Reul JM (1995) Intraperitoneal administration of bacterial endotoxin enhances noradrenergic neurotransmission in the rat preoptic area: relationship with body temperature and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis activity. Eur J Neurosci 7:2418–2430
Maas M, Stapleton M, Bergom C, Mattson DL, Newman DK, Newman PJ (2005) Endothelial cell PECAM-1 confers protection against endotoxic shock. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H159–H164
Mancuso G, Midiri A, Biondo C, Beninati C, Gambuzza M, Macrì D, Bellantoni A, Weintraub A, Espevik T, Teti G (2005) Bacteroides fragilis-derived lipopolysaccharide produces cell activation and lethal toxicity via toll-like receptor 4. Infect Immun 73:5620–5627
Matsumura K, Cao C, Ozaki M, Morii H, Nakadate K, Watanabe Y (1998) Electron microscopic evidence for induction of cyclooxygenase-2 in brain endothelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 856:278–280
Newman PJ (1997) Perspective series: cell adhesion in vascular biology. J Clin Invest 100:S25–S29
Nichols NR (1999) Glial responses to steroids as markers of brain aging. J Neurobiol 40:585–601
Nishioku T, Dohgu S, Takata F, Eto T, Ishikawa N, Kodama KB, Nakagawa S, Yamauchi A, Kataoka Y (2009) Detachment of brain pericytes from the basal lamina is involved in disruption of the blood-brain barrier caused by lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis in mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:309–316
Pasinetti GM (1998) Cyclooxygenase and inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: experimental approaches and clinical interventions. J Neurosci Res 54:1–6
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Quan N, Sundar SK, Weiss JM (1994) Induction of interleukin-1 in various brain regions after peripheral and central injections of lipopolysaccharide. J Neuroimmunol 49:125–134
Quan N, Whiteside M, Herkenham M (1998) Time course and localization patterns of interleukin-1β messenger RNA expression in brain and pituitary after peripheral administration of lipopolysaccharide. Neuroscience 83:281–293
Quan N, He L, Lai W (2003) Endothelial activation is an intermediate step for peripheral lipopolysaccharide induced activation of paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res Bull 59:447–452
Raivich G, Bohatschek M, Kloss CUA, Werner A, Jones LL, Kreutzberg GW (1999) Neuroglia activation repertoire in the injured brain: graded response, molecular mechanisms and cues to physiological function. Brain Res Rev 30:77–105
Saavedra JM, Pavel J (2006) The discovery of a novel macrophage binding site. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:509–526
Schmued LC, Hopkins KJ (2000) Fluoro-Jade B: a high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res 874:123–130
Schnydrig S, Korner L, Landweer S, Ernst B, Walker G, Otten U, Kunz D (2007) Peripheral lipopolysaccharide administration transiently affects expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, corticotropin and proopiomelanocortin in mouse brain. Neurosci Lett 429:69–73
Semmler A, Okulla T, Sastre M, Dumitrescu-Ozimek L, Heneka MT (2005) Systemic inflammation induces apoptosis with variable vulnerability of different brain regions. J Chem Neuroanat 30:144–157
Singh AK, Jiang Y (2004) How does peripheral lipopolysaccharide induce gene expression in the brain of rats? Toxicology 201:197–207
Steiner AA, Chakravarty S, Rudaya AY, Herkenham M, Romanovsky AA (2006) Bacterial lipopolysaccharide fever is initiated via Toll-like receptor 4 on hematopoietic cells. Blood 107:4000–4002
Teismann P, Schulz JB (2004) Cellular pathology of Parkinson’s disease: astrocytes, microglia and inflammation. Cell Tissue Res 318:149–161
Terrazzino S, Bauleo A, Baldan A, Leon A (2002) Peripheral LPS administrations up-regulate Fas and FasL on brain microglial cells: a brain protective or pathogenic event? J Neuroimmunol 124:45–53
Trevin S, Kataoka Y, Kawachi R, Shuto H, Kumakura K, Oishi R (1998) Direct and continuous electrochemical measurement of noradrenaline-induced nitric oxide production in C6 glioma cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 18:453–458
Vila M, Jackson-Lewis V, Guegan C, Wu DC, Teismann P, Choi DK, Tieu K, Przedborski S (2001) The role of glial cells in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol 14:483–489
Xaio H, Banks WA, Niehoff ML, Morley JE (2001) Effect of LPS on the permeability of the blood–brain barrier to insulin. Brain Res 896:36–42
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. Seok Han, Mr. Seung Uk Lee, and Ms. Hyun Sook Kim for their technical help in this study. This work was supported in part by the MRC program of MOST/KOSEF (R13-2005-022-01002-0), and in part by the Regional Core Research Program funded by the Korea Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (Medical & Bio-material Research Center).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Dae Won Chung and Ki-Yeon Yoo contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, D.W., Yoo, KY., Hwang, I.K. et al. Systemic Administration of Lipopolysaccharide Induces Cyclooxygenase-2 Immunoreactivity in Endothelium and Increases Microglia in the Mouse Hippocampus. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30, 531–541 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9477-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9477-0