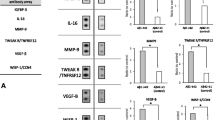
1. The leucine-rich glioma inactivated (LGI) family of genes encodes a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) protein, proteins that are thought to be specifically involved in protein–protein and protein–matrix interactions. Since amyloid beta peptide (Aβ) has been previously shown to induce the expression of another LRR-encoding gene in neural cells, we assessed how Aβ affects LGI gene expression in rat primary cerebral cortical cultures and astrocyte cultures. Both RT-PCR and Western Blotting analyses revealed that Aβ robustly induced the expression of LGI3 in rat astrocyte cultures.
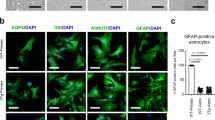
2. Western Blotting analyses also showed that both glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and apolipoprotein E (ApoE) significantly increased coincidentally with the Aβ-induced upregulation of LGI3. Immunocytochemistry showed that LGI3 colocalized with Aβ at plasma membranes and also with internalized Aβ in astrocytes. These findings suggest that activated LGI3 may be involved in the astroglial response against Aβ.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Behl, C., Davis, J., Cole, G. M., and Schubert, D. (1992). Vitamin E protects nerve cells from amyloid β protein toxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 186:944–952.
Buchanan, S. G., and Gay, N. J. (1996). Structural and functional diversity in the leucine-rich repeat family of proteins. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 65:1–44.
Burdick, D., Soreghan, B., Kwon, M., Kosmoski, J., Knauer, M., Henshen, A., Yates, J., Cotman, C., and Glabe, C. (1992). Assembly and aggregation properties of synthetic Alzheimer's A4/beta amyloid peptide analogs. J. Biol. Chem. 267:546–554.
Busciglio, J., Gabuzda, D. H., Matsudaira, P., and Yankner, B. A. (1993). Generation of β-amyloid in the secretory pathway in neuronal and non-neuronal cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90:2092–2096.
Chen, F., Gu, Y., Hasegawa, H., Ruan, X., Arakawa, S., Fraser, P., Westaway, D., Mount, H., and St. George-Hyslop, P. (2002). Presenilin 1 mutations activate Aβ42 secretase but reciprocally inhibit e-secretase cleavage of APP and S3-cleavage of Notch. J. Biol. Chem. 277:36521–36526.
Deb, S., Zhang, J. W., and Gottschall, P. E. (2003). β-amyloid induces the production of active, matrix-degrading proteases in rat cultured rat astrocytes. Brain Res. 970:205–213.
Ebino, J. O., and Yankner, B. A. (2002). A RIP tide in neuronal signal transduction. Neuron 34:499–502.
Eddleston, M., and Mucke, L. (1993). Molecular profile of reactive astrocytes—Implications for their role in neurologic disease. Neuroscience 54:15–36.
Funato, H., Yoshimura, M., Yamazaki, T., Saido, T. C., Ito, Y., Yokohujita, J., Okeda, R., and Ihara, Y. (1998). Astrocytes containing amyloid beta-protein (Abeta)-positive granules are associated with Abeta40-positive diffuse plaques in the aged human brain. Am. J. Pathol. 152:983–992.
Glenner, G. G. (1988). Alzheimer's disease: Its proteins and genes. Cell 52:307–308.
Greenwald, I. (1998). LIN-12/Notch signaling: Lessons from worms and flies. Genes Dev. 12(12):1751–1762.
Gu, W., Wevers, A., Hannsjorg, S., Grzeschik, K.-H., Derst, C., Brodtkorb, E., De Vos, R., and Steinlein, O. K. (2002). The LGI1 gene involved in lateral temporal lobe epilepsy belongs to a new subfamily of leucine-rich repeat proteins. FEBS Lett. 519:71–76.
Haas, C., Sclossmacher, M. G., Hung, A. Y., Vigo-Pelfrey, C., Mellon, A., Ostaszewski, B. L., Lieberburg, I., Koo, E. H., Schenk, D., Teplow, D. B., and Selkoe, D. J. (1992). Amyloid beta-peptide is produced by cultured cells during normal metabolism. Nature 359:322–325.
Jarrett, J. T., Berger, E. P., and Lansbury, P. T., Jr. (1993). The carboxy terminus of the beta amyloid protein is critical for the seeding of amyloid formation: Implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Biochemistry 32:4693–4697.
Kimura, N., Negishi, T., Ishii, Y., Kyuwa, S., and Yoshikawa, Y. (2004). Astroglial responses against Abeta initially occur in cerebral primary cortical cultures: Species differences between rat and cynomolgus monkey. Neurosci. Res. 49(3):339–346.
Kobe, B., and Deisenfofer, J. (1994). The leucine-rich repeat: A versatile binding motif. Trends Biochem. Sci. 19:415–421.
Koh, J., Yang, L. L., and Cotman, C. W. (1990). β amyloid protein increase the vulnerability of cultured cortical neurons to excitotoxic damage. Brain Res. 533:315–320.
LaDu, M. J., Shah, J. A., Reardon, C. A., Getz, G. S., Bu, G., Hu, J., Guo, L., and Van Eldik, L. J. (2001). Apolipoprotein E and apolipoprotein E receptors modulate Ab-induced glial neuroinflammatory responses. Neurochem. Int. 39:427–434.
