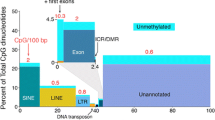
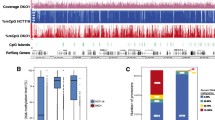
1. DNA methylation is a critical epigenetic modification that silences gene transcription, participates in X-chromosome inactivation in females, and regulates genomic imprinting.
2. We have devised a method to inhibit transcriptional initiation by constructing short methylated oligonucleotides which induce DNA methylation at specific loci.
3. The methodology by which we devise these oligonucleotides is described, using oligonucleotides directed against the oncogene, Bcl-2.
4. The human Bcl-2 gene contains two promoters, each of which contains a CpG island in its core region. Oligonucleotides are designed which can inhibit Bcl-2 transcription and lead to decreased mRNA and protein in vitro. When compared to standard anti-sense oligonucleotide action, these methylated oligonucleotides are far more sensitive and potentially, longer acting.
5. In principle, using this methodology, it should be possible to design methylated oligonucleotides that can methylate CpG islands and thereby downregulate any gene.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Adams, J. M., and Cory, S. (1998). The Bcl-2 protein family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science, 281:1322–1326.
Aiello, A., Delia, D., Borrello, M. G., Biassoni, D., Giardini, R., Fontanella, E., Pezzella, F., Pulford, K., Pierotti, M., and Della Porta, G. (1992). Flow cytometric detection of the mitochondrial BCL-2 protein in normal and neoplastic human lymphoid cells. Cytometry 13:502–509.
Aizman, I., Many, A., Peller, S., Ramot, B., and Kaufmann, Y. (2000). Expression of wild-type p53 and Bcl-2 family genes oscillates with recurrent remission and relapse in an unusual case of low-grade lymphoma. Acta Haematol. 103:177–185.
Baliga, B. C., and Kumar, S. (2002). Role of Bcl-2 family of proteins in malignancy. Hematol Oncol. 20:63–74.
Banerjee, D. (2001). Genasense (Genta Inc). Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs 2:574–580.
Baylin, S. B., Makos, M., Wu, J. J., Yen, R. W., de Bustros, A., Vertino, P., and Nelkin, B. D. (1991). Abnormal patterns of DNA methylation in human neoplasia: Potential consequences for tumor progression. Cancer Cells 3:383–390.
Beard, C., Li, E., and Jaenisch, R. (1995). Loss of methylation activates Xist in somatic but not in embryonic cells. Gene. Dev. 9:2325–2334.
Bestor, T. H. (2000). The DNA methyltransferases of mammals. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9:2395–2402.
Brandeis, M., Kafri, T., Ariel, M., Chaillet, J. R., McCarrey, J., Rasin, A., and Ceder, H. (1993). The ontogeny of allele-specific methylation associated with imprinted genes in the mouse. EMBO J. 12:3669–3677.
Campos, L., Rouault, J. P., Sabido, O., Oriol, P., Roubi, N., Vasselon, C., Archimbaud, E., Magaud, J. P., and Guyotat, D. (1993). High expression of bcl-2 protein in acute myeloid leukemia cells is associated with poor response to chemotherapy. Blood 81:3091–3096.
Cleary, M. L., Smith, S. D., and Sklar, J. (1986). Cloning and structural analysis of cDNAs for bcl-2 and a hybrid bcl-2/immunoglobulin transcript resulting from the t(14;18) translocation. Cell 47:19–28.
Cory, S., and Adams, J. M. (2002). The Bcl2 family: Regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2:647–656.
Cotter, F. E., Waters, J., and Cunningham, D. (1999). Human Bcl-2 antisense therapy for lymphomas. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1489:97–106.
Dole, M., Nunez, G., Merchant, A. K., Maybaum, J., Rode, C. K., Bloch, C. A., and Castle, V. P. (1994). Bcl-2 inhibits chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 54:3253–3259.
Fisher, D. E. (1994). Apoptosis in cancer therapy: Crossing the threshold. Cell 78:539–542.
Gagnon, C., Kelly, S., Manganiello, V., Vaughan, M., Odya, C., Strittmatter, W., Hoffman, A., and Hirata, F. (1981). Modification of calmodulin function by enzymatic carboxylic methylation. Nature 291:515–516.
Herman, J. G., Latif, F., Weng, Y., Lerman, M. I., Zbar, B., Liu, S., Samid, D., Duan, D. S., Gnarra, J. R., Linehan, W. M., and B, B. S. (1994). Silencing of the VHL tumor-suppressor gene by DNA methylation in renal carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91:9700–9704.
Hoffman, A. R., Ciaranello, R. D., and Axelrod, J. (1975). Substrate and inhibitor kinetics of bovine phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 24:544–546.
Hoffman, A. R., Paul, S. M., and Axelrod, J. (1980). The enzymatic formation of catecholestrogens from 2-methoxyestrogens by rat liver microsomes. Endocrinology 107:1192–1197.
Ishii, T., Fujishiro, M., Masuda, M., Teramoto, S., and Matsuse, T. (2004). A methylated oligonucleotide induced methylation of GSTP1 promoter and suppressed its expression in A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 212:211–223.
