Abstract
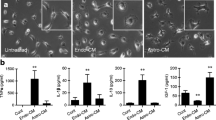
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is formed by brain capillary endothelial cells, astrocytes, pericytes, microglia, and neurons. BBB disruption under pathological conditions such as neurodegenerative disease and inflammation is observed in parallel with microglial activation. To test whether activation of microglia is linked to BBB dysfunction, we evaluated the effect of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on BBB functions in an in vitro co-culture system with rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (RBEC) and microglia. When LPS was added for 6 h to the abluminal side of RBEC/microglia co-culture at a concentration showing no effects on the RBEC monolayer, transendothelial electrical resistance was decreased and permeability to sodium-fluorescein was increased in RBEC. Immunofluorescence staining for tight junction proteins demonstrated that zonula occludens-1-, claudin-5-, and occludin-like immunoreactivities at the intercellular borders of RBEC were fragmented in the presence of LPS-activated microglia. These functional changes induced by LPS-activated microglia were blocked by the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase inhibitor, diphenyleneiodonium chloride. The present findings suggest that LPS activates microglia to induce dysfunction of the BBB by producing reactive oxygen species through NADPH oxidase.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hannson E (2006) Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood–brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:41–53
Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4(7):499–511
Bazzoni G, Dejana E (2004) Endothelial cell-to-cell junctions: molecular organization and role in vascular homeostasis. Physiol Rev 84(3):869–901
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(1):57–69
Chow JC, Young DW, Golenbock DT, Christ WJ, Gusovsky F (1999) Toll-like receptor-4 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction. J Biol Chem 274:10689–10692
Dehouck M-P, Jolliet-Riant P, Brée F, Fruchart J-C, Cecchelli R, Tillement JP (1992) Drug transfer across the blood–brain barrier: correlation between in vitro and in vivo models. J Neurochem 58:1790–1797
Deli MA, Joó F, Krizbai I, Lengyel I, Nunzi GM, Wolff J-R (1993) Calcium/calmodulin stimulated protein kinase II is present in primary cultures of cerebral endothelial cells. J Neurochem 60:1960–1963
Fischer S, Wiesnet M, Renz D, Schaper W (2005) H2O2 induces paracellular permeability of porcine brain-derived microvascular endothelial cells by activation of the p44/42 MAP kinase pathway. Eur J Cell Biol 84(7):687–697
Groemping Y, Rittinger K (2005) Activation and assembly of the NADPH oxidase: a structural perspective. Biochem J 386:401–416
Haorah J, Ramirez SH, Schall K, Smith D, Pandya R, Persidsky Y (2007) Oxidative stress activates protein tyrosine kinase and matrix metalloproteinases leading to blood–brain barrier dysfunction. J Neurochem 101(2):566–576
Hawkins BT, Davis TP (2005) The blood–brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 57(2):173–185
Kortekaas R, Leenders KL, van Oostrom JC, Vaalburg W, Bart J, Willemsen AT, Hendrikse NH (2005) Blood–brain barrier dysfunction in parkinsonian midbrain in vivo. Ann Neurol 57(2):176–179
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19:312–318
Lee SC, Liu W, Dickson DW, Brosnan CF, Berman JW (1993) Cytokine production by human fetal microglia and astrocytes. Differential induction by lipopolysaccharide and IL-1 beta. J Immunol 150(7):2659–2667
Lee HS, Namkoong K, Kim DH, Kim KJ, Cheong YH, Kim SS, Lee WB, Kim KY (2004) Hydrogen peroxide-induced alterations of tight junction proteins in bovine brain microvascular endothelial cells. Microvasc Res 68(3):231–238
Lehnardt S, Massillon L, Follett P, Jensen FE, Ratan R, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ, Vartanian T (2003) Activation of innate immunity in the CNS triggers neurodegeneration through a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8514–8519
Leusen J, Verhoeven A, Roos D (1996) Interactions between the components of the human NADPH oxidase: a review about the intrigues in the phox family. Front Biosci 1:72
Liu B, Hong JS (2003) Role of microglia in inflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases: mechanism and strategies for therapeutic intervention. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:1–7