Mark, R. E., Sheng, J. G., and Griffin, S. T. (1995). Glial cytokines in Alzheimer's disease: Review and pathogenic implications. Hum. Pathol. 26:816–823.
Matsunaga, W., Shirokawa, T., and Isobe, K. (2003). Specific uptake of Aβ 1-40 in rat brain occurs in astrocyte, but not in microglia. Neurosci. Lett. 342:129–131.
Mattson, M. P., Cheng, B., Davis, D., Bryant, K., Lieberburg, I., and Rydel, R. (1992). β-amyloid peptides destabilize calcium homeostasis and render human cortical neurons vulnerable to excitotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 12:376–389.
McGeer, P. L., and McGeer, E. G. (1995). The inflammatory response system of brain: Implication for therapy of Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative diseases. Brain. Res. Rev. 21:195–218.
Negishi, T., Ishii, Y., Kawamura, S., Kuroda, Y., and Yoshikawa, Y. (2002). Cryopreservation of brain tissue for primary culture. Exp. Anim. 51:383–390.
Negishi, T., Ishii, Y., Kyuwa, S., Kuroda, Y., and Yoshikawa, Y. (2003). Primary culture of cortical neurons, type-1 astrocytes, and microglial cells from cynomolgus monkey (Macaca fascicularis) fetuses. J. Neurosci. Methods 131:133–140.
Sastre, M., Steiner, H., Fuchs, K., Cappell, A., Multhaup, G., Condron, M. M., Teplow, D. B., and Haass, C. (2001). Presenilin-dependent γ-secretase processing of β-amyloid precursor protein at a site corresponding to the S3 cleavage of Notch. EMBO Rep. 2:835–841.
Satoh, K., Hata, M., and Yokota, H. (2002). A novel member of the leucine-rich repeat superfamily induced in rat astrocytes by b-amyloid. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 290:756–762.
Schulte, U., Thumfart, J.-O., Klocker, N., Sailer, C. A., Bildi, W., Miniossek, M., Dehn D., Deller T., Eble, S., Abbass, K., Wangler, T., Knaus, H.-G., and Fakler, B. (2006). The epilepsy-linked lgi1 protein assembles into presynaptic Kv1 channels and inhibits inactivation by Kvb1. Neuron 49:697–706.
Seubert, P., Vigo-Pelfrey, C., Esch, F., Lee, M., Dovey, H., Davis, D., Sinha, S., Schlossmacher, M., Whaley, J., Swindlehurst, C., McCormack, R., Wolfert, R., Selkoe, D. J., Lieberburg, I., and Schenk, D. B. (1992). Isolation and quantification of soluble Alzheimer's beta-peptide from biological fluids. Nature 359:325–327.
Shoji, M., Golde, T. E., Ghiso, J., Cheung, T. T., Estus, S., Shaffer, L. M., Cai, X. D., McKay, D. M., Tintner, R., Frangione, B., and Younkin, S. G. (1992). Production of the Alzheimer amyloid beta protein by normal proteolytic processing. Science 258:126–129.
Smits, H. A., Rijsmus, A., Van Loon, J. H., Wat, J. W. Y., Verhoef, J., Boven, L. A., and Nottet, H. S. L. M. (2002). Amyloid-β-induced chemokine production in primary human macrophages and astrocytes. J. Neuroimmnol. 127:160–168.
Suzuki, N., Cheung, T. T., Cai, X. D., Odaka, A., Otvos, L. Jr., Eckman, C., Golde, T. E., and Younkin, S. G. (1994). An increased percentage of long amyloid beta protein secreted by familial amyloid beta protein precursor (beta APP717) mutants. Science 264:1336–1340.
Vigo-Pelfrey, C., Lee, D., Keim, P., Lieberburg, I., and Schenk, D. B. (1993). Characterization of beta-amyloid peptide from human cerebrospinal fluid. J. Neurochem. 61:1965–1968.
Weidemann, A., Eggert, S., Reinhard, F. B. M., Vogel, M., Paliga, K., Bailer, G., Masters, C. L., Beyreuther, K., and Evin, G. (2002) A novel ε-cleavage within the transmembrane domain of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein demonstrates homology with Notch processing. Biochemistry 41:2825–2835.
Wyss-Coray, T., Loike, J. D., Brionne, T. C., Lu, E., Anankov, R., Yan, F., Silverstein, S. C., and Husemann, J. (2003). Adult mouse astrocytes degrade amyloid-β in vitro and in situ. Nat. Med. 9:453–457.
Yankner, B. A., Duffy, L. K., and Kirschner, D. A. (1990). Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid β protein: Reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science 25:279–282.
Younkin, S. G. (1994). The amyloid beta protein precursor mutations linked to familial Alzheimer's disease alter processing in a way that fosters amyloid deposition. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 174:217–223.
Yu, C., Kim, S.-H., Ikeuchi, T., Xu, H., Gasparini, L., Wang, R., and Sisodia, S. S. (2001) Characterization of a presenilin-mediated amyloid precursor carboxyl-terminal fragment g. J. Biol. Chem. 276:43756–43760.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by a grant-in-aid from Research on Human Genome, Tissue Engineering, Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare, Japan. The authors are especially thankful to the MBL Company for producing the LGI3-specific antibody anti-TA142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, N., Ishii, Y., Suzaki, S. et al. Aβ Upregulates and Colocalizes with LGI3 in Cultured Rat Astrocytes. Cell Mol Neurobiol 27, 335–350 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9127-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9127-8