Johnstone, R. W., Ruefli, A. A., and Lowe, S. W. (2002). Apoptosis: A link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell 108:153–164.
Jones, P. A., and Buckley, J. D. (1990). The role of DNA methylation in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 54:1–23.
Jones, P. A., and Takai, D. (2001). The role of DNA methylation in mammalian epigenetics. Science 293:1068–1070.
Kirkin, V., Joos, S., and Zornig, M. (2004). The role of Bcl-2 family members in tumorigenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1644:229–249.
Kloog, Y., Flynn, D., Hoffman, A. R., and Axelrod, J. (1980). Enzymatic carboxymethylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 97:1474–1480.
Manna, P. P., and Frazier, W. A. (2004). CD47 mediates killing of breast tumor cells via Gi-dependent inhibition of protein kinase A. Cancer Res. 64:1026–1036.
McDonnell, T. J., Troncoso, P., Brisbay, S. M., Logothetis, C., Chung, L. W., Hsieh, J. T., Tu, S. M., and Campbell, M. L. (1992). Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 52:6940–6944.
Miyashita, T., and Reed, J. C. (1993). Bcl-2 oncoprotein blocks chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in a human leukemia cell line. Blood 81:151–157.
Otterson, G. A., Khleif, S. N., Chen, W., Coxon, A. B., and Kaye, F. J. (1995). CDKN2 gene silencing in lung cancer by DNA hypermethylation and kinetics of p16INK4 protein induction by 5-aza 2’deoxycytidine. Oncogene 11:1211–1216.
Panning, B., and Jaenisch, R. (1996). DNA hypomethylation can activate Xist expression and silence X-linked genes. Genes. Dev. 10:1991–2002.
Raffo, A. J., Perlman, H., Chen, M. W., Day, M. L., Streitman, J. S., and Buttyan, R. (1995). Overexpression of bcl-2 protects prostate cancer cells from apoptosis in vitro and confers resistance to androgen depletion in vivo. Cancer Res. 55:4438–4445.
Reed, J. C. (1997). Bcl-2 family proteins: Regulators of apoptosis and chemoresistance in hematologic malignancies. Semin. Hematol. 34:9–19.
Reed, J. C. (2002). Apoptosis-based therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov 1:111–121.
Reed, J. C., Tsujimoto, Y., Epstein, S. F., Cuddy, M., Slabiak, T., Nowell, P. C., and Croce, C. M. (1989). Regulation of bcl-2 gene expression in lymphoid cell lines containing normal #18 or t(14;18) chromosomes. Oncogene Res. 4:271–282.
Sartorius, U. A., and Krammer, P. H. (2002). Upregulation of Bcl-2 is involved in the mediation of chemotherapy resistance in human small cell lung cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 97:584–592.
Seto, M., Jaeger, U., Hockett, R. D., Graninger, W., Bennett, S., Goldman, P., and Korsmeyer, S. J. (1988). Alternative promoters and exons, somatic mutation and deregulation of the Bcl-2-Ig fusion gene in lymphoma. EMBO J. 7:123–131.
Tsujimoto, Y., Cossman, J., Jaffe, E., and Croce, C. M. (1985). Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science 228:1440–1443.
Van Hille, B., Lohri, A., Reuter, J., and Herrmann, R. (1996). Assessment of drug-induced dysregulations among seven resistance-associated genes in human tumour cell lines. Anticancer Res. 16:3531–3536.
Vu, T. H., and Hoffman, A. R. (1994). Promoter-specific imprinting of the human insulin-like growth factor-II gene. Nature 371:714–717.
Wilson, B. E., Mochon, E., and Boxer, L. M. (1996). Induction of bcl-2 expression by phosphorylated CREB proteins during B-cell activation and rescue from apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:5546–5556.
Xiong, Z., and Laird, P. W. (1997). COBRA: A sensitive and quantitative DNA methylation assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:2532–2534.
Yao, X. M., Hu, J. F., Daniels, M., Shiran, H., Zhou, X. J., Yien, H. F., Lu, H. Q., Zeng, Z. L., Wang, Q. X., Li, T., and Hoffman, A. R. (2003). A methylated oligonucleotide inhibits IGF2 expression and enhances survival in a model of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Invest. 111:265–273.
Yoder, J. A., Soman, N. S., Verdine, G. L., and Bestor, T. H. (1997). DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferases in mouse cells and tissues. Studies with a mechanism-based probe. J. Mol. Biol. 270:385–395.
Zhu, X., Leav, I., Leung, Y. K., Wu, M., Liu, Q., Gao, Y., McNeal, J. E., and Ho, S. M. (2004). Dynamic regulation of estrogen receptor-beta expression by DNA methylation during prostate cancer development and metastasis. Am. J. Pathol. 164:2003–2012.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr Xiaoming Yao and Dr Jie Wu for assistance with the laboratory work in this project. Supported by NIH grant DK36054 and the Research Service of the Department of Veterans Affairs to ARH, and Department of Defense Grant no. W81XWH-04-1-0597 and NIH Grant no. R43 CA86664-01 to JFH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffman, A.R., Hu, J.F. Directing DNA Methylation to Inhibit Gene Expression. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26, 423–436 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9057-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9057-5