Mander PK, Jekabsone A, Brown GC (2006) Microglia proliferation is regulated by hydrogen peroxide from NADPH oxidase. J Immunol 76(2):1046–1052
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1995) The inflammatory response system of brain: implications for therapy of Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Rev 21:195–218
Nakagawa S, Deli MA, Nakao S, Honda M, Hayashi K, Nakaoke R, Kataoka Y, Niwa M (2007) Pericytes from brain microvessels strengthen the barrier integrity in primary cultures of rat brain endothelial cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 27:687–694
Nishioku T, Hashimoto K, Yamashita K, Liou SY, Kagamiishi Y, Maegawa H, Katsube N, Peters C, von Figura K, Saftig P, Katunuma N, Yamamoto K, Nakanishi H (2002) Involvement of cathepsin E in exogenous antigen processing in primary cultured murine microglia. J Biol Chem 277(7):4816–4822
Nishioku T, Dohgu S, Takata F, Eto T, Ishikawa N, Kodama KB, Nakagawa S, Yamauchi A, Kataoka Y (2008) Detachment of brain pericytes from the basal lamina is involved in disruption of the blood–brain barrier caused by lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis in mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29(3):309–316
Pawate S, Shen Q, Fan F, Bhat NR (2004) Redox regulation of glial inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide and interferon gamma. J Neurosci Res 77(4):540–551
Perriere N, Demeuse N, Garcia E, Regina A, Debray M, Andreux JP, Couvreur P, Schermann JM, Temsamani J, Couraud PO, Deli MA, Roux F (2005) Puromycin-based purification of rat brain capillary endothelial cell cultures. Effect on the expression of blood–brain barrier specific properties. J Neurochem 93:279–289
Qian L, Block ML, Wei SJ, Lin CF, Reece J, Pang H, Wilson B, Hong JS, Flood PM (2006) Interleukin-10 protects lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in primary midbrain cultures by inhibiting the function of NADPH oxidase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319(1):44–52
Qian L, Wei SJ, Zhang D, Hu X, Xu Z, Wilson B, El-Benna J, Hong JS, Flood PM (2008) Potent anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of TGF-beta1 are mediated through the inhibition of ERK and p47phox-Ser345 phosphorylation and translocation in microglia. J Immunol 181(1):660–668
Qin L, Liu Y, Wang T, Wei SJ, Block ML, Wilson B, Liu B, Hong JS (2004) NADPH oxidase mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity and proinflammatory gene expression in activated microglia. J Biol Chem 279:1415–1421
Qin L, Li G, Qian X, Liu Y, Wu X, Liu B, Hong JS, Block ML (2005) Interactive role of the toll-like receptor 4 and reactive oxygen species in LPS-induced microglia activation. Glia 52(1):78–84
Sankarapandi S, Zweier JL, Mukherjee G, Quinn MT, Huso DL (1998) Measurement and characterization of superoxide generation in microglial cells: evidence for an NADPH oxidase-dependent pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 353:312–321
Schreibelt G, Kooij G, Reijerkerk A, van Doorn R, Gringhuis SI, van der Pol S, Weksler BB, Romero IA, Couraud PO, Piontek J, Blasig IE, Dijkstra CD, Ronken E, de Vries HE (2007) Reactive oxygen species alter brain endothelial tight junction dynamics via RhoA, PI3 kinase, and PKB signaling. FASEB J 21(13):3666–3676
Zipser BD, Johanson CE, Gonzalez L, Berzin TM, Tavares R, Hulette CM, Vitek MP, Hovanesian V, Stopa EG (2007) Microvascular injury and blood–brain barrier leakage in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 28(7):977–986
Zlokovic BV (2008) The blood–brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 57(2):178–201
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research [(B) 17390159], Grants-in-Aid for Young Scientists [(Start-up) 18890227 and (Start-up) 20800066], and Grants-in-Aid for Young Scientists [(B) 19790199, (B) 21790102, (B) 21790255, (B) 21790257, and (B) 21790526] from JSPS, Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan (H19-nanchi-ippan-006), the Nakatomi Foundation, Research Foundation ITSUU Laboratory, and Kakihara Science and Technology Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sumi, N., Nishioku, T., Takata, F. et al. Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Microglia Induce Dysfunction of the Blood–Brain Barrier in Rat Microvascular Endothelial Cells Co-Cultured with Microglia. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30, 247–253 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9446-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9446-7